Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Treatment II: Non-Cellular Lupus Therapeutics
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: ABBV-599 (a combination of a selective Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, elsubrutinib [ELS], and a selective Janus kinase inhibitor, upadacitinib [UPA]) targets a spectrum of signaling pathways associated with SLE, which may extend the immunologic effects of either alone. In the phase 2 SLEek study (NCT03978520), patients with moderately to severely active SLE were randomized 1:1:1:1:1 to receive once daily ABBV-599 high dose (HD; ELS 60 mg + UPA 30 mg), ABBV-599 low dose (LD; ELS 60 mg + UPA 15 mg), ELS 60 mg, UPA 30 mg, or placebo (PBO). After a planned interim analysis, the ABBV-599 LD and ELS 60 mg groups were discontinued due to lack of efficacy. Through 48 weeks, treatment with ABBV-599 HD or UPA 30 mg resulted in significant improvements in SLE disease activity and flares compared with PBO. Here, we report results from the SLEek long-term extension (LTE) study (NCT04451772) through 104 weeks.
Methods: In the LTE study, patients continued their original randomized treatment from the SLEek study except for the PBO group, who were rerandomized 1:1 to ABBV-599 HD or ABBV-599 LD at week 48. This analysis included the continued groups: ABBV-599 HD, UPA 30 mg, and PBO to ABBV-599 HD. Efficacy measures included SLE Responder Index (SRI-4), BILAG–based Combined Lupus Assessment (BICLA), Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS), mean glucocorticoid dose, and flares. