Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 11:30AM-1:00PM
Background/Purpose: Belimumab (BEL) has demonstrated efficacy in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in 4 positive pivotal trials. This study assessed the efficacy and safety of intravenous (IV) BEL plus standard therapy (ST) in patients (pts) with active lupus nephritis (LN).
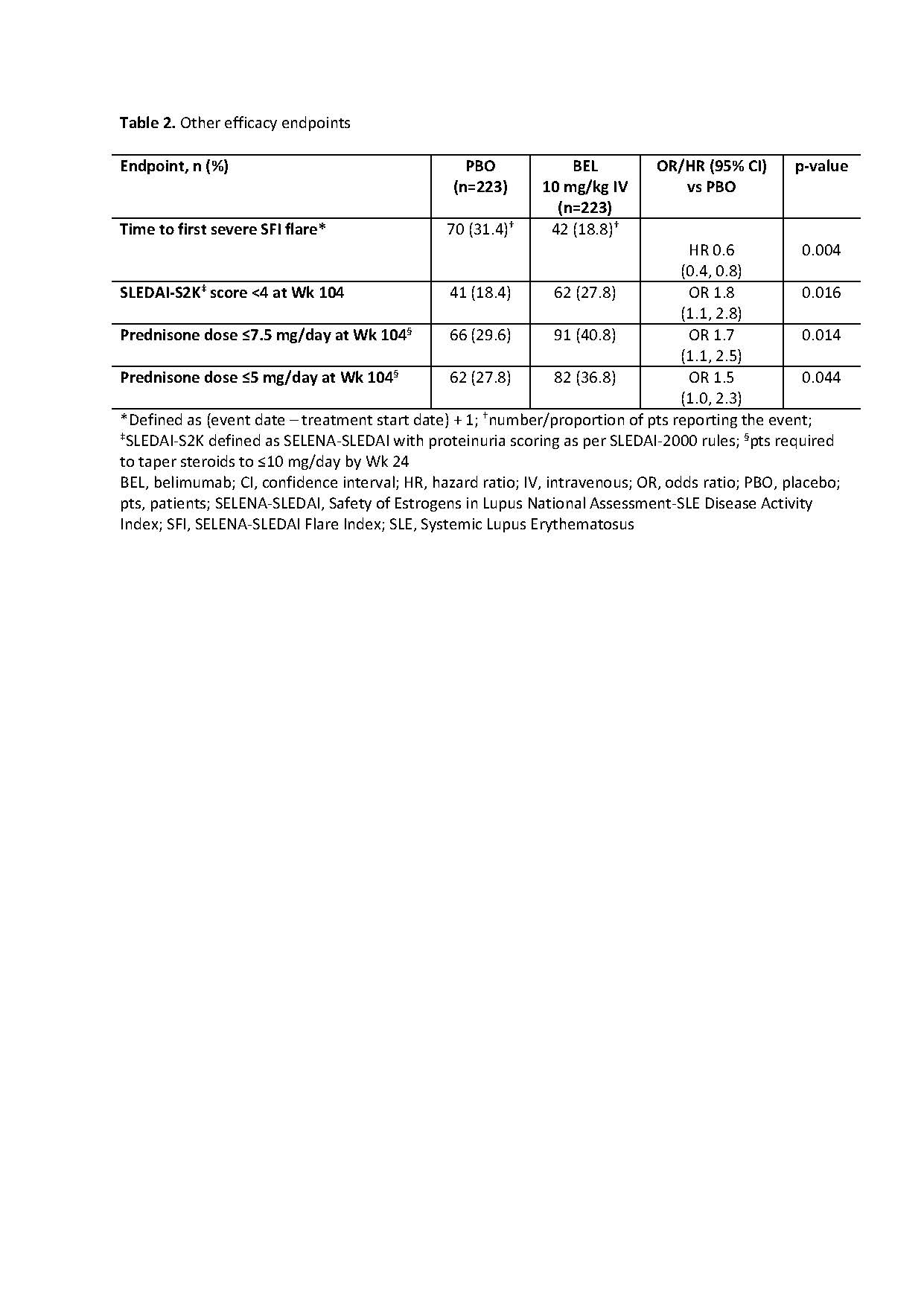
Methods: This Phase 3, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled study (GSK Study BEL114054; NCT01639339) randomized (1:1) adults with SLE and biopsy-proven LN (class III, IV, and/or V) to monthly BEL 10 mg/kg IV or PBO, plus ST. Randomization was stratified by race and treatment regimen (high-dose corticosteroids + either cyclophosphamide followed by azathioprine, or mycophenolate mofetil [MMF] followed by MMF). Primary endpoint: Primary Efficacy Renal Response (PERR; urine protein-creatinine ratio [uPCR] ≤0.7; estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] no worse than 20% below pre-flare value or ≥60 ml/min/1.73m2; no rescue therapy) at Week (Wk) 104. Key secondary endpoints: Complete Renal Response (CRR; uPCR < 0.5; eGFR no worse than 10% below pre-flare value or ≥90 ml/min/1.73m2; no rescue therapy) at Wk 104; Ordinal Renal Response (ORR; CRR, PRR or no response) at Wk 104; PERR at Wk 52; time to renal-related event (defined in Table 1) or death. Wk 104 PERR/CRR were analyzed in subgroups: treatment regimens, LN class, race. Additional evaluations included: time to first severe SFI flare (defined in Table 2); proportions of pts with SLEDAI-S2K (defined in Table 2) score < 4 and with prednisone dose ≤7.5/5 mg/day, both at Wk 104; changes from baseline in biomarkers (anti-dsDNA, anti-C1q, C3, C4) at Wk 104; safety.
Results: Randomized pts: 448 (efficacy: 223/group; safety: 224/group). The study met its primary and key secondary endpoints (Table 1). Risk of a renal-related event or death was lower over the study with BEL vs PBO (HR [95% CI] 0.5 [0.3, 0.8]; p=0.001). Table 2 displays additional endpoints. The odds of PERR/CRR responses at Wk 104 on BEL vs PBO were numerically greater for listed subgroups, except pure class V LN (Figure); however, in class V, a numerically greater proportion of BEL vs PBO pts achieved PERR/CRR response at Wk 52 (PERR: 44.4% vs 33.3%; CRR: 36.1% vs 27.8%, respectively).
