Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Effectiveness of exercise programs in ankylosing spondylitis: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Virginie Pécourneau1, Adeline Ruyssen-Witrand1, Thomas Barnetche2, Alain Cantagrel1, Arnaud Constantin1.
1 Centre de Rhumatologie, HÃxpital Purpan, 31059, Toulouse Cedex 9, France.
2 Service de Rhumatologie, HÃxpital Pellegrin Tripode, 33076, Bordeaux Cedex, France.
Disclosure : none.
Background/Purpose: Current recommendations for management of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) encompass appropriate medication and exercises as the cornerstones of treatment. The aim of our study is to assess the efficacy of exercise programs on disease activity and function in AS patients through a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Methods: A systematic literature search was performed on Medline and Cochrane databases up to February 2013. Randomized controlled trials examining the effectiveness of exercise programs for AS patients were included. Outcomes analyzed were evolution of BASDAI and BASFI after the completion of exercise programs. Modalities of exercise were compared and the use of biotherapy reported. Efficacy was assessed by weighted mean differences (WMDs) of exercise program versus control groups. Heterogeneity was assessed with Cochran’s Q-test and I2. Standardized mean differences (SMDs) were pooled through meta-analysis using the inverse variance model.
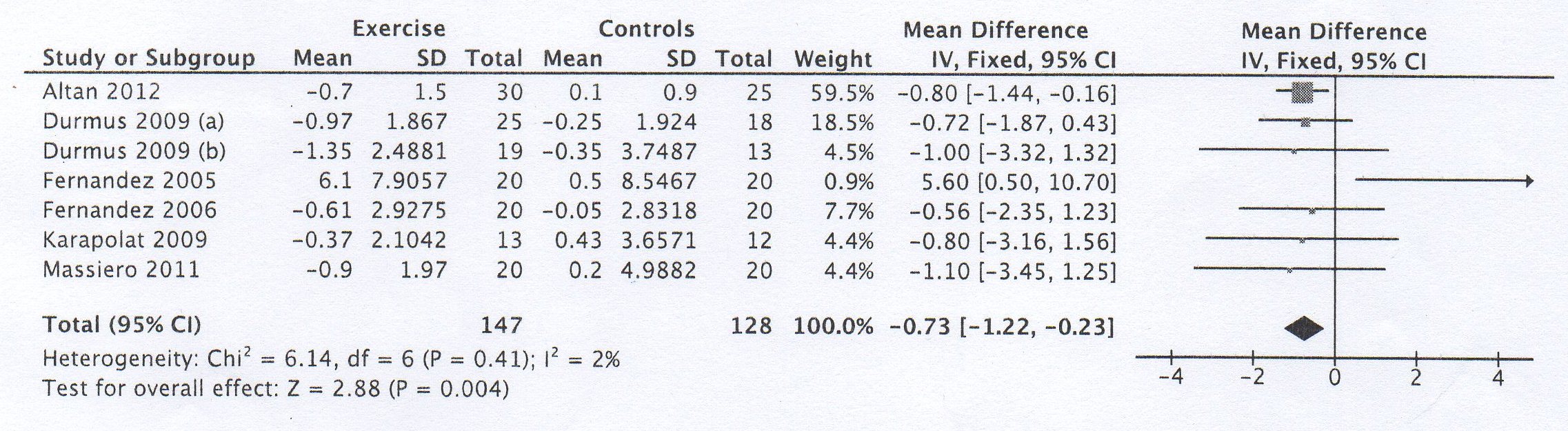
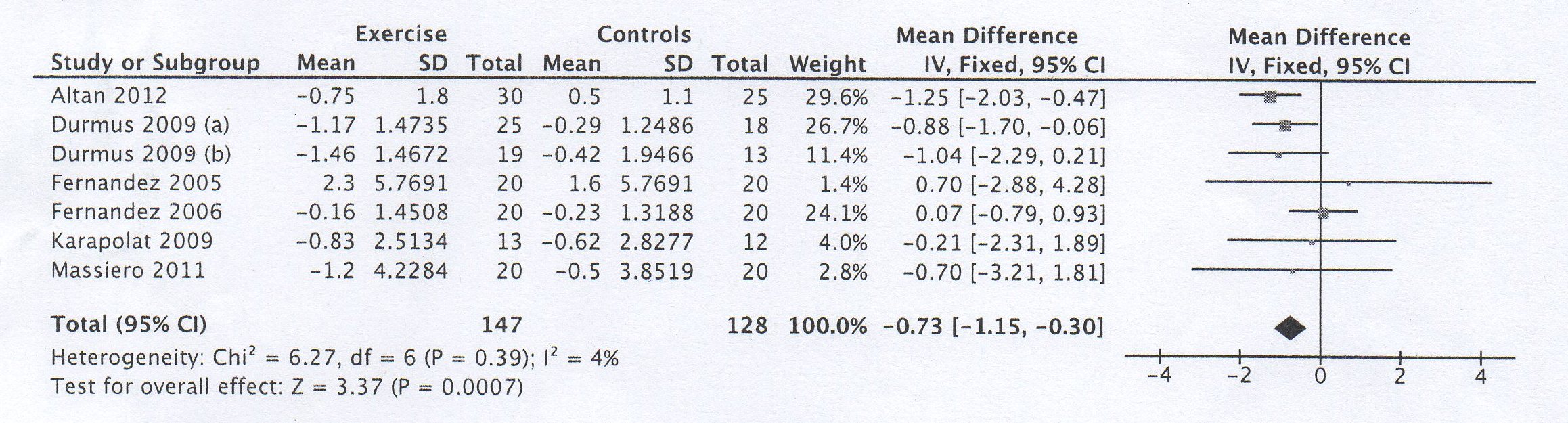
Results: After screening of 167 abstracts, a total of 23 trials were selected for detailed evaluation and 7 trials were finally included, assessing home based exercise programs (2/7), swimming (1/7), Pilates training (1/7) or supervised exercises (2/7), with a total of 275 AS patients. Two trials included patients with anti-TNF therapy. All trials except one showed a decrease of BASDAI and BASFI in exercise groups. The WMDs (95% CI) were -0.73 (-1.15, -0.30) (I²=4%, p=0.0007) for BASDAI and -0.73 (-1.22, -0.23) (I²= 2%, p=0.004) for BASFI in favor of exercise programs.
Conclusion: Even if the small numbers of patients and the quality of exercise programs constitute potential limitations of the randomized clinical trials included in this meta-analysis, its results support the potential of exercise programs to improve disease activity and function in AS.
Fig 1 — Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials assessing the impact of exercise program on BASDAI in AS patients.
Fig 2 — Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials assessing the impact of exercise program on BASFI in AS patients.
Disclosure:
V. Pécourneau,
None;
A. L. Constantin,
None;
A. G. Cantagrel,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-exercise-program-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-meta-analysis-of-randomized-controlled-trials/