Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Olokizumab (OKZ), a humanized monoclonal antibody targeting IL-6, was studied in patients with active Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) despite methotrexate (MTX) (NCT02760368, NCT02760407) [1]. Here we present the results of a global phase III; randomized placebo (PBO) controlled clinical trial (RCT) in patients with RA with an incomplete response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi).
Methods: Patients with active RA who had failed TNFi (NCT02760433) were enrolled in this double-blind RCT conducted in 11 countries including the USA. Patients were randomized in a 2:2:1 ratio to receive subcutaneous (SC) injections of OKZ 64 mg every 2 weeks (q2w), OKZ 64 mg once every 4 weeks (q4w) or PBO, plus MTX. At week (Wk) 16, all subjects in the PBO group were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either OKZ regimens. After Wk 24, subjects could continue in an open-label study or entered a Safety Follow-Up Period for another 20 weeks.
The primary endpoint was the percent of patients achieving an American College of Rheumatology 20 response rate (ACR20) at Wk 12. Secondary endpoints at WK 12 included the percentage of subjects achieving a Disease Activity Score 28-joint count – C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) < 3.2, improvement of physical ability from baseline to Wk 12 measured by the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ - DI), ACR50 response and percentage of subjects achieving a Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) ≤2.8. Safety outcomes were assessed. A hierarchical statistical scheme was pre-defined to control for multiple comparisons.
Results: 368 subjects were randomized and 320 patients (87%) completed the 24-week treatment period. Baseline characteristics were comparable across arms (Table 1).
Both regimens of OKZ were statistically significantly better than PBO in achieving the primary endpoint (Table 2). The efficacy of OKZ was maintained to Wk 24.
Overall incidences of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were 65.5% in OKZ q2w, 65.0% in OKZ q4w and 50.7% in PBO. Subsequent randomization of PBO arm to OKZ at Wk 16 did not substantially change the TEAE incidence rate per treatment group: 64.3% in any OKZ q2w and 59.7% in any OKZ q4w. The majority of TEAEs in all groups were of mild or moderate severity.
Incidence of treatment-emergent serious adverse events (TESAEs) were: 12 (7.0%) in subjects treated with OKZ q2w; 6 (3.2%) in subjects treated with OKZ q4w (Table 3).
The most frequently reported TESAEs across all treatment groups were infections and infestations: 2 (1.1%) in OKZ q4w group, 2 (1.2%) in OKZ q2w group.
No serious opportunistic infections including active tuberculosis, major adverse cardiovascular events, gastrointestinal perforations or deaths were reported.
Conclusion: In this global Phase III trial in patients with active RA inadequately controlled by TNFi, treatment with OKZ 64 mg q2w and OKZ 64 mg q4w plus MTX was associated with significant improvements in the signs and symptoms of RA compared to PBO plus MTX over a 24-week period.
Treatment with OKZ q2w and q4w in this difficult to treat population was generally well tolerated and was similar with the established safety profile of IL-6 inhibitors.
