Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: AxSpA
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Since the 2016 update of the management recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), new evidence has emerged on the efficacy and safety of biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) in axSpA. Our aim was to summarize this new evidence to inform the taskforce of the 2022 update of the ASAS-EULAR recommendations for the management of axSpA on this topic.
Methods: Systematic literature review of studies published between 2016-2021 on the efficacy and safety of bDMARDs in axSpA (including r-axSpA and nr-axSpA) (PROSPERO registration CRD42021257588). Eligible study designs included randomised controlled trials (RCTs), strategy trials and observational studies (the latter only for safety and extra-musculoskeletal manifestations). All relevant efficacy/safety outcomes were included. Risk ratios (RR) were used as effect measure for efficacy.
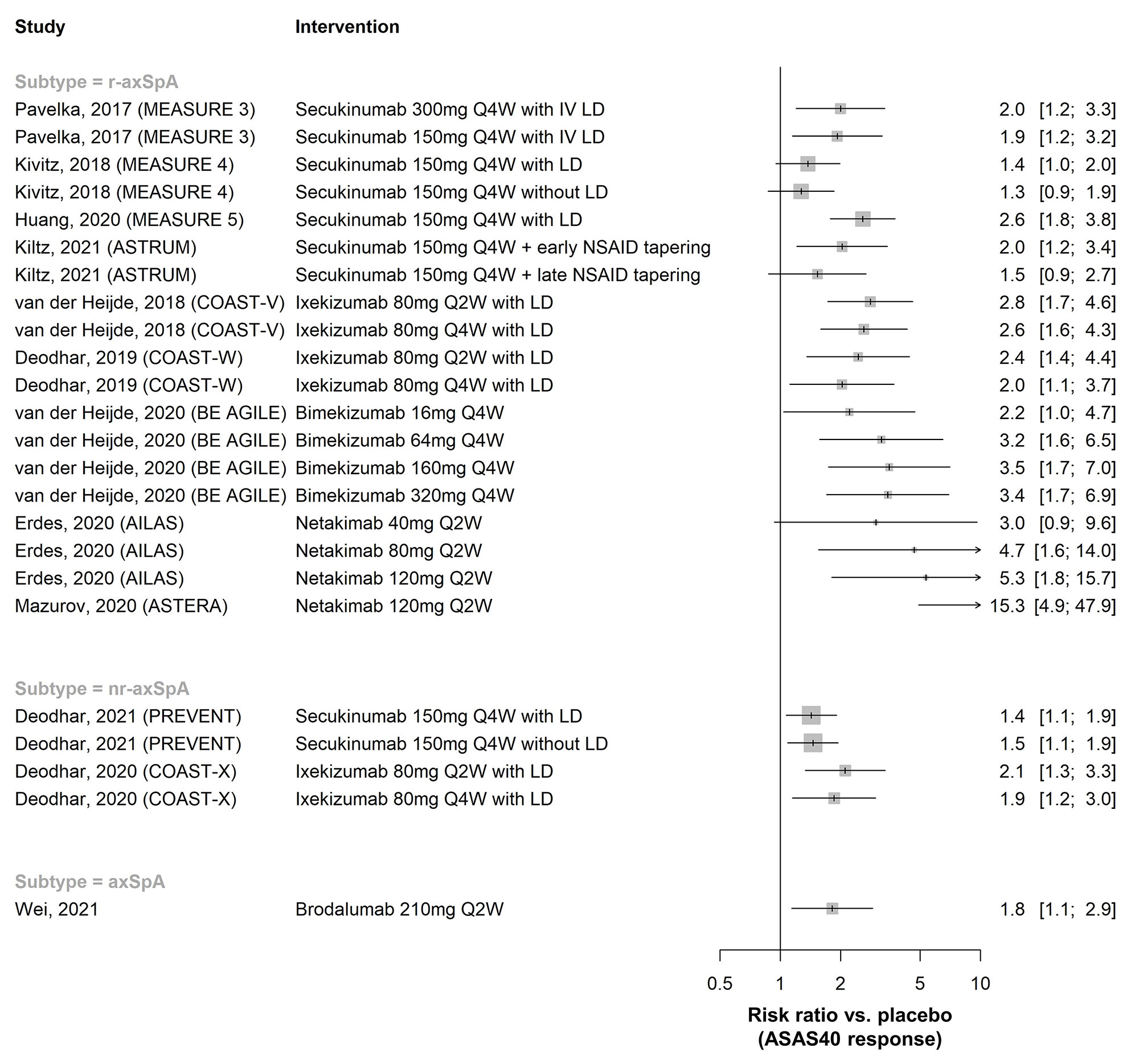
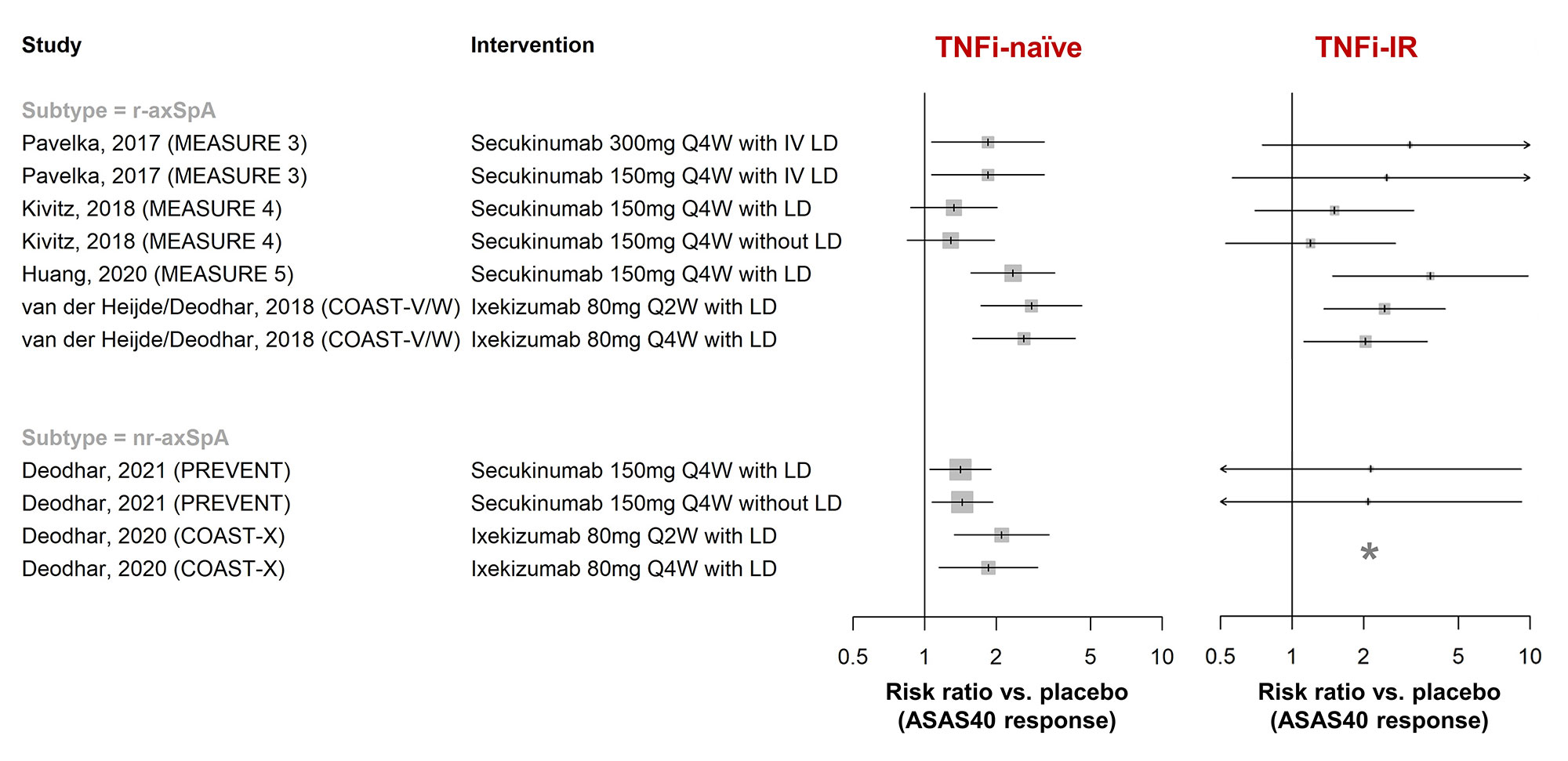
Results: In total, 148 publications (91 full-text articles and 57 conference abstracts) were included. Efficacy of golimumab and certolizumab was confirmed in r-axSpA and nr-axSpA, respectively. Equivalence between adalimumab/etanercept/infliximab biosimilars and originators was demonstrated (n=1 each). Fourteen placebo-controlled RCTs investigated efficacy of interleukin-17 inhibitors (IL-17i: secukinumab [n=7], ixekizumab [n=3], netakimab [n=2], brodalumab [n=1], bimekizumab [n=1]) and found clinically relevant effects (RR versus placebo to achieve ASAS40 response 1.3-15.3 [r-axSpA, n=9], 1.4-2.1 [nr-axSpA, n=2]; Figure 1). Efficacy of secukinumab/ixekizumab was demonstrated both in TNFi-naïve and TNFi-inadequate responders, with response rates being higher