Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment I: Emerging Therapies (0488–0491)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-2:15PM
Background/Purpose: Brepocitinib is a small-molecule tyrosine kinase 2/Janus kinase 1 inhibitor that has shown promising results in an oral formulation for plaque psoriasis and alopecia areata and is under investigation for PsA.
Methods: This Phase 2b, randomized placebo (PBO)-controlled trial compared the efficacy and safety of once-daily (QD) oral doses of brepocitinib (10, 30, and 60 mg) vs PBO in patients (pts) with active PsA (NCT03963401). Eligible pts were aged 18–75, met CASPAR (ClASsification criteria for Psoriatic ARthritis), and had active PsA despite treatment or intolerance to NSAIDs/DMARDs; stable doses of conventional synthetic DMARDs were allowed, and up to 30% of pts with prior use of one TNF inhibitor were allowed. Pts were randomized (2:2:1:2) to receive brepocitinib 60 mg QD, 30 mg QD, 10 mg QD, or PBO for 16 weeks, advancing to brepocitinib 30 or 60 mg QD from Week 16 to 52. Primary endpoint: pts meeting ACR20 response at Week 16. Selected secondary, exploratory, and safety endpoints are reported.
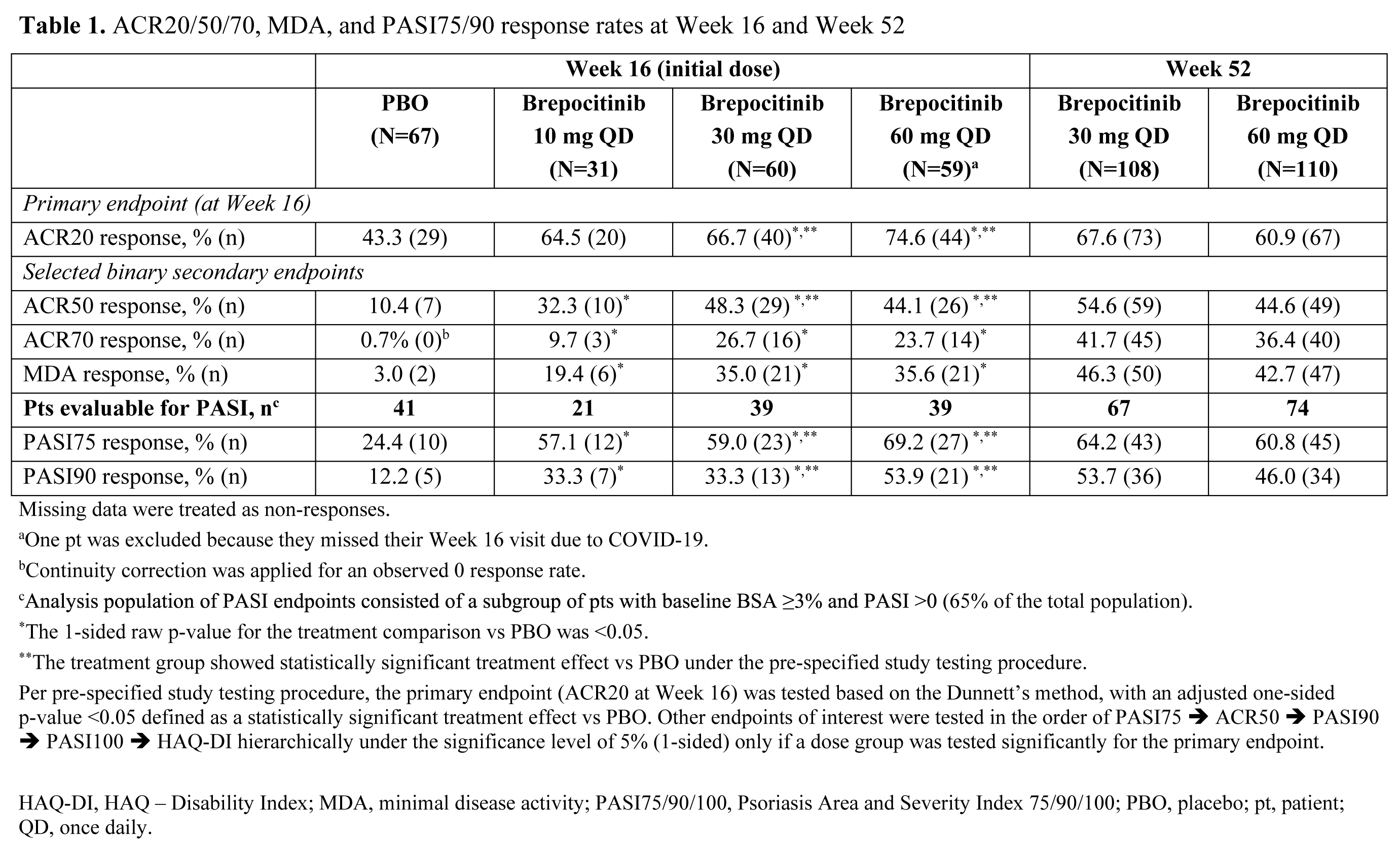
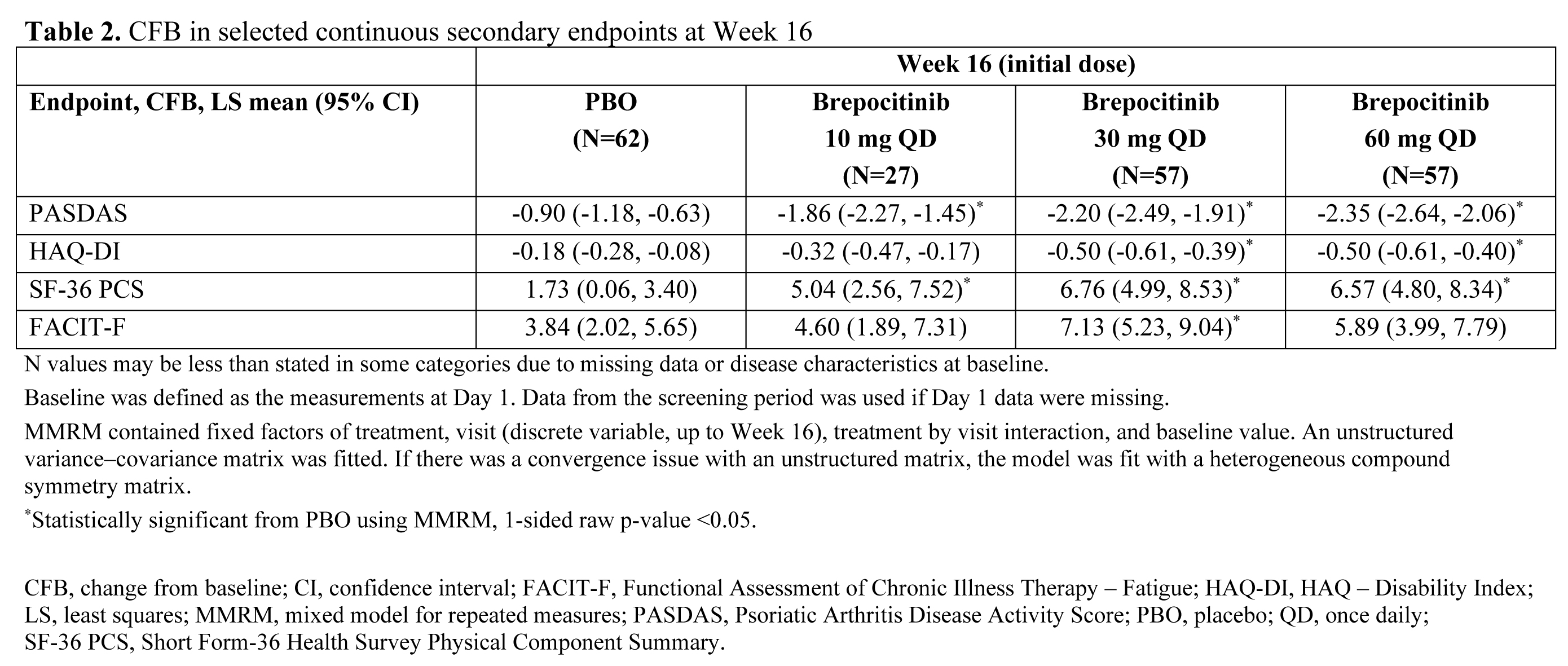
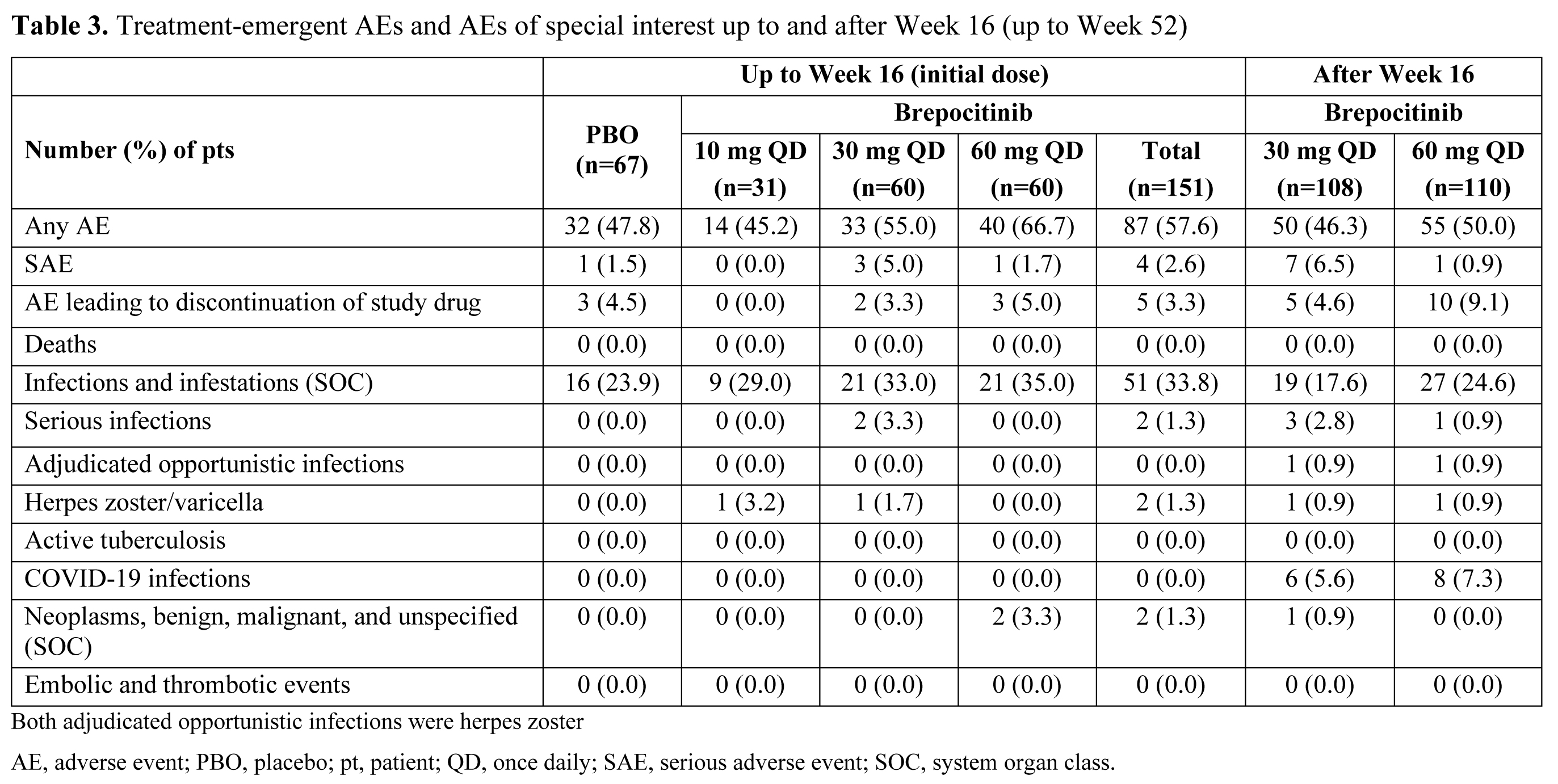
