Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Rituximab, a monoclonal antibody targeting CD20 positive B cells failed to show effectiveness in SLE, including EXPLORER and LUNAR trials.However, real world data in lupus have shown positive outcomes in patients treated with rituximab. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of rituximab (RTX) in extra-renal lupus. We also analysed the efficacy of rituximab in early disease versus late use.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with SLE based on SLICC criteria who received RTX from 2015 to 2021 for extra-renal indications were recruited into the study. Their baseline and follow up data were collected from electronic medical records. Patients were categorised into early (RTX within 1 year of diagnosis) & late (after 1year) group.Continuous data were analysed using t-test and categorical data were compared using Chi-square/Fisher’s exact test as appropriate.
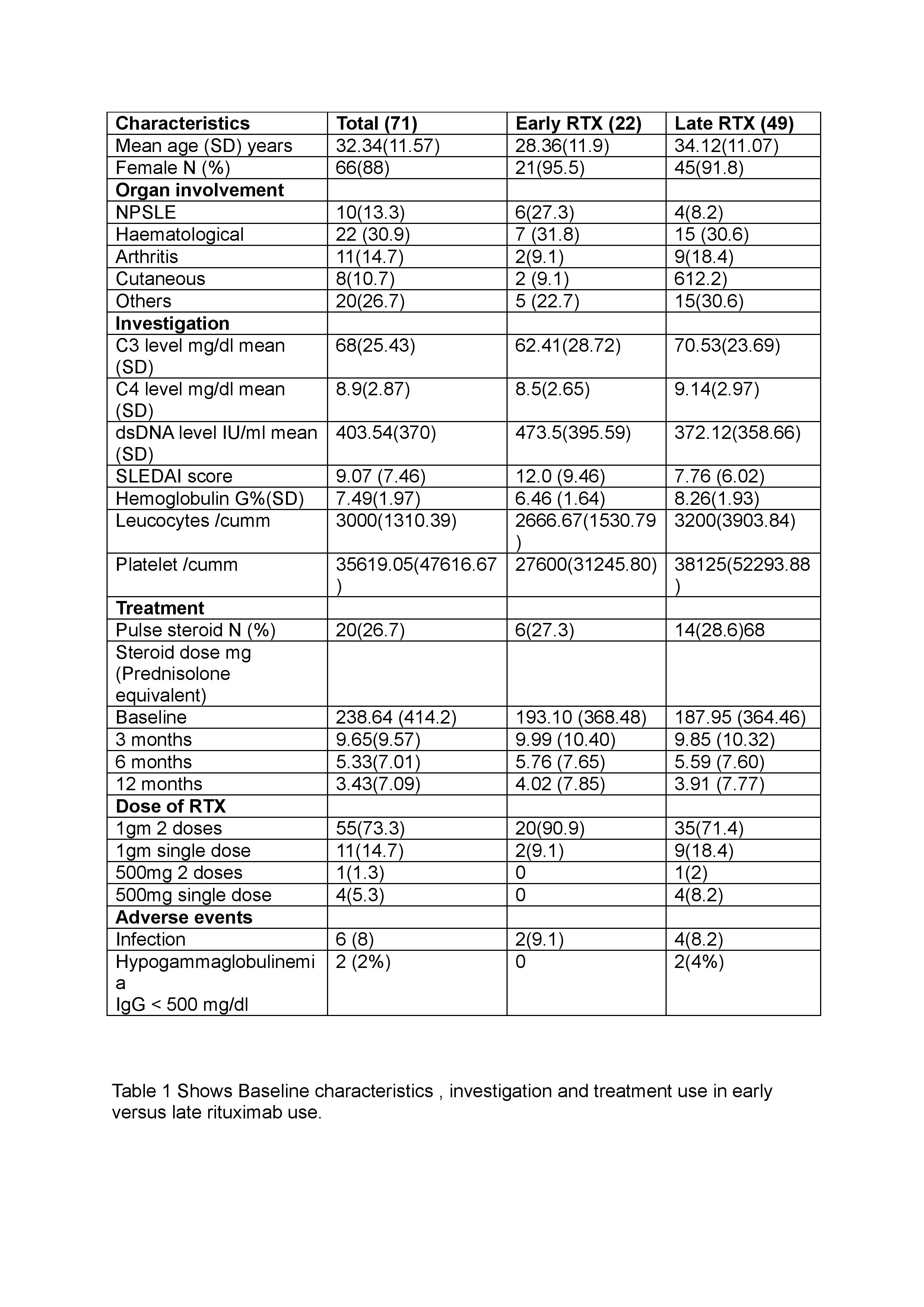
Among the 2300 SLE patients we screened, 104 had been given RTX for extra-renal indications. 71 cases who had at least 12 months of follow-up data were included in our study.
22 (30.98%) patients had received RTX within 1 year of diagnosis (early RTX group) and 49 (69.01 %) patients after 1 year of diagnosis (late RTX group). Out of the total 71 patients, 16 (22.53%) were treatment naive and 55 (77.4%) were refractory to previous immunosuppression.
