Session Information
Date: Wednesday, October 29, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatment II: Phenotyping and Personalization (2639–2644)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:45AM-10:00AM
Background/Purpose: Kidney dysfunction is common in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, there has been limited and conflicting evidence on the effectiveness of biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs) in RA patients with kidney dysfunction.
Methods: This study used the CorEvitas RA registry, a large prospective registry of RA patients from multiple US institutions. We included patients with moderate-to-high clinical disease activity index (CDAI) who newly initiated each class of b/tsDMARDs (TNFi, CTLA4-Ig, IL-6i, BCDT, or JAKi) during the registry follow-up from Oct 2001 to Dec 2023. The index date was set at the b/tsDMARDs initiation. The exposure of interest was a reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73m2) at the index date, in comparison to non-reduced eGFR (≥60 mL/min/1.73m2). Outcomes included CDAI remission (REM), CDAI-remission or low disease activity (REM/LDA), and each outcome without concomitant glucocorticoid (GC) use. The patients were followed until the first occurrence of an outcome or the last study visit. Propensity scores (PS) for baseline reduced eGFR were used for overlap weighting. Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional hazards models before and after weighting examined the association between baseline reduced eGFR and treatment outcomes. Sensitivity analysis using an alternative exposure of chronic kidney disease (CKD) G3a or worse (eGFR ≤ 60 mL/min/1.73m2 for ≥3 months) was also performed. Given that low eGFR may potentially lead to more MTX discontinuation, four-way decomposition causal mediation analysis evaluated whether MTX discontinuation mediated the association among those who used MTX at baseline.
Results: We identified 12,076 new b/tsDMARDs treatment courses (TNFi 5,318; CTLA4-Ig 2,265; IL-6i 1,679; BCDT 1,059; JAKI 1,755) among 9,569 patients. At baseline, median age was 59.0 years, 80.2% were female, and median eGFR was 52.3 mL/min/1.73m2 in the reduced eGFR group and 92.8 mL/min/1.73m2 in the non-reduced eGFR group. Patients with low eGFR were older, had more comorbidities, and used NSAIDs less often (Table 1). After PS overlap weighting, patient characteristics were well-balanced. Reduced eGFR was associated with less achievement