in TNFi-naïve patients (Figure 2). Trials of IL-23 and IL-12/23 inhibitors (IL-23i: risankizumab [n=1]; IL-12/23i: ustekinumab [n=3]) failed to show relevant benefits compared to placebo and were stopped. Discontinuation of TNFi (n=3) and IL-17i (n=1) resulted in high rates of flare (45-80% within 48 weeks), while tapering of TNFi by spacing was non-inferior to standard-dose treatment in maintaining disease control (n=2). The first axSpA treat-to-target trial did not meet its primary endpoint (ASAS-HI 30% improvement) but showed improvements in secondary outcomes (ASAS20/40). No new risks with TNFi were found in observational studies (no data yet for IL-17i in observational studies). Secukinumab and etanercept were associated with increased risk of uveitis compared to monoclonal TNFi in one and two observational studies, respectively.
Conclusion: New evidence supports the efficacy and safety of TNFi (originators/biosimilars) and IL-17i in r-axSpA and nr-axSpA, while IL-12/23i and IL-23i failed to show relevant effects. This systematic review provides important new insights into the management of patients with bDMARDs, across the entire spectrum of axSpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Webers C, Ortolan A, Sepriano A, Falzon L, Baraliakos X, Landewé R, Ramiro S, van der Heijde D, Nikiphorou E. Efficacy and Safety of Biological DMARDs: A Systematic Literature Review Informing the 2022 Update of the ASAS-EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-biological-dmards-a-systematic-literature-review-informing-the-2022-update-of-the-asas-eular-recommendations-for-the-management-of-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-biological-dmards-a-systematic-literature-review-informing-the-2022-update-of-the-asas-eular-recommendations-for-the-management-of-axial-spondyloarthritis/