Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a progressive, multi-organ disease with limited treatment options. Interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13 have been implicated in the general fibrotic pathway and pathogenesis of SSc and are promising targets. Romilkimab (RKB) is an engineered humanized bispecific immunoglobulin-G4 antibody that binds and neutralizes both IL-4/IL-13. We report a Phase IIa randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (NCT02921971, Sanofi funded) employing RKB in SSc.
Methods: Patients with dcSSc (disease duration ≤36 months, mRSS 10-35) with or without immunosuppressive background therapy were randomized (1:1) to subcutaneous RKB 200mg or placebo (PBO) for 24 weeks and stratified based upon history of SSc-ILD. The primary endpoint was mean change in mRSS from baseline to Week 24 and FVC/DLco and HAQ-DI served as secondary endpoints. All analyses employed a 1-sided p-value < 0.05 as reaching statistical significance.
Results: Ninety-seven patients with similar baseline characteristics between arms (Table 1), including the use of background therapy (PBO 59.2% vs. RKB 52.1%) were randomized. Six (12.2%) and 4 (8.3%) patients discontinued study treatment early in the PBO and RKB arms, respectively. The primary endpoint showed an absolute change in mRSS of -2.45 (0.85) and -4.76 (0.86) for the PBO and RKB groups, respectively with a difference of -2.31 (1.21) favoring RKB (p-value = 0.029) (Table 2). Subgroup analysis based upon stratification criteria did not yield a significant difference (interaction p-value=0.731). Subgroup analysis based on background therapy showed a similar treatment effect with a placebo subtracted difference in mRSS of -2.69 (1.83) and -2.38 (1.59) (Table 2), suggesting an additive effect between background therapy and RKB. Secondary endpoints did