Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0510–0542) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: AxSpA Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To investigate the effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) treatment on lipid profiles and identify risk factors for elevated total cholesterol (TC) after the treatment in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients.
Methods: A retrospective cohort study analyzed AS patients who received first-line anti-TNF treatment. Patients excluding underage and those on lipid-lowering agents, with at least nine months of follow-up were included. One-way ANOVA with repeated measures assessed the impact of anti-TNF inhibitors on disease activity and lipid profile (TC, Low-density lipoprotein [LDL], High-density lipoprotein [HDL], and triglycerides [TG]). Univariable and multivariable linear regression identified risk factors for elevated TC after 3 months of anti-TNF treatment.
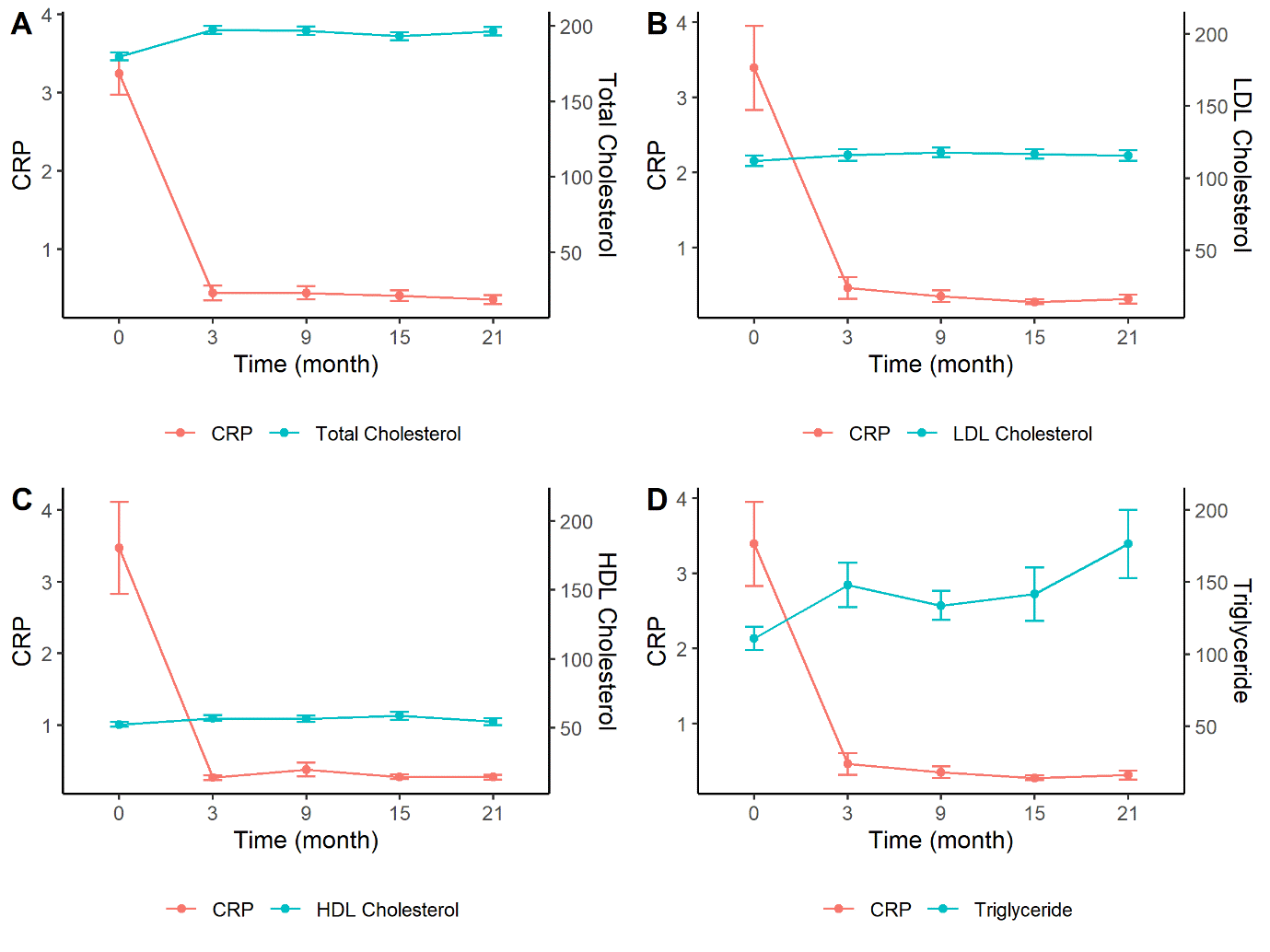
Results: A total of 320 AS patients were enrolled (78.4% male, mean age 34.3 ± 10.8 years). TC and TG levels significantly increased particularly within the first 3 months of anti-TNF treatment, while LDL and HDL levels did not show significant changes. Changes in inflammatory markers and lipid particles (TC, LDL, TG) were strongly correlated over time, but HDL showed no significant correlation. Older age, higher baseline ESR, and lower baseline LDL levels were identified as risk factors for elevated TC after 3 months of anti-TNF treatment.
Conclusion: In AS patients, anti-TNF treatment has been found to increase lipid particles, potentially due to its anti-inflammatory effects. Future research should explore the clinical implications of dyslipidemia, particularly the occurrence of cardiovascular events, following anti-TNF treatment in AS patients.
CRP, c-reactive protein; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kwon I, nam b, Choi N, Shin J, lee S, Kim T. Effects of Anti-tumor Necrosis Factor Treatment on Lipid Profiles in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-anti-tumor-necrosis-factor-treatment-on-lipid-profiles-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-anti-tumor-necrosis-factor-treatment-on-lipid-profiles-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/