Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
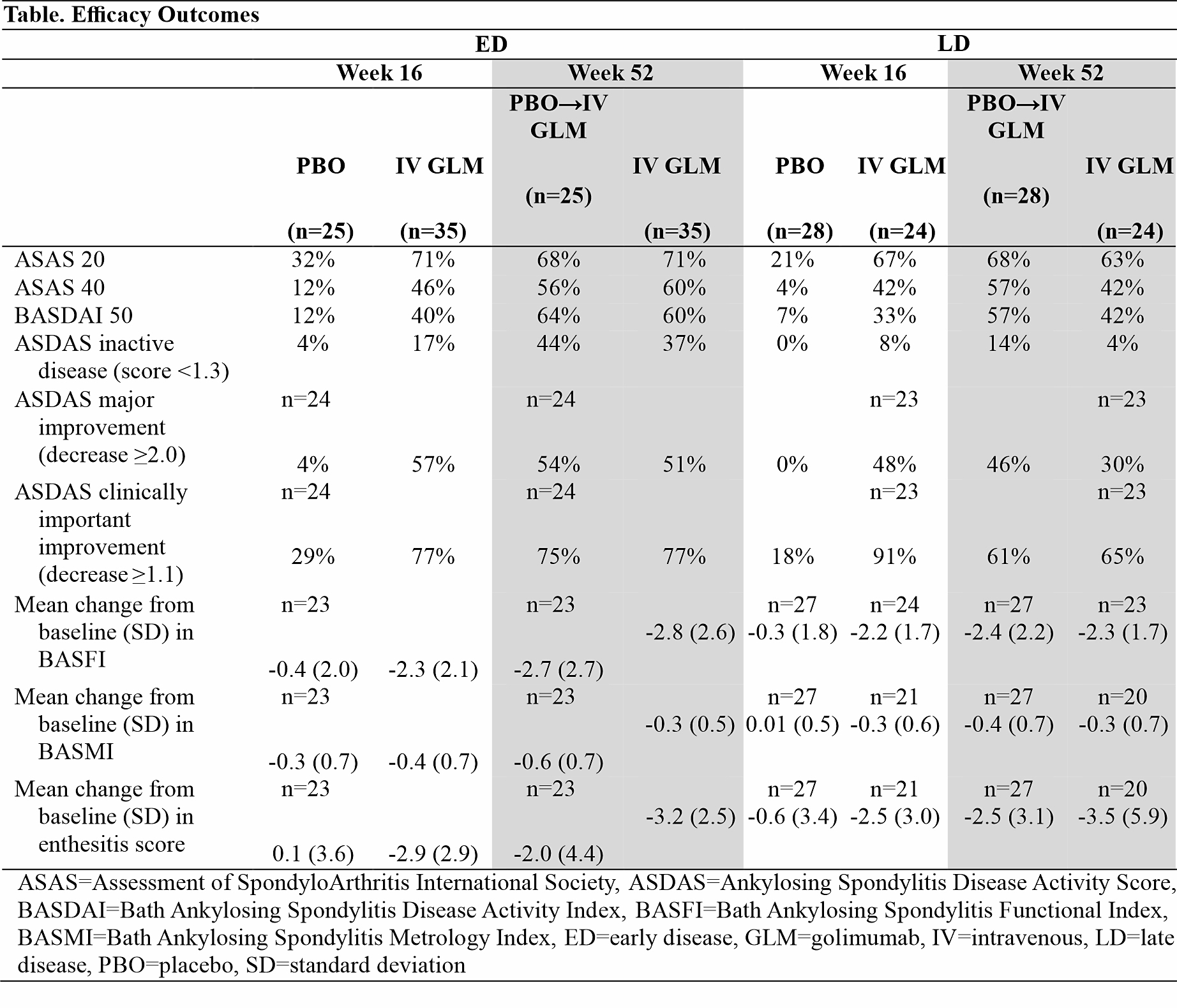
Background/Purpose: The GO-ALIVE study assessed efficacy and safety of intravenous golimumab (IV GLM) in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS).1,2 In this post hoc analysis, we assessed IV GLM efficacy and safety in AS patients with early disease (ED) vs late disease (LD) based on patient-reported duration of inflammatory back pain (IBP).
Methods: In this Phase 3, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled trial, patients with active AS were randomized (1:1) to receive IV GLM 2 mg/kg at Week (W) 0, W4, then every 8 weeks (Q8W) or PBO at W0, W4, and W12 with crossover to IV GLM at W16, W20, then Q8W through W52. The primary endpoint was the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society 20% improvement response (ASAS 20) at W16. In this post hoc analysis, 208 patients were grouped into quartiles based on self-reported duration of IBP symptoms. Efficacy and safety in 60 patients with ED (1st quartile) were compared with 52 patients with LD (4th quartile).
Results: For the overall study population, mean duration of IBP symptoms was 10.9 years and mean time since diagnosis was 5.5 years. For ED patients, the mean duration of IBP symptoms ranged from 2.3 years (IV GLM) to 2.6 years (PBO), and for LD patients ranged from 23.5 years (IV GLM) to 24.4 years (PBO). At W16, ASAS 20 was achieved by 72% IV GLM vs 32% PBO patients with ED and by 67% IV GLM vs 21% PBO patients with LD. Patients with ED had numerically better response than those with LD in Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index (BASMI), and across more stringent endpoints, including ASAS 40, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index 50% improvement (BASDAI 50), and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) inactive disease and major improvement (Table). Response rates at W16 among IV GLM-treated patients were generally consistent through 1 year in both ED and LD subgroups; also in ED and LD subgroups, patients crossing over to IV GLM at W16 demonstrated response at W52 consistent with patients who started IV GLM at W0. At W16, improvements in enthesitis score were similar for patients with ED (mean change -2.9 for IV GLM vs 0.1 for PBO) and LD (mean change ‑2.5 for IV GLM vs 0.6 for PBO); improvements were maintained at W52 for ED and LD patients. Treatment-emergent adverse events and serious adverse events through 1 year were 46% and 3% for patients with ED compared with 61% and 2% for patients with LD, respectively.
Conclusion: While IV GLM provided clinically meaningful improvements in signs and symptoms of AS in patients regardless of disease duration, response generally appeared numerically better in patients with ED than in patients with LD. This supports the principle of prompt diagnosis and early treatment.
References
- Deodhar A, et al. J Rheumatol. 2018;45:341-348.
- Reveille J, et al. J Rheumatol. 2019;46:1277-1283.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deodhar A, Kafka S, Hsia E, Lo K, Lilianne K, Xu S, Reveille J. Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Golimumab in Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients with Early versus Late Disease Through Week 52 of GO-ALIVE Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-intravenous-golimumab-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-patients-with-early-versus-late-disease-through-week-52-of-go-alive-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-intravenous-golimumab-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-patients-with-early-versus-late-disease-through-week-52-of-go-alive-study/