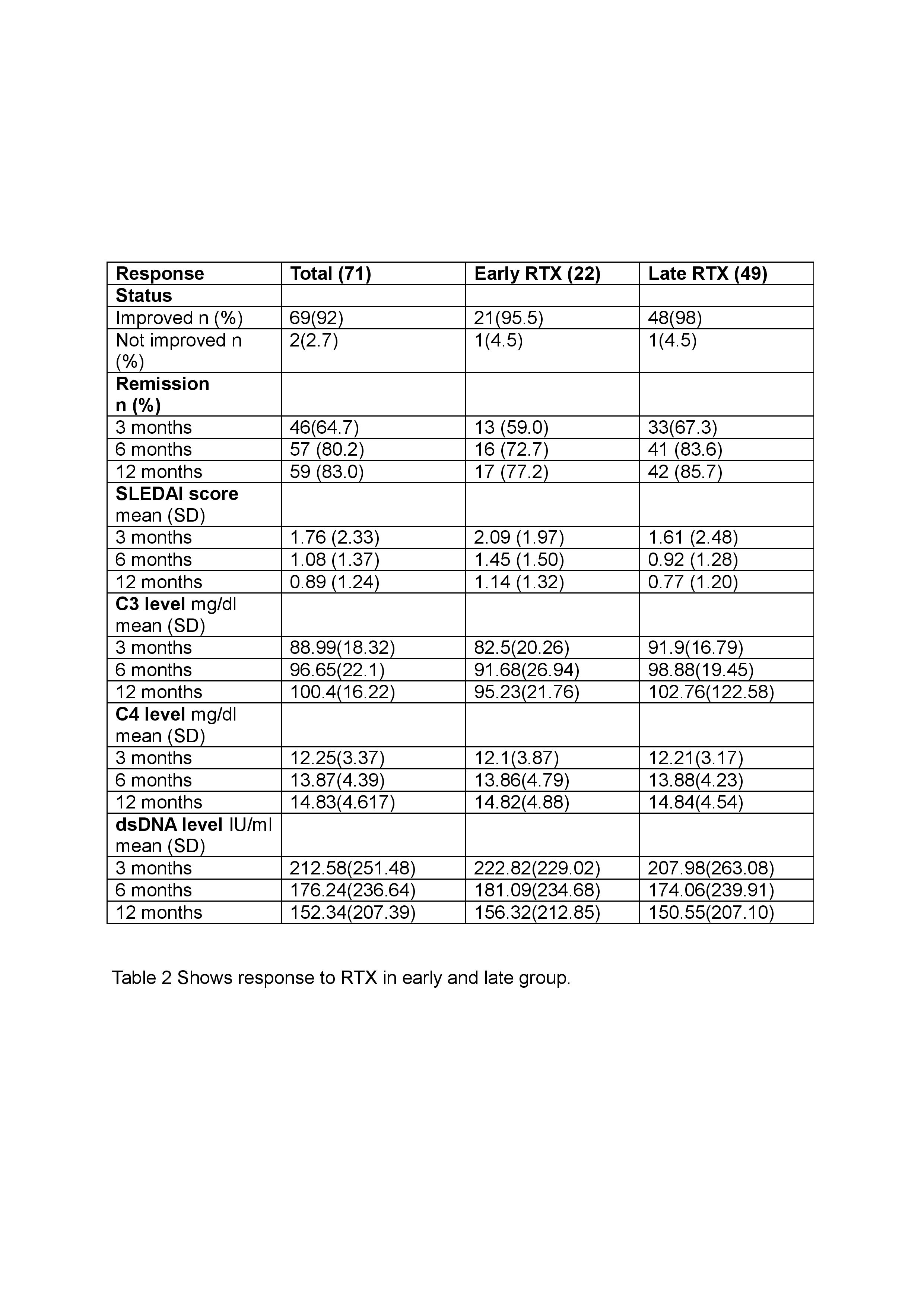
We had categorised the response after 6 months of RTX administration as ‘improved’ and ‘not improved’. At 1 year, patients were classified into complete response, partial response or worsening.
Results: Mean age (SD) of patient was 32.34 (11.57), 88% of patients were female. Most common organ system involvement which warranted RTX use in our cohort was haematological (30.9%). 92 % of patients showed improvement.
When we compared the early RTX group vs the late RTX group, we found that 95.5% in the early group had improvement vs 98% in late group (p value 0.56) after 6 months of RTX administration. 83% of patients had complete remission at 1 year (77.2% in early vs 85.7% in late group with p value 0.58).
When we analysed the data in the treatment naïve and refractory group, we noticed improvement in 93.8% in treatment naive vs 98.2 % in refractory group with p value 0.40.
Steroid requirement was significantly different in both early RTX and late RTX groups.
Mean change in SLEDAI from baseline to 6 months was significantly more in early RTX group compared to late RTX group (p value 0.12), but we did not notice any significant difference between treatment naïve and refractory group ( p= 0.5).
No major adverse events or infusion related adverse reactions were noted during the study period.
Conclusion: Rituximab is an effective treatment option for patients with active extra-renal lupus who are non-responsive to standard immunosuppressive therapy. There was no difference in response to use of rituximab in the early or late course of disease. Treatment naive and refractory patients also responded similarly to rituximab.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
DAS J, MANWATKAR A, MATHEW J. Effectiveness & Safety of Early versus Late Use of Rituximab in Extra-renal Lupus: Real World Experience from a Tertiary Care Centre [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-safety-of-early-versus-late-use-of-rituximab-in-extra-renal-lupus-real-world-experience-from-a-tertiary-care-centre/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-safety-of-early-versus-late-use-of-rituximab-in-extra-renal-lupus-real-world-experience-from-a-tertiary-care-centre/