Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Filgotinib (FIL), an orally administered, potent, selective inhibitor of Janus kinase 1 (JAK1), has shown good efficacy and was well tolerated for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The objective of this study is to compare efficacy and safety of FIL with and without methotrexate (MTX) in patients with RA who were naïve to MTX therapy.
Methods: This phase 3, double-blind, active-controlled study randomized patients with moderately to severely active RA (2:1:1:2) to FIL 200mg daily + MTX weekly (up to 20mg), FIL 100mg + MTX, FIL 200mg (+placebo [PBO]), or MTX (+PBO) for up to 52 weeks; results through week 24 are presented. Primary efficacy endpoint was proportion of patients achieving ACR20 response at week 24; additional assessments included ACR50 and ACR70 responses; DAS28-CRP score ≤3.2 and < 2.6, and changes in van der Heijde mTSS, HAQ-DI, SF-36 PCS, and FACIT-Fatigue. Safety endpoints included types and rates of adverse events (AEs). Logistic regression adjusting for stratification factors with nonresponder imputation was used for treatment comparisons for ACR response and other binary endpoints. Mixed-effect model adjusting for baseline value, stratification factors, treatment, visit, and treatment by visit interaction as fixed effects with observed cases was used for continuous endpoints.
Results: Of 1,252 randomized patients, 1,249 received study drug (416 FIL 200mg+MTX; 207 FIL 100mg+MTX; 210 FIL 200mg monotherapy; 416 MTX monotherapy) and were analyzed; 1,130 completed week 24. Most (76.9%) were female; mean time since RA diagnosis was 2.2 years (median 0.4 years); mean (standard deviation [SD]) DAS28-CRP was 5.7 (1.0); and 35.9% were using oral steroids at baseline. At week 24, significantly