of CDAI-REM (crude HR 0.71 [95% CI: 0.62, 0.82]) and CDAI-LDA/REM (crude HR, 0.88 [95% CI: 0.81, 0.95]). Restricting the outcomes to those without GC use modestly strengthened these associations. These results were similar after weighting (Figure 1). Sensitivity analyses using CKD G3a as the exposure demonstrated comparable results. Among baseline MTX users, MTX discontinuation did not completely explain the association between kidney dysfunction and less CDAI-REM achievement.
Conclusion: Although b/tsDMARDs remain effective treatments for RA with kidney dysfunction, patients with reduced eGFR are approximately 30% less likely to achieve remission. Tailored treatment strategies are therefore required to optimize disease control in this high-risk population.
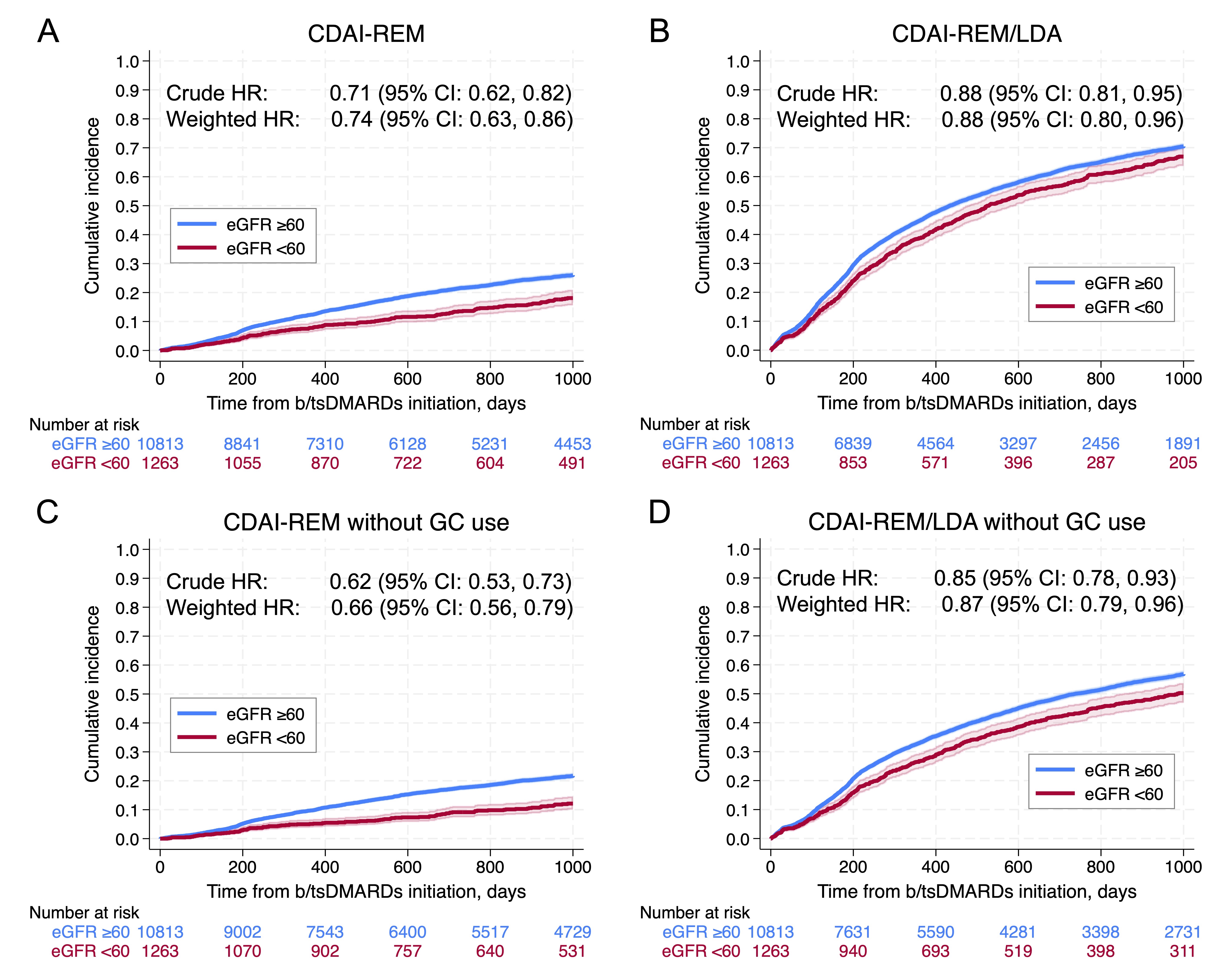 Table 1. Baseline characteristics of RA patients by baseline eGFR before weighting
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of RA patients by baseline eGFR before weighting
.jpg) Figure 1. Achievement of CDAI-REM and CDAI-REM/LDA after initiating b/tsDMARDs by baseline eGFR:
Figure 1. Achievement of CDAI-REM and CDAI-REM/LDA after initiating b/tsDMARDs by baseline eGFR:
Kaplan–Meier cumulative incidence curves (95% CI) for (A) CDAI-REM, (B) CDAI-REM/LDA, (C) CDAI-REM without GC use, and (D) CDAI-REM/LDA without GC use are visualized by reduced eGFR ( < 60) versus non-reduced eGFR (≥60) at baseline. Time zero represents initiation of b/tsDMARDs. Crude HR (95% CI) and HR (95% CI) after propensity-score overlap weighting (weighted HR) of reduced eGFR for achieving outcomes are described. CDAI, Clinical Disease Activity Index; REM, remission; REM/LDA, remission or low disease activity; GC, glucocorticoid; b/tsDMARDs, biologic or targeted synthetic disease‑modifying antirheumatic drugs; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fukui S, Ørbo H, Tedeschi S, Guan H, Harrold L, Litman H, Solomon D. Effectiveness of Biological and Target-Synthetic Treatment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Kidney Dysfunction: A Large Prospective Registry Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-biological-and-target-synthetic-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-kidney-dysfunction-a-large-prospective-registry-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-of-biological-and-target-synthetic-treatment-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-kidney-dysfunction-a-large-prospective-registry-study/
