Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (bari), an oral selective JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor, has been shown to be safe and efficacious compared to placebo (PBO) in two Phase 3 trials in patients (pts) with moderate to severe RA and an inadequate response (IR) to conventional DMARDs (cDMARDs).1,2 The objective of this analysis was to evaluate efficacy and safety of bari 4 mg vs. PBO in the United States (US) vs. the “rest of world” (ROW) subpopulations of these two studies.
Methods: Eligibility requirements included ≥6 swollen and tender joints and no prior biologic DMARD use. In RA-BUILD, cDMARD-IR pts with hsCRP≥3.6 mg/L were randomized to PBO or bari (2 or 4 mg) once daily (QD).1 In RA-BEAM, MTX-IR pts with x-ray erosions and hsCRP≥6.0 mg/L were randomized to PBO QD, bari 4 mg QD, or adalimumab 40 mg biweekly.2 Primary endpoint in both trials was ACR20 at Wk 12 for bari 4 mg vs. PBO. This post-hoc analysis combined data from both trials providing overall samples for bari 4 mg (N=714) and PBO (N=716). The geographically-defined subpopulations were US/Puerto Rico [US/PR] and ROW. Descriptive statistics were utilized for efficacy and safety analyses.
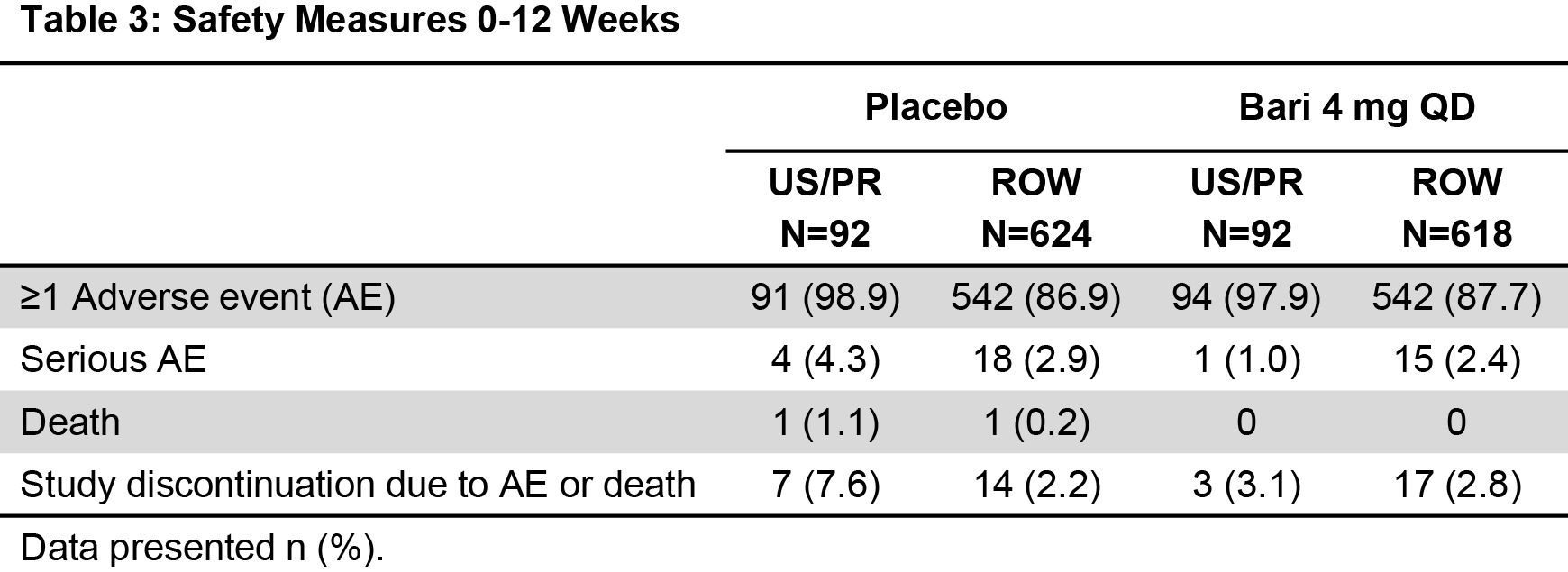
Results: There were 188 US/PR and 1,242 ROW pts in this analysis. The proportions of pts who were White or Black/African-American were higher in US/PR; Asians were more represented in ROW. US/PR pts were slightly older, with fewer years of RA, and a lower percentage were RF/ACPA positive or used corticosteroids. More US/PR pts had previously used 1 cDMARD and more ROW had previously used ≥3cDMARDs (Table 1). Bari 4 mg demonstrated better responses vs. PBO across US/PR and ROW for multiple efficacy outcomes, including ACR20/50/70, LDA, remission, DAS28-CRP, and HAQ-DI (Table 2). Comparing US/PR and ROW efficacy, no systematic differences were observed. No significant safety differences were identified for US/PR or ROW pts at Wk 12 for bari 4 mg vs. PBO in the incidence of ≥1 adverse event (AE), serious AE, or discontinuation due to AE or death (Table 3). There was 1 death in PBO in each subpopulation.
Conclusion: In this post-hoc, pooled analysis from two Phase 3 trials in cDMARD-IR patients, bari 4 mg demonstrated efficacy compared to PBO in US/PR patients. References: 1Dougados M et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74(S2):79; 2Taylor P et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015;67(suppl 10):3928.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wells AF, Greenwald M, Bradley JD, Alam J, Arora VK, Kartman CE. Efficacy and Safety of Baricitinib in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and an Inadequate Response to Conventional Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs: A United States Subpopulation Analysis from Two Phase 3 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-baricitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-an-inadequate-response-to-conventional-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-a-united-states-subpopulation-analysis-from-t/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-baricitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-an-inadequate-response-to-conventional-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-a-united-states-subpopulation-analysis-from-t/