more patients in the FIL 200mg+MTX (81.0%; P< 0.001) and FIL 100mg+MTX (80.2%; P< 0.05) arms achieved an ACR20 response compared to MTX monotherapy (71.4%)(Table 1). Compared to MTX monotherapy, more patients receiving FIL with or without MTX achieved ACR50 and ACR70 responses, DAS28-CRP < 2.6 and ≤3.2, and reported improvements in SF-36 PCS (Table 1). The onset of activity was rapid, with significantly more patients achieving ACR50 and DAS28-CRP < 2.6 with FIL than MTX at week 2. The FIL safety profile was consistent with prior studies through week 24 (Table 2).
Conclusion: The JAK1 inhibitor FIL in combination with MTX led to significant improvements in RA signs and symptoms, physical function, and patient-reported outcomes compared to MTX alone and was well tolerated in patients with early active RA naïve to MTX. Clinically meaningful response to FIL occurred as early as 2 weeks after treatment initiation.
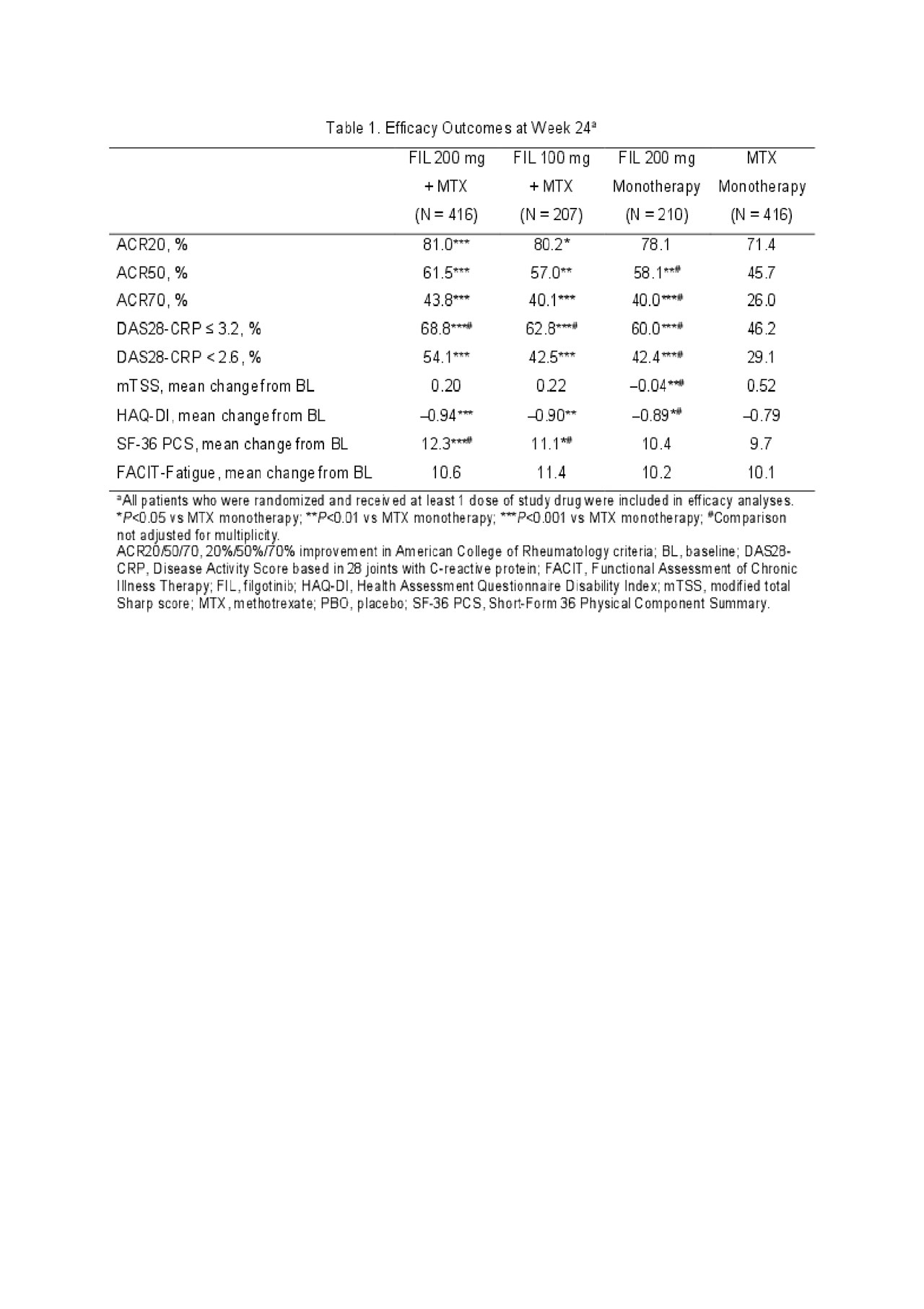
ACR 2019 Finch 3 LBA_FINAL_TABLE 1
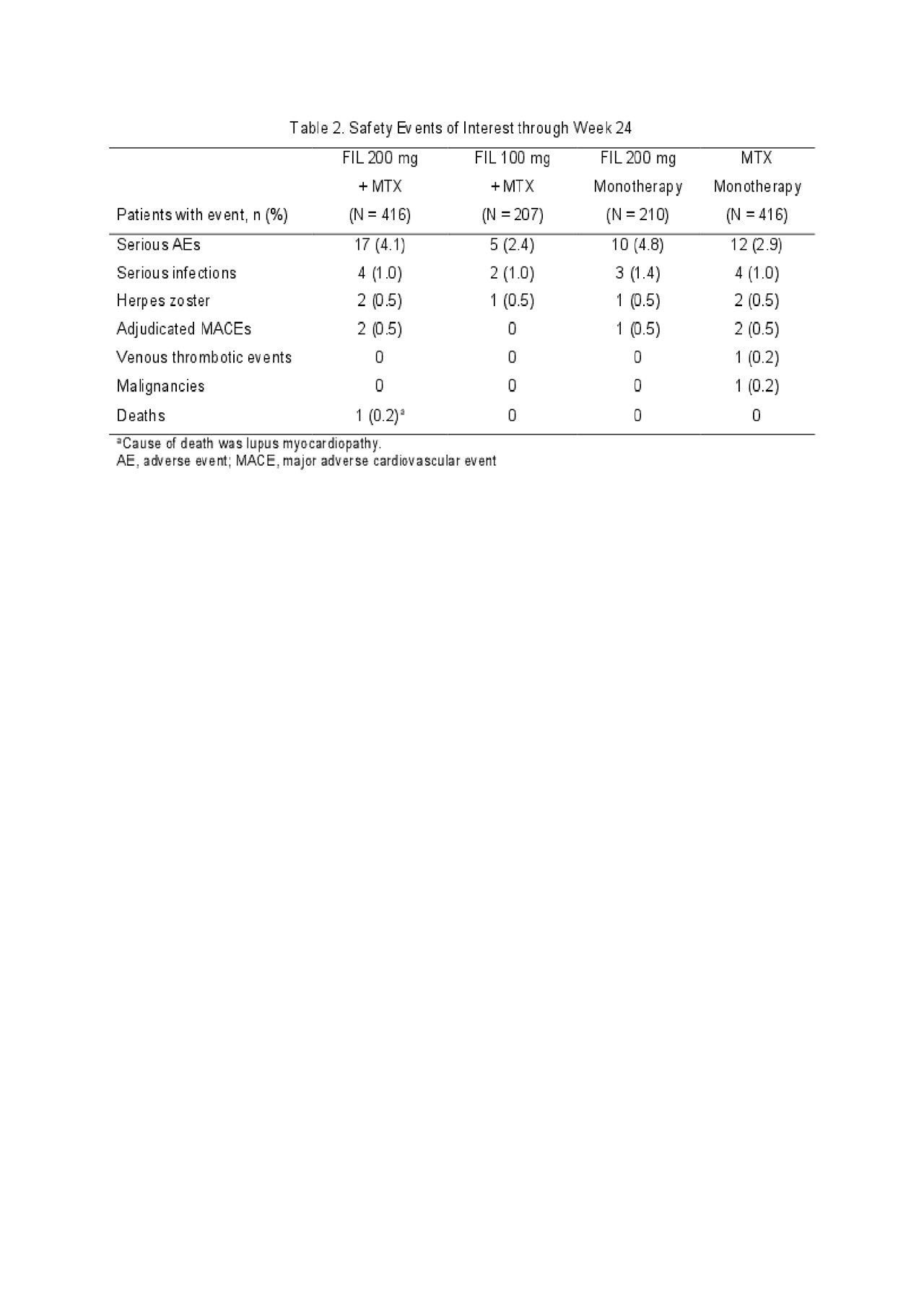
ACR 2019 Finch 3 LBA_FINAL_TABLE 2
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Westhovens R, Rigby W, van der Heijde D, Ching D, Bartok B, Matzkies F, Yin Z, Guo Y, Tasset C, Sundy J, Mozaffarian N, Messina O, Landewé R, Atsumi T, Burmester G. Efficacy and Safety of Filgotinib for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Naïve to Methotrexate Therapy: FINCH3 Primary Outcome Results [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-filgotinib-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-naive-to-methotrexate-therapy-finch3-primary-outcome-results/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-filgotinib-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-naive-to-methotrexate-therapy-finch3-primary-outcome-results/
