Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Belimumab (BEL) is a B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) inhibitor approved as an add-on to standard of care (SoC) for patients with autoantibody-positive SLE with active disease. This meta-analysis was performed to investigate the efficacy of BEL vs placebo (PBO) plus SoC when participants were stratified by whole blood BLyS mRNA levels and by type 1 interferon-inducible gene signature (IFN-1) status at study baseline.
Methods: This study (GSK study 208651) is a post hoc analysis of two Phase 3 trials (BLISS-76 [BEL110751] and -52 [BEL110752]) in which patients received intravenous BEL 10 mg/kg plus SoC or PBO plus SoC. The population for the analysis included all randomized patients with an mRNA sample that passed quality control who received at least one dose of BEL or PBO. Co‑primary endpoints were SLE Responder Index (SRI)-4 response within each subgroup and the correlation between baseline BLyS mRNA and IFN-1 levels overall. For binary endpoints, a logistic regression model was used to estimate the odds of SRI response for BEL vs PBO within BLyS mRNA subgroups (high/medium/low tertiles according to quantitative PCR mRNA delta cycle threshold), IFN-1 (high/low) subgroups (according to the median mRNA level of IFI27, IFI44, IFI44L, and RSAD2, defined with reference to samples from 25 healthy volunteers and the trough in bimodal distribution) and overall. To assess SRI-4 response, patients were required to have a Safety of Estrogens in Lupus Erythematosus National Assessment-SLE Disease Activity Index score ≥4 at baseline. The correlation between BLyS gene expression and IFN-1 was analyzed by Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient and further by Chi Square test to compare subgroups.
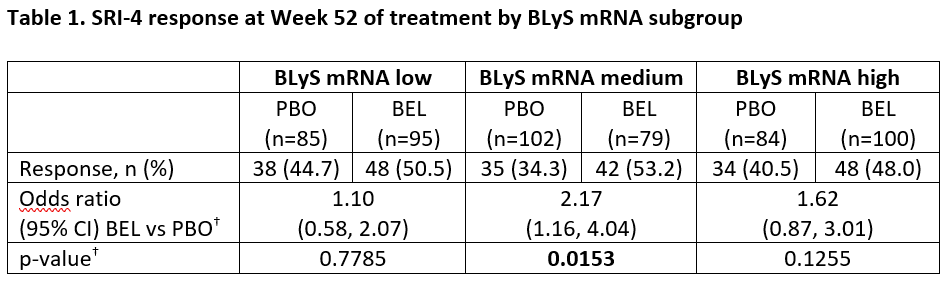
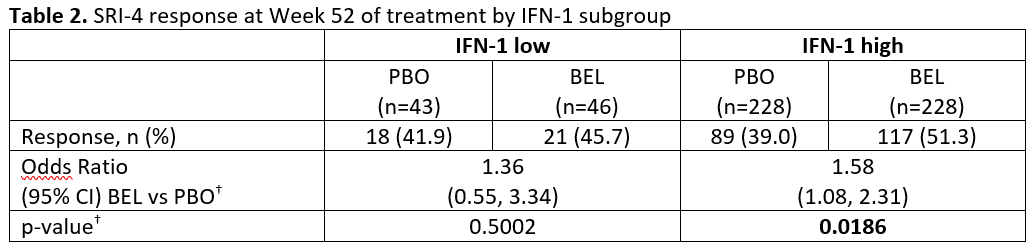
Results: This analysis was based on N=281 (BEL) and N=273 (PBO). Baseline demographics were similar across the BLyS and IFN subgroups. There were more SRI-4 responders at Week 52 for BEL vs PBO in all three BLyS mRNA subgroups but the odds ratio (OR) only achieved statistical significance for the BLyS medium subgroup (Table 1). Baseline BLyS gene expression and IFN-1 were significantly correlated (Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient 0.7799; 95% CI: 0.7451, 0.8106; p< 0.0001). The percentage of responders at Week 52 was greater for BEL vs PBO for both the low and high IFN-1 subgroups and the OR achieved statistical significance in the high IFN subgroup (Table 2).
Conclusion: This study demonstrated a tendency toward better response to BEL as add-on therapy vs SoC alone in patients who had higher baseline BLyS mRNA and IFN-1. However, this was an exploratory analysis, the sample size was opportunistic, with the consequence that the BLyS and IFN-1 subgroups were not explicitly powered to detect a difference in response rates. More studies are necessary to understand whether these biomarkers should be used as treatment decision tools.
Study funding: GSK. Medical writing support: Jennie McLean, PhD, Fishawack Indicia Ltd, UK (funded by GSK).
–<2 g/24 hours vs ≥2 g/24 hour equivalent- and race -African descent or indigenous American descent vs other- BLyS, B-lymphocyte stimulator; BEL, belimumab; CI, confidence interval; PBO, placebo; SELENA-SLEDAI; Safety of Estrogens in Lupus Erythematosus National Assessment – Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index; SRI-4, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Responder Index
–<2 g/24 hour vs ≥2 g/24 hour equivalent- and race -African descent or indigenous American descent vs other- BEL, belimumab; CI, confidence interval; IFN-1, type 1 interferon-inducible gene signature; PBO, placebo; SELENA-SLEDAI; Safety of Estrogens in Lupus Erythematosus National Assessment – Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index; SRI-4, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Responder Index
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jones-Leone A, Flint S, Levy R, Roth D, Henderson R, Wilkinson C, Ji B, Bass D. Efficacy Analysis of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Treated with Belimumab or Placebo Plus Standard Therapy in Phase 3 Trials by Baseline Levels of BLyS mRNA and Type 1 Interferon Inducible Gene Signature Status [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-analysis-of-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-treated-with-belimumab-or-placebo-plus-standard-therapy-in-phase-3-trials-by-baseline-levels-of-blys-mrna-and-type-1-interferon-inducibl/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-analysis-of-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-treated-with-belimumab-or-placebo-plus-standard-therapy-in-phase-3-trials-by-baseline-levels-of-blys-mrna-and-type-1-interferon-inducibl/