References:1. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/home
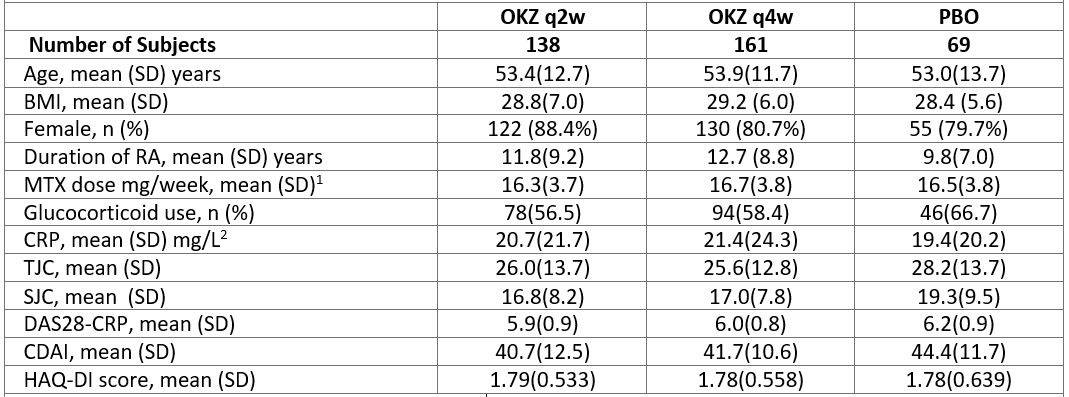 Table 1. Demographic and Other Baseline Characteristics (intent-to-treat population). 1, 100% patients were on MTX; 2, upper limit of normal 6 mg/L; SD, standard deviation; BMI, body mass index; TJC, tender joint count; SJC, swollen joint count
Table 1. Demographic and Other Baseline Characteristics (intent-to-treat population). 1, 100% patients were on MTX; 2, upper limit of normal 6 mg/L; SD, standard deviation; BMI, body mass index; TJC, tender joint count; SJC, swollen joint count
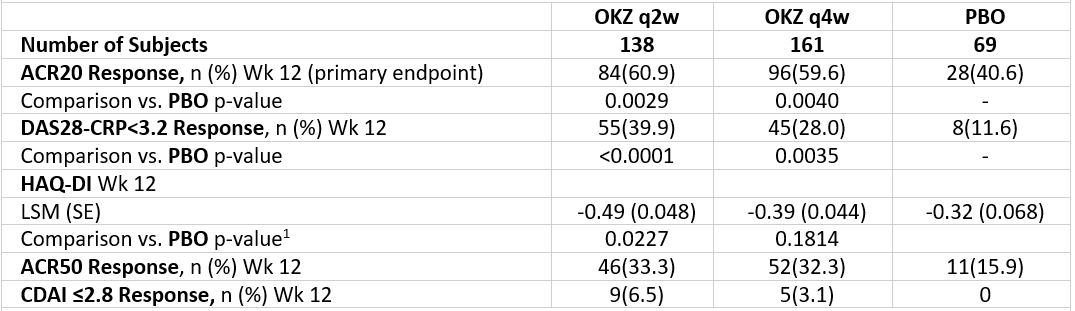 Table 2. Key efficacy results (intent-to-treat population) NRI. NRI, non-responder imputation; LSM, least squares mean; respectively; 1, following the gate-keeping strategy, testing for both OKZ regimens was stopped after the HAQ-DI endpoint testing for formal comparison; SE, Standard Error.
Table 2. Key efficacy results (intent-to-treat population) NRI. NRI, non-responder imputation; LSM, least squares mean; respectively; 1, following the gate-keeping strategy, testing for both OKZ regimens was stopped after the HAQ-DI endpoint testing for formal comparison; SE, Standard Error.
 Table 3. Number and percentage of TESAE (Safety Population). Adverse effects that occurred after the first administration of PBO and prior to any administration of OKZ at or after Week 16 are summarized as a TEAE under PBO.
Table 3. Number and percentage of TESAE (Safety Population). Adverse effects that occurred after the first administration of PBO and prior to any administration of OKZ at or after Week 16 are summarized as a TEAE under PBO.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Feist E, Fatenejad S, Grishin S, Korneva E, Luggen M, Nasonov E, Samsonov M, Fleischmann R. Efficacy and Safety of Olokizumab in a Phase III Trial of Patients with Moderately to Severely Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Inadequately Controlled by TNF-α Inhibitor Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-olokizumab-in-a-phase-iii-trial-of-patients-with-moderately-to-severely-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-inadequately-controlled-by-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitor-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-olokizumab-in-a-phase-iii-trial-of-patients-with-moderately-to-severely-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-inadequately-controlled-by-tnf-%ce%b1-inhibitor-therapy/
