Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Fenebrutinib (GDC-0853, FEN) is an orally administered, highly selective, non-covalent, and reversible small molecule inhibitor of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK).1 We report the efficacy and safety of FEN compared with placebo (PBO) in combination with background methotrexate (MTX) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and an inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor (TNF-IR), identified as a population with existing unmet medical need.
Methods: This multicenter, randomized, double-blind Phase 2 study included two cohorts of patients with moderate-to-severe RA: cohort 1 (MTX-IR patients) and cohort 2 (TNF-IR patients). Primary (cohort 1) and key secondary (cohorts 1 and 2) endpoints were a 50% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology scores (ACR50) at Week 12, with pre-specified alpha of 0.2. Patients in cohort 2 (TNF-IR) were randomized to PBO and to FEN 200 mg BID arms for 12 weeks with the continuation of background MTX dose; the safety and efficacy results for this cohort are reported here (cohort 1 data has been reported previously2).
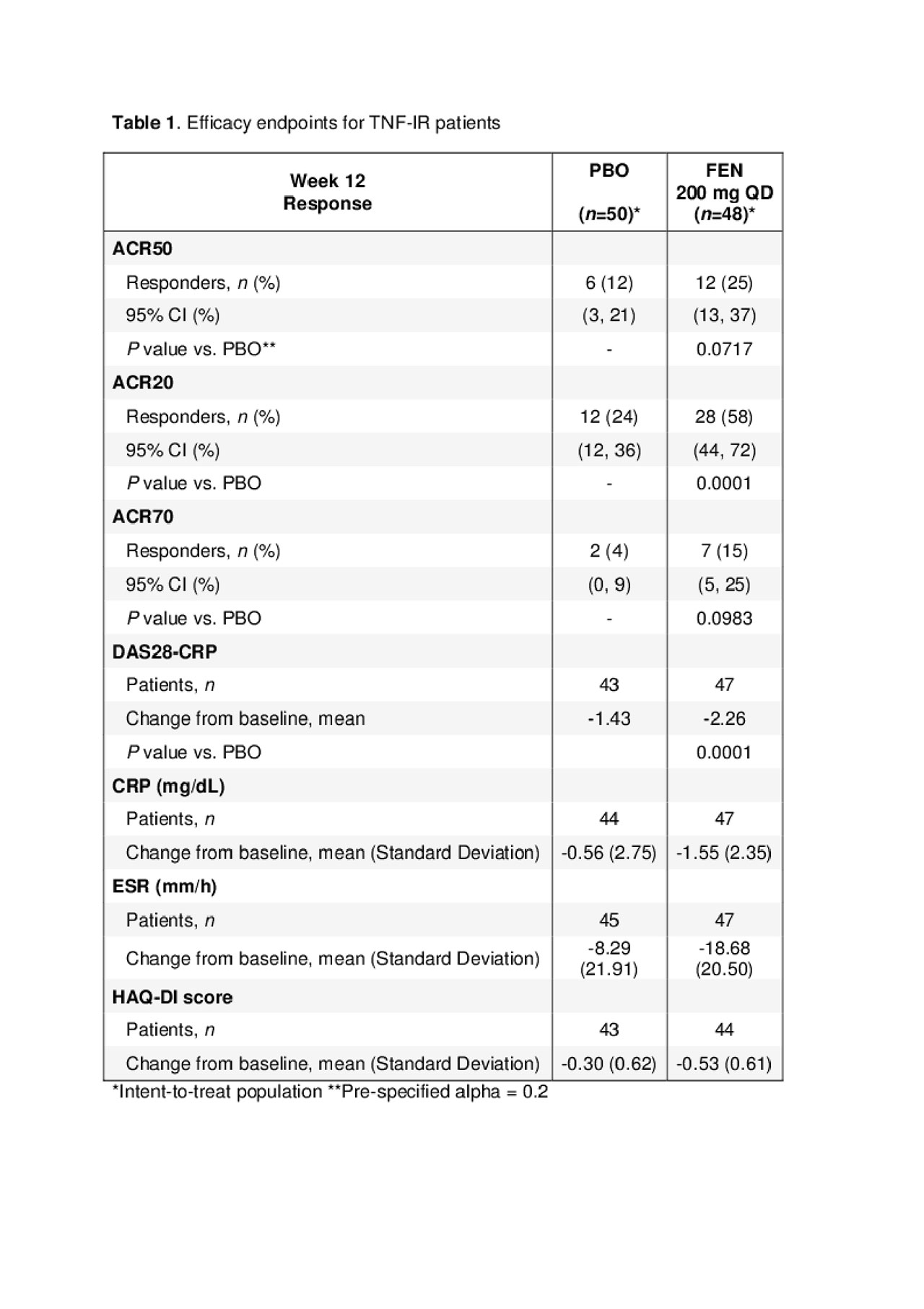
Results: Demographics and disease characteristics for the TNF-IR cohort were balanced in the PBO (n=49) and FEN (n=49) arms with mean age of 55 and 51 years, respectively, and 76% female patients/arm. Median duration of RA disease was 8.7 years (PBO) and 7.2 years (FEN). The mean baseline doses for MTX were 16.6 mg (PBO) and 15.7 mg (FEN). Corticosteroid mean doses were 8.3 and 7.5 mg prednisone-equivalents in the 33% and 39% of patients using corticosteroids in the PBO and FEN arms at baseline, respectively. Baseline mean values for DAS28-CRP and HAQ-DI were similar (6.0 and 5.9, and 1.76 and 1.45, respectively) for PBO and FEN arms. The majority of patients in the PBO (90%) and FEN (98%) arms completed the 12-week study. ACR20/50/70 responses (Table 1) were greater for FEN versus PBO and generally increased over time, with plateau of ACR50 after W8 for all patients. ACR50 response at W12 was greater for FEN (25% vs 12%, p-value=0.07 [pre-specified type-1 error rate=0.20 two sided]). At W12, DAS28-CRP decreased by -1.43 (PBO) and -2.26 (FEN) from baseline. More patients in the PBO arm (45%) than in the FEN arm (22%) reported at least one AE; no serious AEs were reported. There were 37 AEs in the PBO arm and 22 AEs in the FEN arm (including one case of herpes zoster), with one AE (worsening RA) leading to treatment withdrawal in the PBO group. No deaths or malignancies were reported. There were no clinically significant changes in hematology or immunoglobulin parameters. In two patients treated with FEN, Grade 3 chemistry abnormalities were observed (low phosphorous, high uric acid). No Grade 4 or 5 abnormalities were reported. Although no Grade 3 creatinine elevations were observed, there was an increased mean change from baseline in creatinine in the FEN arm (5.1 µmol/L) in comparison to PBO arm (-0.4 µmol/L) at W12.
Conclusion: FEN demonstrated higher efficacy rates across disease activity measures vs. PBO at W12 in the TNF-IR population. The safety profile of FEN in this population is acceptable.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cohen S, Tuckwell K, Kunder R, Katsumoto T, Zhao R, Berman A, Damjanov N, Fedkov D, Jeka S, Genovese M. Efficacy and Safety of Fenebrutinib, a BTK Inhibitor, Compared to Placebo in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Active Disease Despite TNF Inhibitor Treatment: Randomized, Double Blind, Phase 2 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-fenebrutinib-a-btk-inhibitor-compared-to-placebo-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-active-disease-despite-tnf-inhibitor-treatment-randomized-double-blind-phase-2-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-fenebrutinib-a-btk-inhibitor-compared-to-placebo-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-active-disease-despite-tnf-inhibitor-treatment-randomized-double-blind-phase-2-study/