not show a statistically significant difference between RKB vs. PBO arms, although there was numerically less decline in FVC with RKB (Table 2). Exploratory endpoints suggested possible effect of RKB on overall pain, Raynaud’s, digital ulcers, and EQ-5D-5L (Table 2). Adverse events (AE) were balanced between the two groups (PBO 83.7% and RKB 83.3%). There were 5 and 4 patients with serious AEs in the PBO and RKB arms, respectively. One death occurred in each arm (PBO – cardiomyopathy, RKB – scleroderma renal crisis).
Conclusion: Patients with dcSSc who were treated with RKB showed a statistically significant reduction in mRSS compared to those receiving placebo. None of the secondary outcomes were met, although RKB was associated with a smaller decline in FVC than placebo. Romilkimab was well tolerated with no major safety concerns.
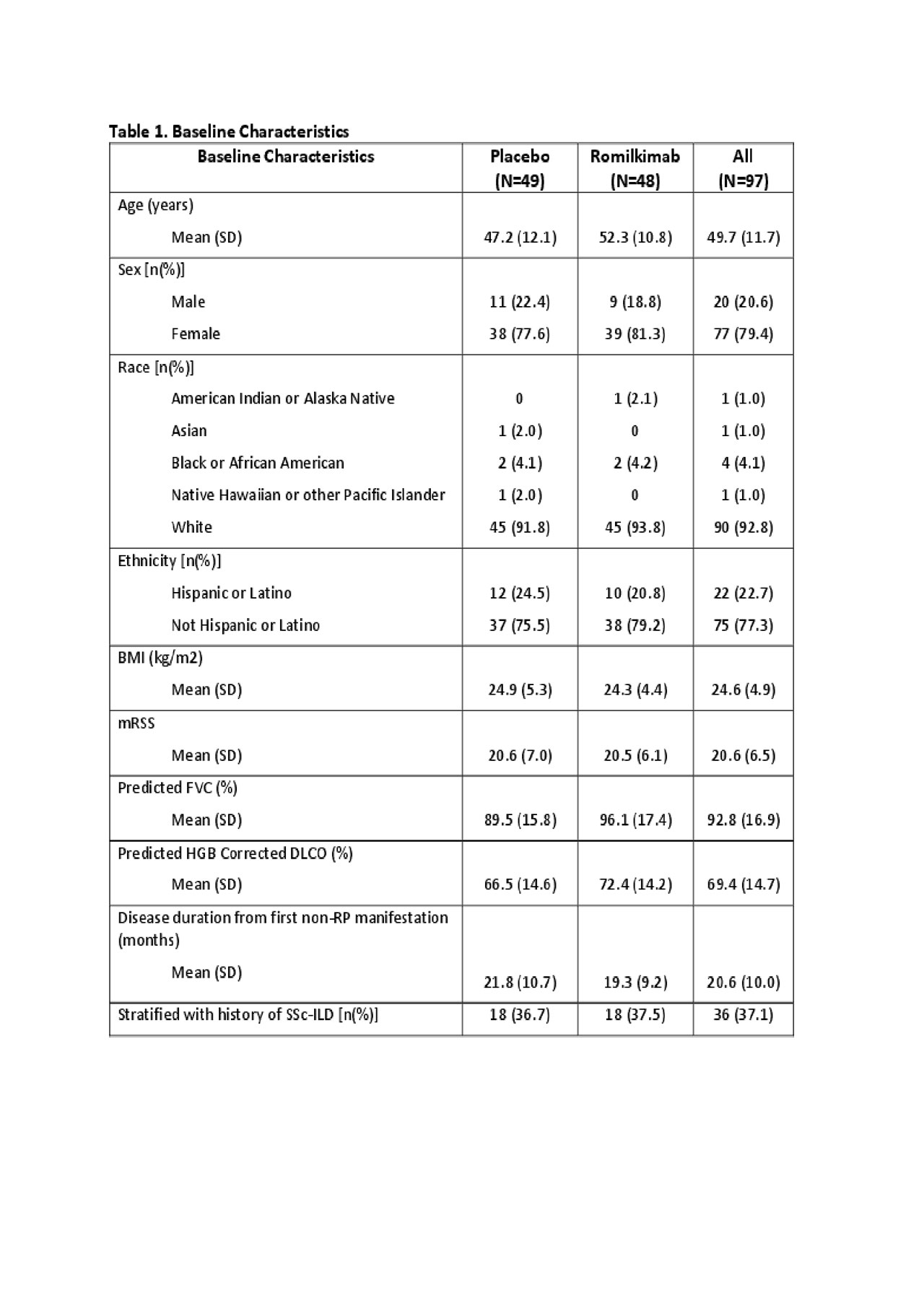
SAR156597_ACT14604 Results_abstract 24MAY2019_Final Draft_Post Internal Publication Review Table 01
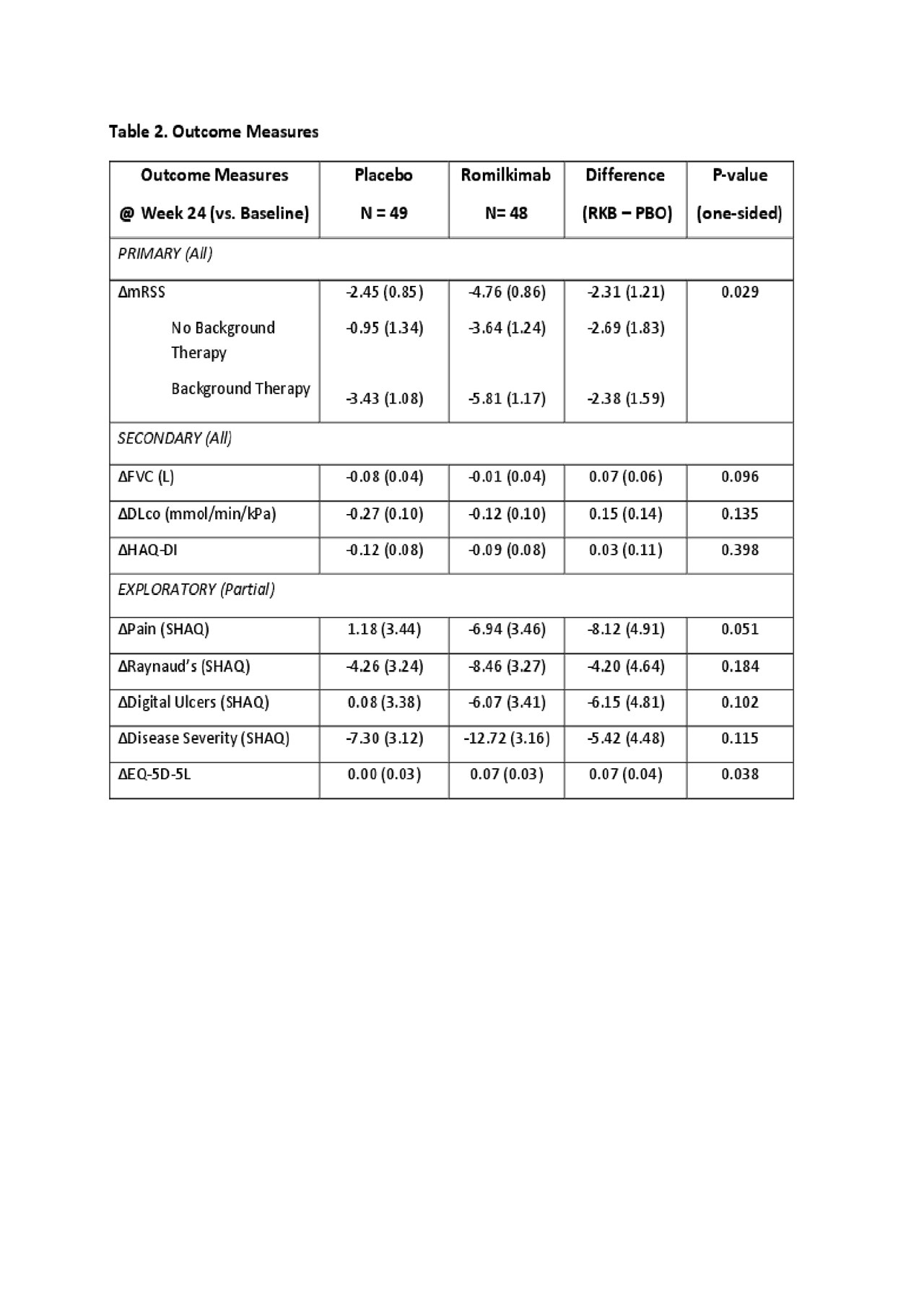
SAR156597_ACT14604 Results_abstract 24MAY2019_Final Draft_Post Internal Publication Review Table 02
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Allanore Y, Denton C, Khanna D, Soubrane C, Esperet C, Marrache F, Bejuit R, Lahmar A, Wung P. Efficacy and Safety of Romilkimab in Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis (dcSSc): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, 24-week, Proof of Concept Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-romilkimab-in-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis-dcssc-a-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-24-week-proof-of-concept-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-romilkimab-in-diffuse-cutaneous-systemic-sclerosis-dcssc-a-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-24-week-proof-of-concept-study/
