Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Biologics suppress hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication and play an important role in eradicating HBV by stimulating HBV-specific cytotoxic T-cell responses. We found that HBV reactivates or flares after biologics therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection and in those with inactive hepatitis B surface antigen (HBs-Ag). The guideline, prevention of immunosuppressive-induced reactivation of HBV infection, recommend nucleoside analogs for treating patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who are positive for HBs-Ag. We aimed to determine the efficacy and safety of biological therapy in patients with RA carrying hepatitis B by evaluating clinical characteristics and changes in serological and biological markers of HBV flare.
Methods: Six patients with RA who screened positive for HBs-Ag were prescribed with entecavir (ETV) under the direction of a hepatologist when HBV-DNA levels decreased to < 2.1 log copies/mL. The patients were also treated with infliximab (n = 1), etanercept (n = 2), adalimumab (n = 2) and tocilizumab (n = 1) (Table). We evaluated the disease activity score of RA (DAS28-ESR), HBV markers and genotype before starting treatment as well as changes in the amount of HBV-DNA, HBs-Ag and alanine aminotransferase (ALT).
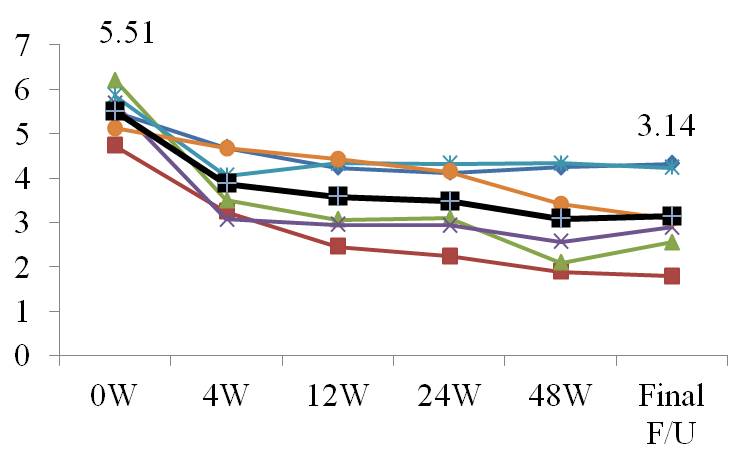
Results: The average age, duration of RA and DAS28-ESR at baseline was 54.7 years, 10.9 years and 5.51, respectively. The minimum HBs-Ag value is 12.2 and three patients had values over >2000 before starting ETV therapy. The pre-treatment values of HBV-DNA and ALT were 4.28 log copies/mL and 20.2 U/L, respectively. Flare of HBV was not confirmed during 2.1 years the patients were treated with these agents. Hepatitis B viral DNA was undetectable in all cases at final follow-up (Table). The DAS28-ESR was 3.14 at final follow-up and disease RA activity remained low (Figure).
Conclusion: Antiviral prophylaxis protected against HBV reactivation in patients with RA, indicating that biologics are relatively safe for treating such patients. Biologics could serve as a useful treatment for hepatitis B carriers who are simultaneously prescribed with nucleoside analogs under the control of a hepatologist.
Table: Changes in the amount of HBs-Ag, HBV-DNA, and ALT
|
|
Patient 1 |
Patient 2 |
Patient 3 |
Patient 4 |
Patient 5 |
Patient 6 |
|
Age, years |
56 |
33 |
58 |
63 |
64 |
54 |
|
HBs-Ag at baseline, mIU/mL |
233.9 |
2000< |
2000< |
2000< |
12.2 |
332 |
|
HBs-Ag at final F/U, mIU/mL |
259.2 |
2000< |
2000< |
2000< |
17.3 |
215.1 |
|
HBV DNA at baseline, log/mL |
4.8 |
3.6 |
7.6 |
4.9 |
2.3 |
2.5 |
|
HBV DNA at final F/U, log/mL |
undetectable |
undetectable |
undetectable |
undetectable |
undetectable |
undetectable |
|
ALT at baseline, U/L |
13 |
12 |
58 |
13 |
8 |
17 |
|
ALT at final F/U, U/L |
10 |
14 |
15 |
15 |
10 |
15 |
|
Biologics |
ETN |
IFX |
ADA |
TCZ |
ETN |
ADA |
Disclosure:
M. Tada,
Japan Osteoporosis Found grant 2013,
2;
T. Koike,
Takeda Pharmaceutical, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Chugai Pharmaceutical, Eisai, Abbott Japan, Teijin Pharma, Banyu Pharmaceutical and Ono Pharmaceutical,
8;
A. Tamori,
None;
T. Okano,
None;
Y. Sugioka,
None;
K. Mamoto,
None;
K. Inui,
None;
H. Nakamura,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-biologics-agents-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-hepatitis-b-carrier/