Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: Orthopedics, Low Back Pain, & Rehabilitation – ACR/ARP Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: ADAMTS5, a member of the ADAMTS enzyme family, is a key enzyme in the degradation of cartilage in the early stages of knee osteoarthritis (OA). Recently studies have reported that electroacupuncture (EA), which combines acupuncture with pulsed electrical stimulation of acupoints, may be an effective therapy for OA. The aim of this study is to evaluate the effect of EA on ADAMTS5 expression in the synovial membrane and joint deformity in OA model rats.
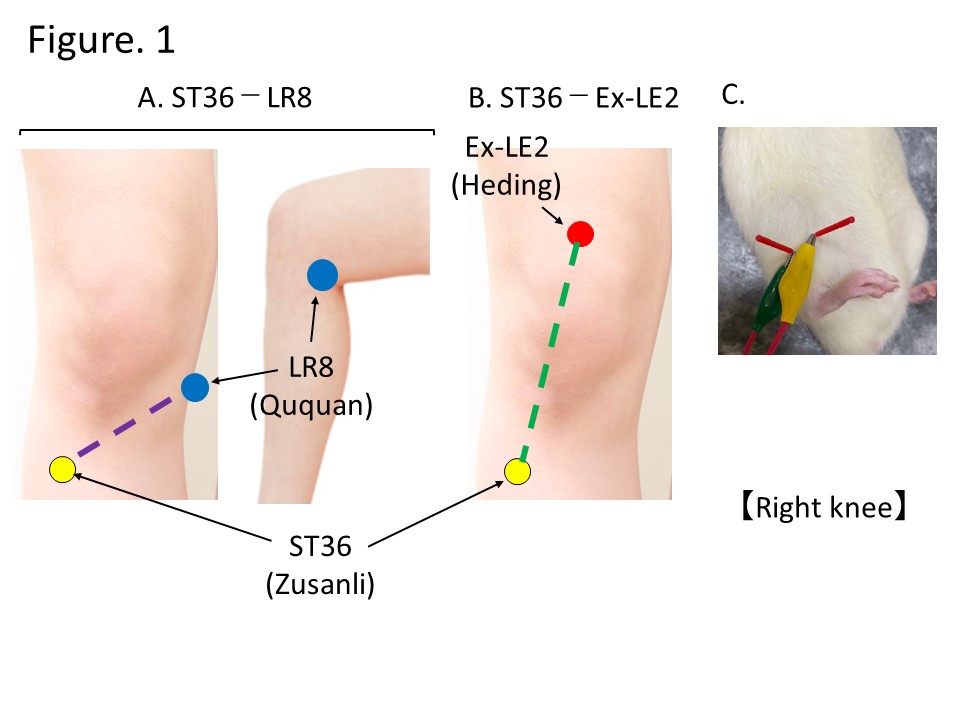
Methods: Rats were divided into five groups: control group, sham surgery group, OA group, EA treatment group for ST36 (Zusanli) and LR8 (Ququan) acupoints after OA surgery (OA + LR8) group, and EA treatment group for ST36 and Ex-LE2 (Heding) acupoints after OA surgery (OA + Ex-LE2) group. The destabilized medial meniscus rat OA model was used. EA (2 Hz, 1.5 mA) was applied three times a week, for 30 minutes each time, for four weeks post-surgery. The rotarod test was performed before surgery and on day 28 post-surgery to evaluate loss of motor coordination. In addition, the expression level of c-fos, a known pain marker, in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord was examined using immunofluorescence on day 28 post-surgery to assess knee joint pain. Knee joint deformity was analyzed using Safranin O-fast green staining and the Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) score. Moreover, western blot analysis was carried out to clarify the expression of ADAMTS5 in the synovium of the right knee joint on day 28 post-surgery.