At Wk 104, in pts with baseline autoantibodies, median (IQR) percent change from baseline (BEL vs PBO) in anti-dsDNA was −74.2 (−85.1, −49.5) vs −36.6 (−69.7, 28.6); and anti-C1q was −73.2 (−84.1, −59.0) vs −57.9 (−76.1, −33.2). In pts with low baseline complement levels, median (IQR) percent change from baseline (BEL vs PBO) in C3 was 43.8 (17.1, 88.9) vs 30.0 (13.5, 59.8) and in C4 was 115.5 (60.0, 177.8) vs 66.7 (22.2, 166.7).
Adverse events (AEs; ≥1) were reported for 95.5% of BEL and 94.2% of PBO pts; 12.9% of pts in each group had ≥1 AE resulting in study treatment discontinuation. Serious AEs (≥1) were reported for 25.9% of BEL and 29.9% of PBO pts, most commonly infections and infestations (13.8% of BEL vs 17.0% of PBO pts); 1.8% of BEL and 1.3% of PBO pts developed on-treatment fatal AEs (mainly due to infections).
Conclusion: In this large 2-year LN study, compared with ST alone, BEL plus ST improved renal outcomes, overall SLE disease activity, and biomarker levels, while reducing steroid use, with a favorable safety profile.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Furie R, Rovin B, Houssiau F, Contreras G, Malvar A, Saxena A, Yu X, Teng Y, van Paassen P, Ginzler E, Kamen D, Oldham M, Bass D, van Maurik A, Welch M, Green Y, Ji B, Kleoudis C, Roth D. Effects of Belimumab on Renal Outcomes, Overall SLE Control and Biomarkers: Findings from a Phase 3, Randomized, Placebo-controlled 104-week Study in Patients with Active Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-belimumab-on-renal-outcomes-overall-sle-control-and-biomarkers-findings-from-a-phase-3-randomized-placebo-controlled-104-week-study-in-patients-with-active-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-belimumab-on-renal-outcomes-overall-sle-control-and-biomarkers-findings-from-a-phase-3-randomized-placebo-controlled-104-week-study-in-patients-with-active-lupus-nephritis/