Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1306–1346) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a relatively common serious extra-articular complication in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Although there have been great advances, we do not have strong evidence of the efficacy of the different drugs in the treatment of this complication, which is even scarcer compared to janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi). To systematically evaluate the evidence published in the literature on the efficacy and safety of JAKi in the treatment of RA-associated ILD.
Methods: Literature searches were carried out in the Pubmed, Cochrane Library, Embase and Scopus databases between 01/01/2019 and 01/07/24, according to the Cochrane Manual and the PRISMA guidelines. A combination of the terms and their synonyms “janus kinase inhibitors”, “interstitial lung disease” and “rheumatoid arthritis” were used. Two independent reviewers participated, using a third if there was no agreement.
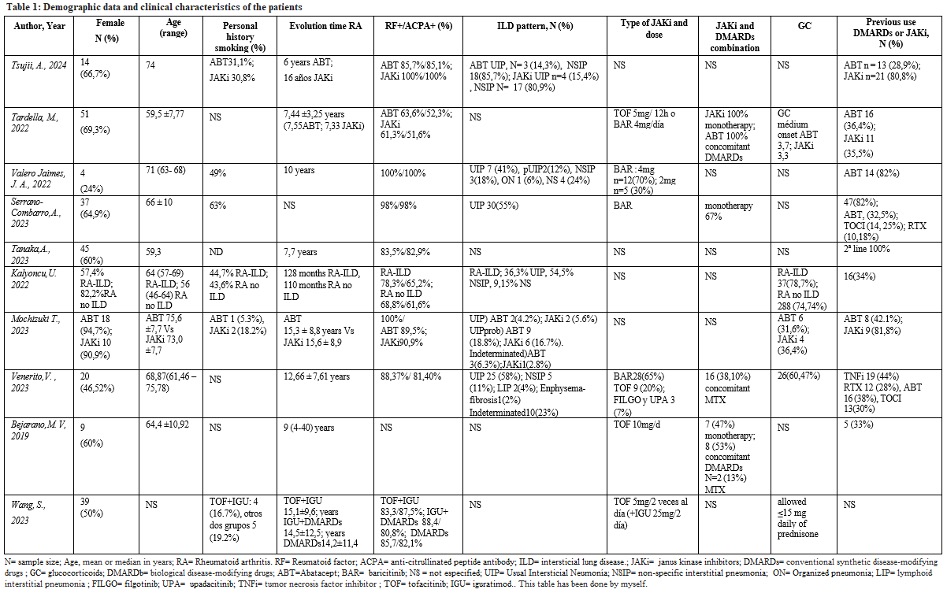
Results: Of a total of 387 references obtained in the initial search, a total of 10 original, 8 retrospective and 2 prospective studies were finally included, including 4 communications. We found no randomised trials, meta-analyses or systematic reviews. Tables 1 and 2 show the characteristics of the included studies, demographic data and clinical characteristics of the patients. The mean age range of the patients oscillated from 59 to 74 years, with a variable percentage of women, generally close to 60%. The follow-up range was from 6 to 36 months. The time of evolution of RA in the included patients varied between 7 and 16 years, with positivity for rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated peptide antibody (ACPA) greater than 80% in most cases. The patterns of ILD reported are highly variable, with the first in frequency being usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) in most studies (up to 58%), followed by non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP). The most frequently used JAKi were tofacitinib and barititinib, which were prescribed as monotherapy in more than half of the patients (60-100%). The methods of assessment of the ILD were highly variable, pulmonary function tests are included (PFT) and high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT). Improved or stabilized HRCT images in more than 80% of patients. Regarding PFT, stabilization was achieved in more than 70% of patients, with a worsening of carbon monoxide difussion capacity test (DLCO) in only 1 study. Only 2 cases of acute exacerbation of ILD were reported in one study, with 1; the rest of the adverse events (AEs) are comparable to what is expected with the safety profile of JAKi, although a higher incidence of such AEs is reported in patients with AR-ILD compared to those with RA without ILD.
Conclusion: JAK inhibitors could be a useful treatment strategy in maintaining stability in RA-associated ILD, including improvement.The low prevalence of ILD during treatment with JAKi suggests that perhaps we should rethink the treatment algorithm in rheumatoid arthritis, even more so in young patients, without contraindications and at risk of developing ILD.Prospective, randomized, controlled studies are needed to confirm this hypothesis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Compán O, Ibañez M, Martínez O, Chacón C, López Pérez R, Felices López B, Miguel Ibáñez B, Blanco L, Cimadevila Santiago S, Turrión Nieves A, Martin Martinez M, Hidalgo Calleja C, Montilla C, Gómez S. Efficacy and safety of janus kinase inhibitors in diffuse interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Systematic review [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-janus-kinase-inhibitors-in-diffuse-interstitial-lung-disease-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-systematic-review/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-janus-kinase-inhibitors-in-diffuse-interstitial-lung-disease-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-systematic-review/

.jpg)
.jpg)