Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Filgotinib (FIL) is an orally administered, potent and selective inhibitor of Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) that has shown good efficacy and was well tolerated for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The objective of this study is to evaluate efficacy and safety of FIL treatment in patients with RA who have had an inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX).
Methods: This phase 3, double-blind, active- and placebo (PBO)-controlled study randomized patients with active RA (3:3:2:3) to FIL 200 mg, FIL 100 mg, active comparator (adalimumab [ADA] 40mg every 2 weeks), or PBO daily for up to 52 weeks; results through week 24 are presented. Patients were also receiving MTX for ≥12 weeks with a stable dose of MTX for ≥4 weeks before initiation of study drug. Primary efficacy endpoint was proportion of patients achieving ACR20 response at week 12; additional clinical assessments were ACR50 and ACR70 responses, DAS28-CRP score ≤3.2 and < 2.6, van der Heijde modified total Sharp score (mTSS), and patient-reported outcomes were HAQ-DI, SF-36 PCS, and FACIT-Fatigue. Safety endpoints included types and rates of adverse events. Logistic regression adjusting for stratification factors with nonresponder imputation was used for superiority test of FIL vs PBO for ACR response and other binary endpoints. Mixed-effect model adjusting for baseline value, stratification factors, treatment, visit, and treatment by visit interaction as fixed effects with observed cases was used for continuous endpoints. Non-inferiority test of FIL to ADA (preserving >50% of ADA response) was performed for DAS28-CRP ≤3.2 and < 2.6.
Results: Of 1,759 patients randomized, 1,755 received study drug and were analyzed, with 475 FIL 200mg; 480 FIL 100mg; 325 ADA; and 475 PBO, of which 89.5%, 90.4%, 88.9%, and 81.3%, respectively, completed week 24 study drug. Most patients (81.8%) were female, mean (standard deviation [SD]) duration of RA was 7.8 (7.6) years, and mean (SD) DAS28-CRP was 5.7 (0.9). At week 12, significantly more patients in the FIL 200mg and 100mg arms achieved an ACR20 response compared to PBO (Table 1). Similarly, compared to PBO, more patients receiving FIL achieved ACR50 and ACR70 responses, DAS28-CRP scores ≤3.2 and < 2.6, had lower radiographic progression, and reported improvements in HAQ-DI, SF-36 PCS, and FACIT-Fatigue scores (Table 1). Non-inferiority of FIL 200mg to ADA was met based on DAS28-CRP ≤3.2. The FIL safety profile was consistent with prior studies through week 24 (Table 2).
Conclusion: The selective JAK1 inhibitor FIL, at doses of 200mg and 100mg led to significant improvement in signs and symptoms of RA, prevented radiographic progression, and improved physical function compared to PBO, and was well tolerated among patients with RA with prior inadequate response to MTX. Efficacy of FIL 200mg was non-inferior to ADA based on DAS28-CRP ≤3.2.

ACR Finch 1 abstract_FINAL_Table 1
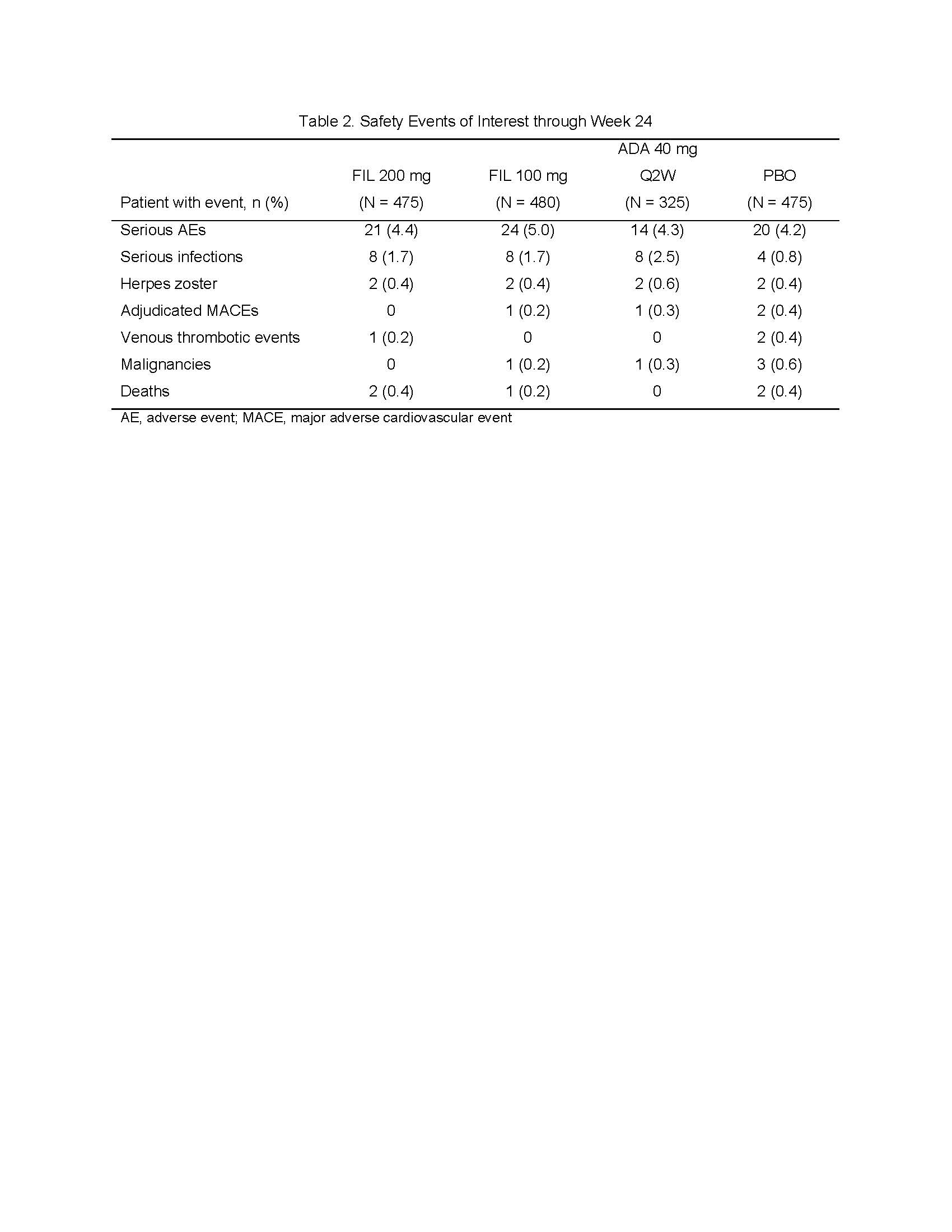
ACR Finch 1 abstract_FINAL_Table 2
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Combe B, Kivitz A, Tanaka Y, van der Heijde D, Matzkies F, Bartok B, Ye L, Guo Y, Tasset C, Sundy J, Mozaffarian N, Landewé R, Bae S, Keystone E, Nash P. Efficacy and Safety of Filgotinib for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis with Inadequate Response to Methotrexate: FINCH1 Primary Outcome Results [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-filgotinib-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-inadequate-response-to-methotrexate-finch1-primary-outcome-results/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-filgotinib-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-inadequate-response-to-methotrexate-finch1-primary-outcome-results/
