Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The efficacy of B cell activator factor/B lymphocyte stimulator inhibitors (BAFFi/BLySi) for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has been proven in clinical trials. However, it remains unclear whether the addition of BAFFi/BLySi to the Standard of Care (SoC) impacts infection risk in SLE. Therefore, the objective of this study was to determine the effects of BAFFi/BLySi on infection in patients with SLE via meta-analysis.
Methods: A systematic literature review was performed in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library databases from inception to Feb 2021 to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of BAFFi/BLySi, including belimumab, tabalumab, blisibimod and atacicept. Relative risks (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to compare infection events, serious infection events and mortality secondary to infection between BAFFi/BLySi and placebo in addition to SoC by using the Mantel-Haenszel random-effect method.
Results: A total of 443 articles were identified and 12 RCTs were included in the final analysis that comprised 8104 patients and 8387 patient-years. Forest plots of RR between BAFFi/BLySi and placebo for infections, serious infections and fatal infections are presented in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3, respectively. There was no statistically significant difference between belimumab, tabalumab, blisibimod or atacicept and placebo in infection (RR=1.03; 95% CI (0.99,1.07)), neither serious infections (RR=0.92; 95% CI (0.76,1.11)) nor fatal infections (RR=1.23; 95% CI (0.53,2.89)). Dose-dependent effect of BAFFi/BLySi on the risk of infections was undetectable (RR=1.03; 95% CI (0.97,1.10)).
Conclusion: Adding BAFFi/BLySi to SoC in patients with SLE was not associated with increased risk of infection, serious infection, nor fatal infection.
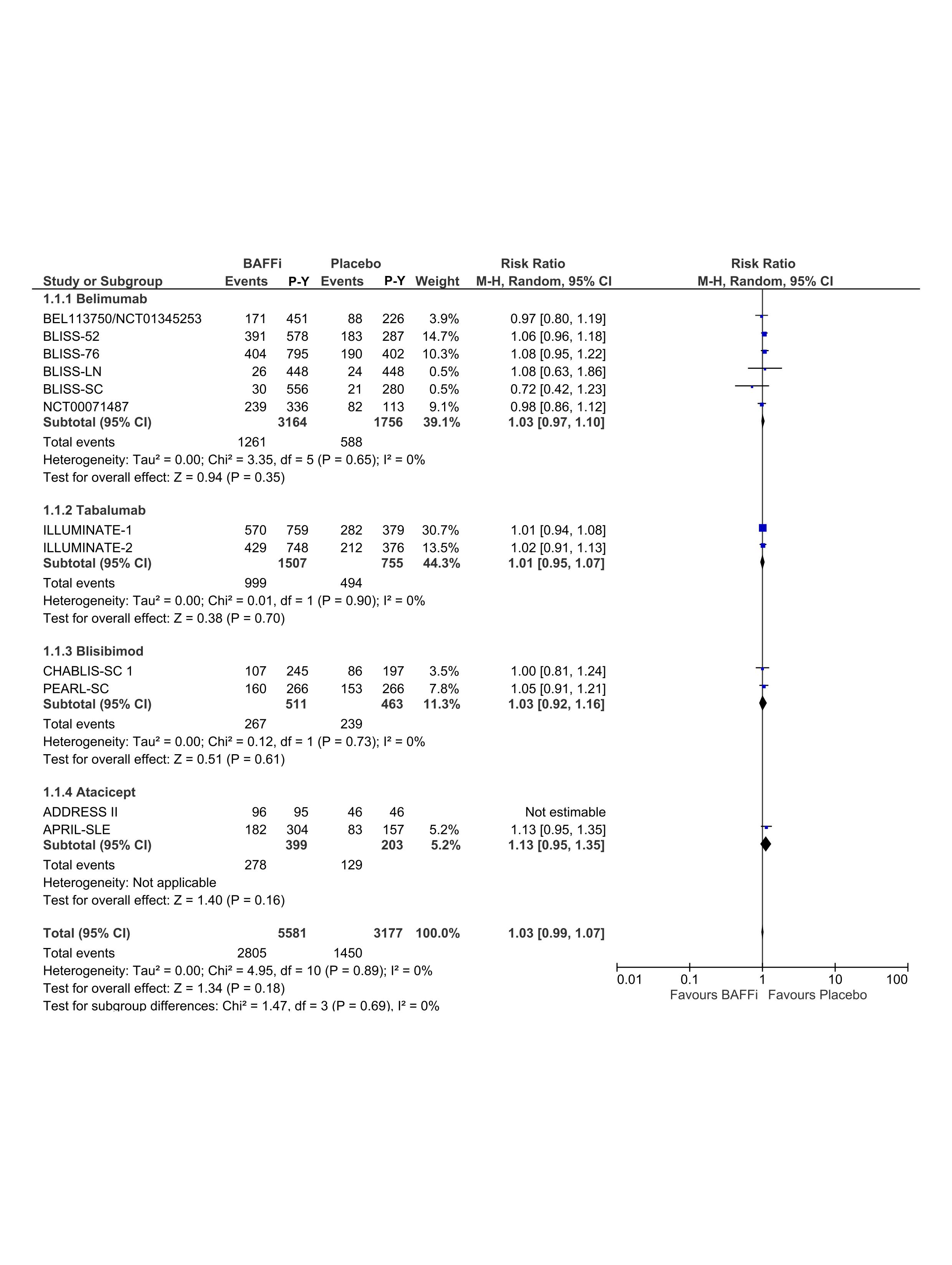 Relative Risks (RRs) of all infections in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) treated with B cell activator factor/B lymphocyte stimulator inhibitors (BAFFi/BLySi) compared with placebo in addition to standard of care. P-Y, patient-year
Relative Risks (RRs) of all infections in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) treated with B cell activator factor/B lymphocyte stimulator inhibitors (BAFFi/BLySi) compared with placebo in addition to standard of care. P-Y, patient-year
