Background/Purpose: Vascular involvement (VI) is one of the major causes of mortality and morbidity in Behcet’s Disease (BD). There are no controlled studies for the management of major vascular involvement in BD. According to the EULAR recommendations for the management of BD, only immunosuppressive (IS) agents such as corticosteroids, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide or cyclosporine A are recommended for VI. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effects of anticoagulant (AC) treatment on the development of new vascular events in patients with BD followed up for vascular disease (VBD), retrospectively.
Methods : In this retrospective study, 637 patients with BD (F/M: 283/354, mean age: 38.5±11.1 years) classified according to ISG criteria from 8 Rheumatology centers in Turkey, were included. The demographic data, clinical characteristics of first vascular event and relapses, treatment protocols and data about complications were acquired from files, retrospectively.
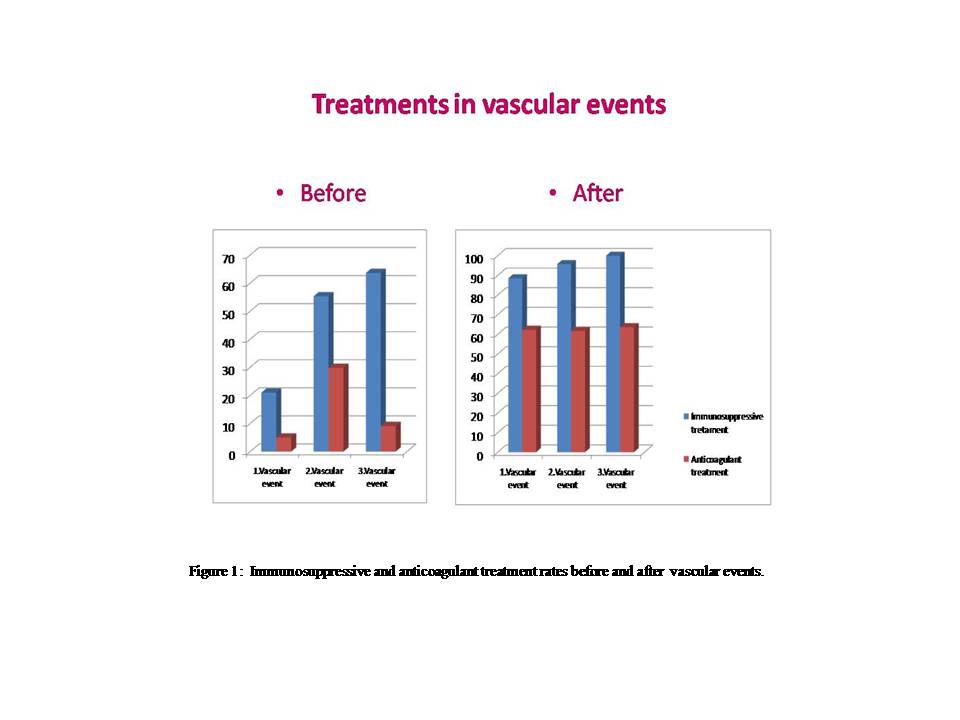
Results : Two hundred eighty-one BD patients (44.1%) were of mucocutaneus type, whereas 356 patients (55.9%) had major organ involvement [Uveitis: 42.4% (n=270), neurologic involvement: 6.9% (n=44), gastrointestinal involvement 1.9%(n=12)]. VBD developed in 20.6% (N=131) patients during the follow-up. When the first vascular event developed, the mean disease duration was 3.5 (0-28) years and mean age 33.2±8 years. After the first vascular event, IS treatment was given to 88.5% (n=105) and AC treatment to 62.6% (n=76) of the patients. Minor hemorrhage (as a complication related to AC treatment) was observed in 3 (3.9%) patients. A second vascular event developed in 35.9% (n=47). The rate of new vascular event development was similar between the patients taking only ISs and AC+IS treatments after first vascular event (27.2% vs 29.6%, p=0.78). Relapse rate was significantly higher in group taking only ACs (91.6%, p=0.002). During follow-up, a third vascular event developed in 23.4% (n=11) patients. The rate of new vascular event development was again similar between the patients taking only IS and AC+IS treatments. There was no relationship between the total duration of AC treatment and number of vascular events. However, total number of vascular events negatively correlated with the age during the first vascular event (r:-0.215, p=0.02).
Conclusion : In this study, we did not find any additional positive effect of AC treatment used in combination with ISs in the course of vascular involvement in patients with BD. Severe complications related to AC treatment were also not detected. Our results suggest that short-duration of IS treatments is the major problem in BD patients associated with vascular relapses during follow-up.
Figure 1: Immunosuppressive and anticoagulant treatment rates before and after vascular events.
Disclosure:
F. Alibaz-Oner,
None;
A. Karadeniz,
None;
S. Yilmaz,
None;
A. Balkarli,
None;
G. Kimyon,
None;
A. Yazici,
None;
M. Cinar,
None;
S. Yilmaz,
None;
F. Yildiz,
None;
S. Yasar Bilge,
None;
E. Bilgin,
None;
B. N. Şeniz,
None;
A. Omma,
None;
G. Yildirim Cetin,
None;
Y. Cagatay,
None;
M. Sayarlioglu,
None;
Y. Pehlivan,
None;
U. Kalyoncu,
None;
O. Karadag,
None;
T. Kasifoglu,
None;
E. Erken,
None;
S. Pay,
None;
A. Cefle,
None;
B. Kisacik,
None;
A. M. Onat,
None;
V. Cobankara,
None;
H. Direskeneli,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-anticoagulant-treatment-on-the-incidence-of-new-vascular-events-in-patients-with-behcets-disease-with-vascular-involvement/