Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Several candidate biomarkers for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) have been reported including STAT1, ADAR, CCL2, CXCL10, and miR-146a. This study examines the effects of treatment on their levels.
Methods :
Leukocytes were collected from 103 SLE patients (59 had 2 or more visits) fulfilling ACR criteria and 65 healthy donors (HD). Gene expression of type I- interferon (I-IFN) signature genes (ISGs) and chemokines was analyzed by Taqman qPCR and determined by ΔΔCT method. IFN score was calculated from Mx1, OAS1, and Ly6e. Biomarkers expression, multiple comparisons of therapies, linear correlations, and slope comparisons were analysed by Wilcoxon/Kruskal-Wallis Test, Steel method with control, Spearman Rho constant (ρ), and ANCOVA respectively.
Results:
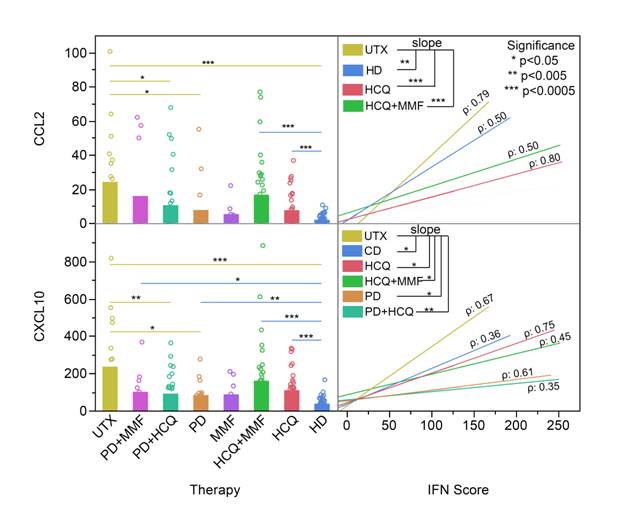
STAT1, ADAR, CCL2, and CXCL10, but not miR-146a, were significantly elevated (p< 0.0001) in SLE patients. STAT1, ADAR, CCL2, and CXCL10 showed significant correlations (p<0.003) to IFN score in both HD and SLE. Next, therapies were analyzed for significant effects on the biomarkers. The effects of interest would be those that reduce the biomarkers levels below untreated (UTX) SLE and that are not significantly elevated above HD. As a further measurement, the slopes of biomarkers that significantly correlated to IFN score were compared to determine if the therapy was capable of reducing (directly or indirectly) the biomarkers response to I-IFN. A lack of correlation and/or decreased slope may indicate disruption of the relationship between biomarkers and I-IFN by the therapy. Alone or in combination, prednisone (PD), hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) did not have significant effects on IFN score, STAT1, or miR-146a. Both CCL2 and CXCL10 were affected by the therapy (see figure). CCL2 was significantly higher (p<0.0009) in UTX SLE and in HCQ- and HCQ+MMF-treated SLE and CXCL10 was significantly higher (p<0.009) in UTX SLE, SLE treated with HCQ, HCQ+MMF, PD, and PD+MMF compared to HD. CCL2 and CXCL10 maintained a significant correlation (p<0.009; ρ> 0.35) with IFN score in UTX SLE, HCQ, and HCQ+MMF SLE. Furthermore, comparing CCL2 and CXCL10 vs IFN score, UTX SLE patients display a significantly higher slope (p<0.009) than HD, HCQ, and HCQ+MMF. CCL2 in HCQ-, PD-, and PD+HCQ- treated SLE was significantly lower (p<0.038) than UTX SLE, nor significantly correlated with IFN score, except for HCQ. But only PD and PD+HCQ had significantly lower CXCL10 than UTX SLE. When comparing CXCL10 vs IFN score, UTX SLE display a significantly higher (p<0.02) slope than PD-, PD+MMF-, and PD+HCQ-treated SLE patients.
Conclusion:
CCL2 and CXCL10 levels were significantly lower for several treatments compared to UTX. Therapies appear to attenuate the response of CCL2 and CXCL10 to I-IFN. Overall, CCL2 and CXCL10 are candidate markers of response to treatment for SLE.
Disclosure:
P. R. Dominguez-Gutierrez,
None;
A. Ceribelli,
None;
M. Satoh,
None;
E. S. Sobel,
None;
W. H. Reeves,
None;
E. K. L. Chan,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-treatment-on-the-expression-of-ccl2-and-cxcl10-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-patients/