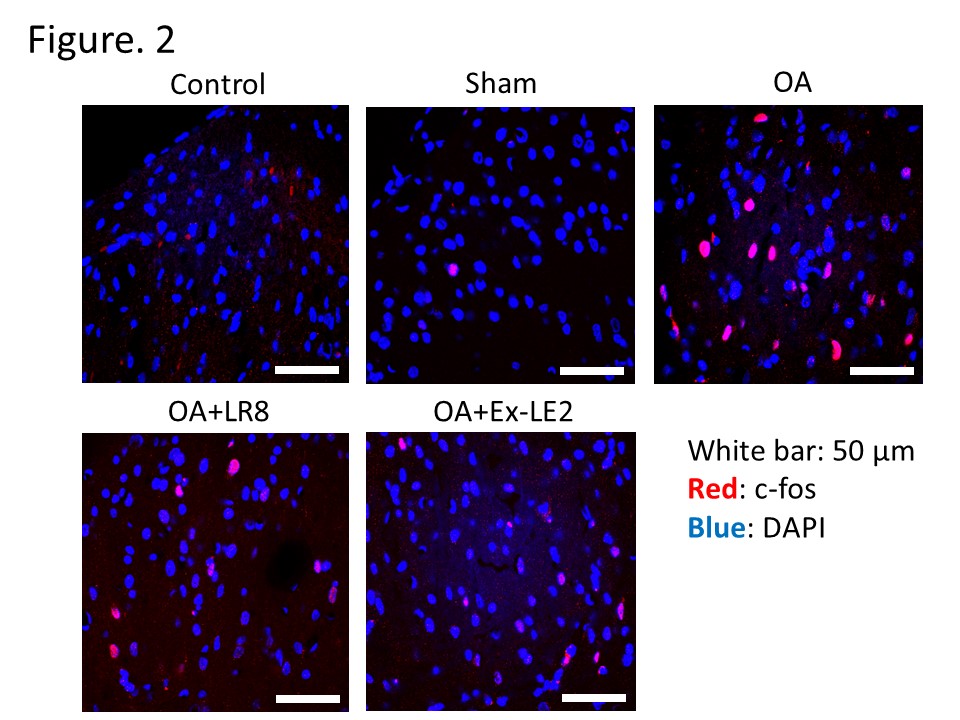
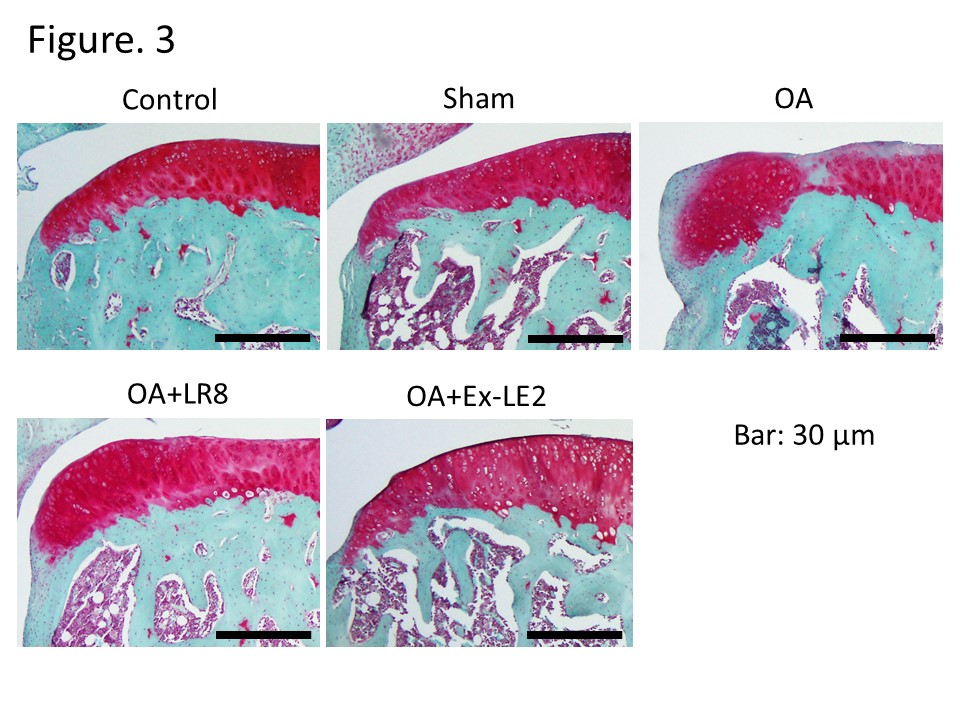
Results: Rats in the OA group showed a remarkable decrease in the time spent on the rod on day 28 compared with the control group, but this decrease was significantly inhibited in both the OA + LR8 and OA + Ex-LE2 groups. The number of c-fos-positive cells in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord was significantly higher in the OA group compared with the control group. However, this increase was significantly suppressed in both the OA + LR8 and OA + Ex-LE2 groups. Furthermore, an increase in the level of OARSI score and the increased expression of ADAMTS5 in the synovium were observed in the OA group. These changes were significantly inhibited in the OA + Ex-LE2 group but not in the OA + LR8 group.
Conclusion: These results indicate that EA treatment for ST36 and Ex-LE2 reduces the expression of c-fos in spinal cord dorsal horn and prevents the onset and progression of OA by inhibiting the expression of ADAMTS5 in the synovium. The effects of EA were found to differ depending on the acupoints used.
Location of the acupoints used in this experiment. A. ST36 (Zusanli) and LR8 (Ququan) in humans. B. ST36 (Zusanli) and Ex-LE2 (Heding) in humans. C. Actual image of EA administered to rats (Combination of ST36 and LR8).
Images of c-fos immunoreactivity (red) in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord (L3) in each group on day 28 post-surgery (white bar = 50 μm).
Representative Safranin O-fast green staining of knee joint in each group on day 28 post-surgery (bar = 30 μm).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ikemoto H, Chuluunbat O, Okumo T, Adachi N, Hisamitsu T, Sunagawa M. Effects of Electroacupuncture on Pain and Joint Deformity in Rat Models of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Study on the Differences in Acupoints Used [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-electroacupuncture-on-pain-and-joint-deformity-in-rat-models-of-knee-osteoarthritis-a-study-on-the-differences-in-acupoints-used/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-electroacupuncture-on-pain-and-joint-deformity-in-rat-models-of-knee-osteoarthritis-a-study-on-the-differences-in-acupoints-used/