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were summarized using the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities v26.0. Efficacy (as observed) and safety were assessed through 104 weeks.
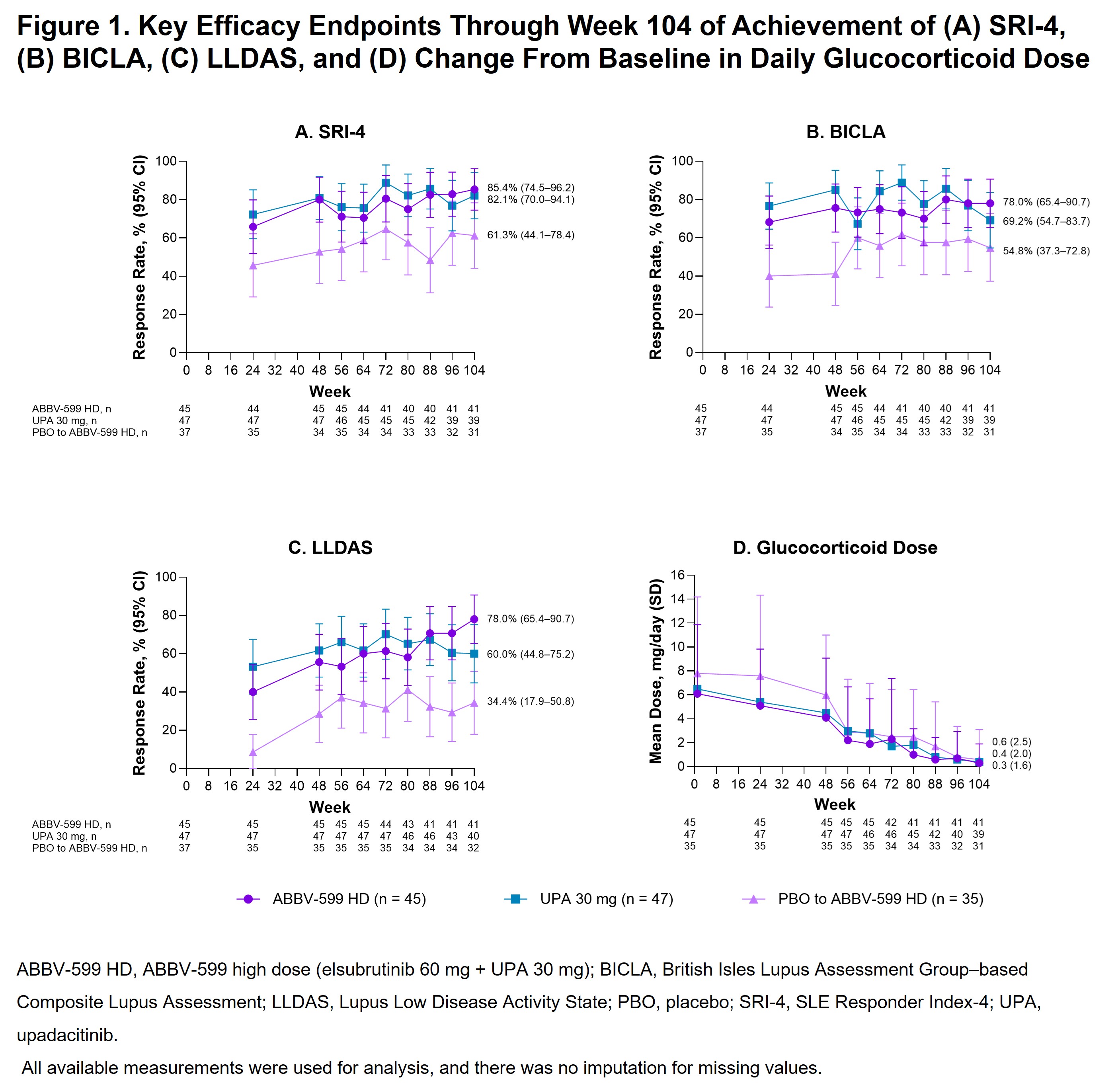
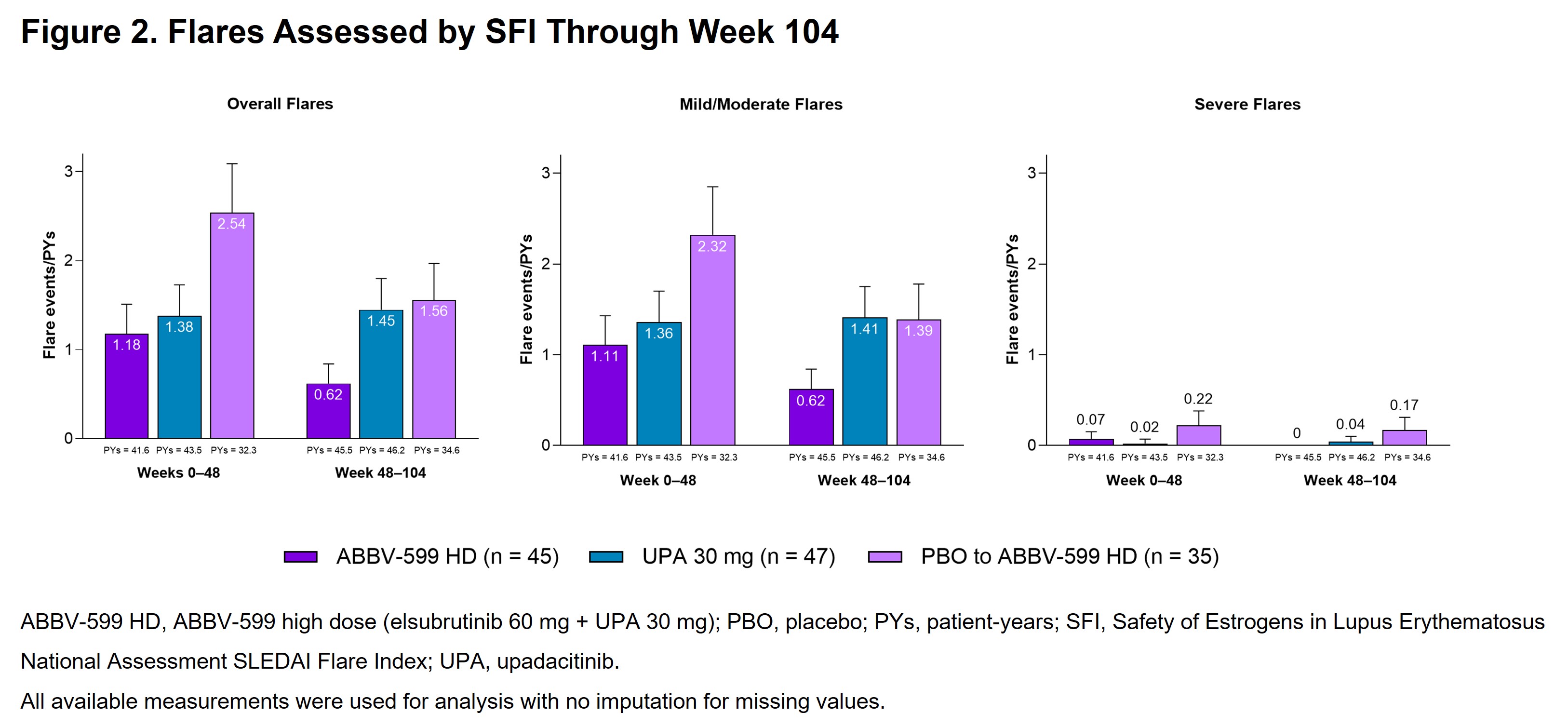
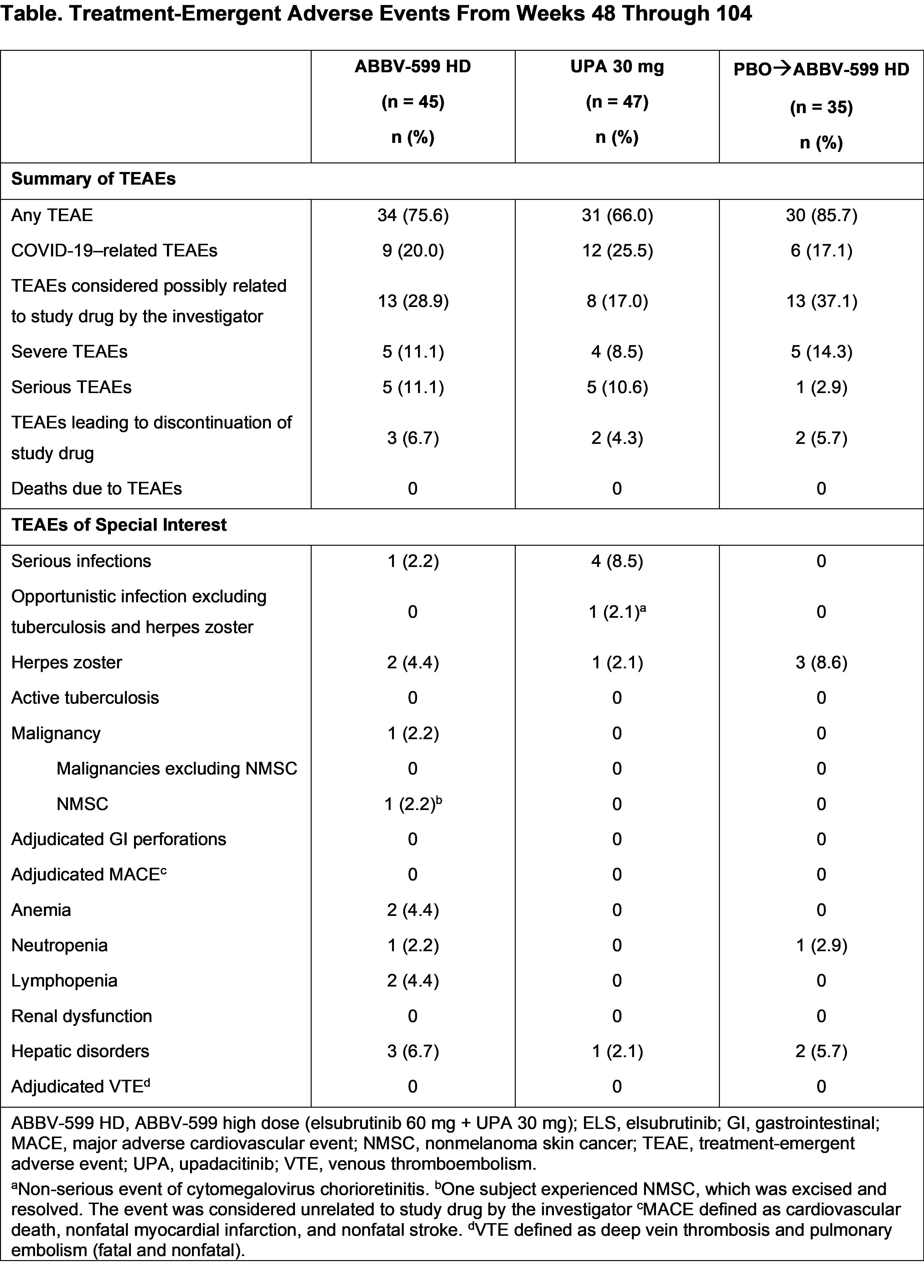
Results: The LTE included 127 patients (ABBV-599 HD, n = 45; UPA 30 mg, n = 47; PBO to ABBV-599 HD, n = 35). Baseline characteristics were balanced across groups. The proportion of patients achieving SRI-4 increased from weeks 48 through 104 to 85.4% (95% CI, 74.5–96.2), 82.1% (95% CI, 70.0–94.1), and 61.3% (95% CI, 44.1–78.4) in the ABBV-599 HD, UPA 30 mg, and PBO to ABBV-599 HD groups, respectively (Figure 1A). Other secondary endpoints (BICLA, LLDAS, and number of flares per patient-years) were either maintained or improved through week 104 in the ABBV-599 HD and UPA 30 mg groups and improved from weeks 48 through 104 in the PBO to ABBV-599 HD group (Figure 1B, 1C and Figure 2). In all 3 groups, patients were nearly glucocorticoid free by week 104 (Figure 1D). TEAEs occurred in 75.6%, 66.0%, and 85.7% of patients in the ABBV-599 HD, UPA 30 mg, and PBO to ABBV-599 HD groups, respectively (Table). No cases of venous thromboembolism or major adverse cardiovascular events occurred.
Conclusion: In patients with moderately to severely active SLE, ABBV-599 HD or UPA 30 mg resulted in maintenance or further improvement in lowered disease activity, flare reduction, and decreased glucocorticoid use through 104 weeks of treatment. Patients who switched from PBO to ABBV-599 HD at week 48 improved in all measures through week 104. No new safety signals were identified.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Merrill J, Saxena A, Aringer M, Tanaka Y, Zeng X, Wung P, Cheng L, Doan T, Kafka S, DCruz D, D'Silva K. Efficacy and Safety of ABBV-599 (Elsubrutinib and Upadacitinib Combination) and Upadacitinib Monotherapy for the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Results Through 104 Weeks in a Long-Term Extension Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-abbv-599-elsubrutinib-and-upadacitinib-combination-and-upadacitinib-monotherapy-for-the-treatment-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-results-through-104-weeks-in-a-long-term-ext/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-abbv-599-elsubrutinib-and-upadacitinib-combination-and-upadacitinib-monotherapy-for-the-treatment-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-results-through-104-weeks-in-a-long-term-ext/