Results: A total of 218 pts were randomized and treated. Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were generally similar across groups, and the majority of pts (93.1%) completed the Week 16 visit. At Week 16, significantly higher proportions of pts in the brepocitinib 30 and 60 mg QD groups achieved an ACR20 response vs PBO (Table 1). Brepocitinib 30 and 60 mg QD groups achieved significantly higher response rates vs PBO, starting as early as Week 4, and response rates continued to increase to Week 16 for ACR20/50/70, Minimal Disease Activity, and Psoriasis Activity and Severity Index 75/90. Responses were maintained to Week 52 (Table 1). Brepocitinib 30 and 60 mg QD were associated with significant improvements in disease activity and quality of life outcomes (e.g. fatigue, functioning) at Week 16 vs PBO (Table 2). Improvements in dactylitis and Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada enthesitis resolution were observed at Week 16 in the brepocitinib 60 mg group vs PBO; resolution continued to improve or remain steady through Week 52 in the 30 mg and 60 mg groups, respectively. In the 16-week treatment period, there were more pts with adverse events (AEs) in the brepocitinib 30 mg (n=33) and 60 mg (n=40) QD groups vs PBO (n=32). Most AEs were mild in severity (165/250 [66%]) at Week 16. Key safety findings are shown in Table 3. There were 17 serious AEs (SAEs) in 12 pts during this study, including 7 SAEs in 6 pts through Week 16. The overall safety profile over 52 weeks was consistent with approved Janus kinase inhibitors, including cases of serious herpes zoster infections and changes in select lab parameters. There were no major adverse cardiovascular events, venous thromboembolic events, or deaths.
Conclusion: Brepocitinib demonstrated superior efficacy vs PBO across numerous PsA disease domains in pts with active PsA at Week 16, with improvements in more refractory domains continuing over 52 weeks. There were more AEs in the brepocitinib groups vs PBO over 16 weeks. The overall safety of brepocitinib was consistent with other approved Janus kinase inhibitors.
Acknowledgments: Funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Helliwell P, Silwinska-Stanczyk P, Miakisz M, Ostor A, Peeva E, Vincent M, Sikirica V, Winnette R, Qiu R, Li G, Feng G, Beebe J, Martin D. Efficacy and Safety of Brepocitinib (Tyrosine Kinase 2/Janus Kinase 1 Inhibitor) for the Treatment of Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from a Phase 2b Randomized Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-brepocitinib-tyrosine-kinase-2-janus-kinase-1-inhibitor-for-the-treatment-of-active-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-a-phase-2b-randomized-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-brepocitinib-tyrosine-kinase-2-janus-kinase-1-inhibitor-for-the-treatment-of-active-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-a-phase-2b-randomized-controlled-trial/