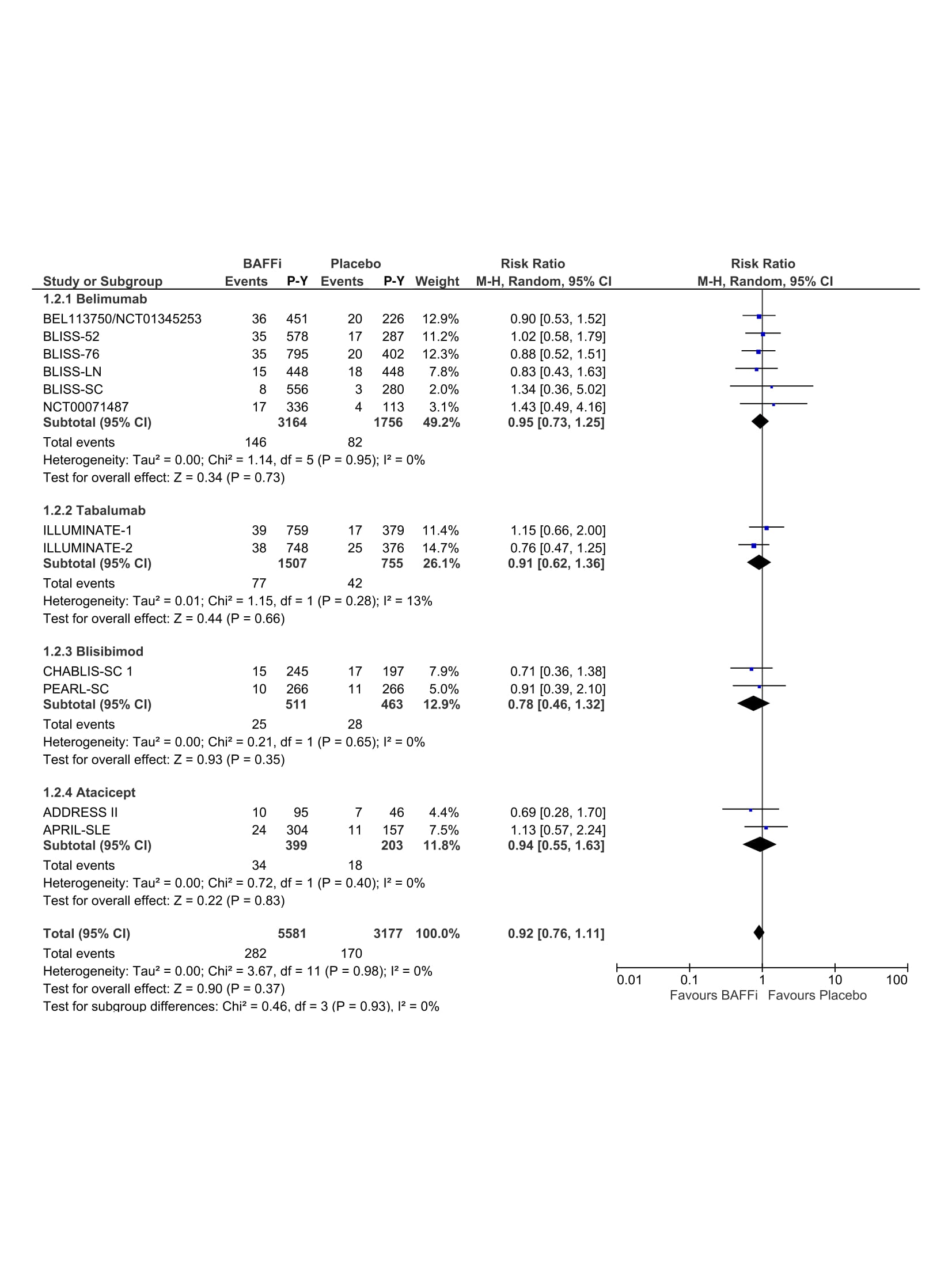 RRs of serious infections in patients with SLE treated with BAFFi/BLySi compared with placebo in addition to standard of care. P-Y, patient-year
RRs of serious infections in patients with SLE treated with BAFFi/BLySi compared with placebo in addition to standard of care. P-Y, patient-year
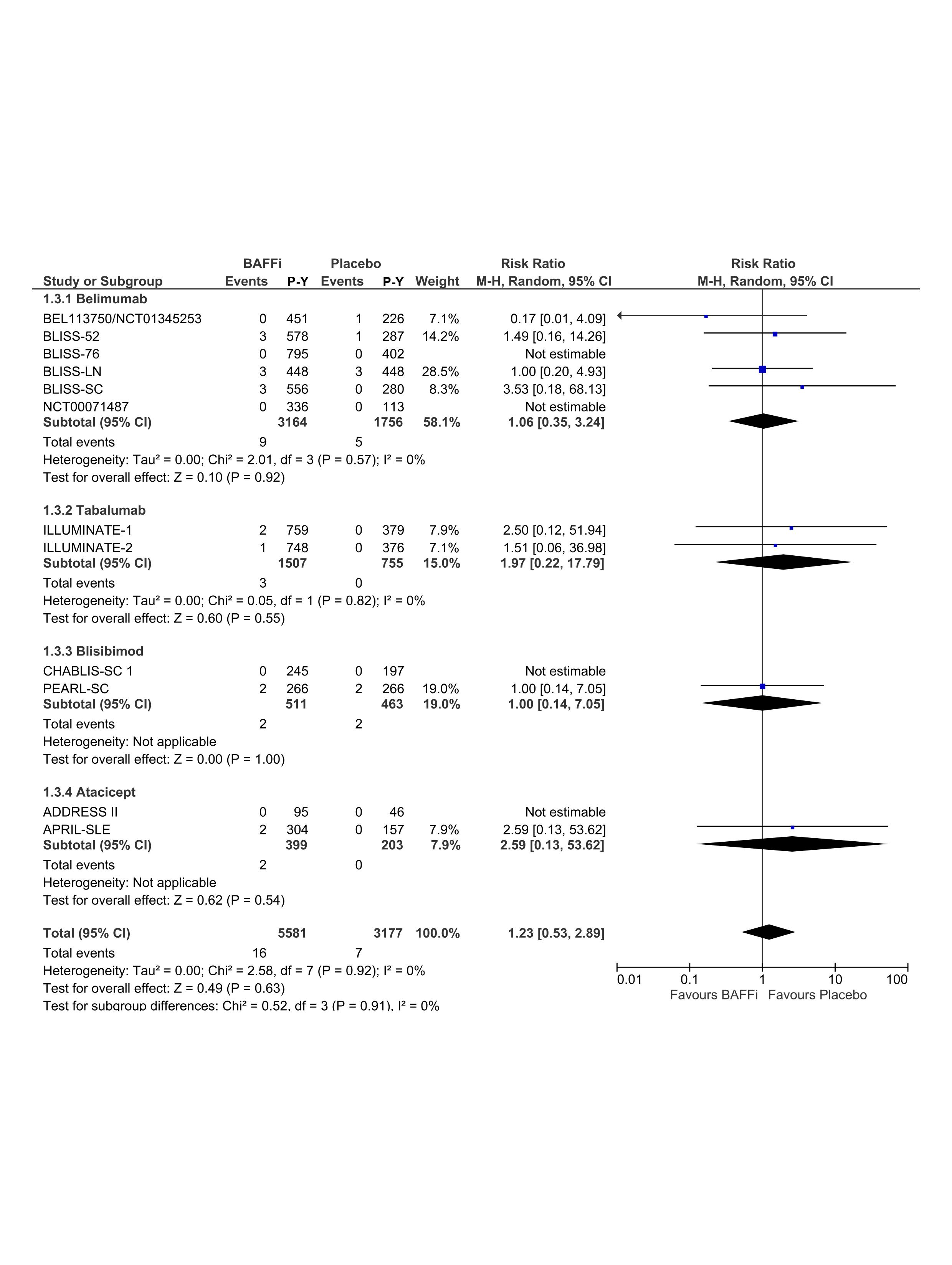 RRs of fatal infections in patients with SLE treated with BAFFi/BLySi compared with placebo in addition to standard of care. P-Y, patient-year
RRs of fatal infections in patients with SLE treated with BAFFi/BLySi compared with placebo in addition to standard of care. P-Y, patient-year
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ni R, Zheng J, Guo R. Effects of B Cell Activating Factors/B Lymphocyte Stimulator Inhibitors Added to Standard of Care on Infection in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-b-cell-activating-factors-b-lymphocyte-stimulator-inhibitors-added-to-standard-of-care-on-infection-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-of-r/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-b-cell-activating-factors-b-lymphocyte-stimulator-inhibitors-added-to-standard-of-care-on-infection-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-of-r/
