Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments Poster II: Comparative Effectiveness, Biosimilars, Adherence & the Real World
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: COMPANION-B was a prospective real-world observational study designed to provide evidence on the effectiveness of SB4, a biosimilar of ETN compared to ETN originator in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients in routine care. The goal was to evaluate whether stable RA patients with low disease activity or in remission who elected to transition to SB4 had a similar rate of disease worsening over 12 months vs. patients who continued with ETN. Due to insufficient enrollment, the decision was made to conduct only descriptive analyses. Disease worsening (study endpoint) was defined as a composite of occurrence of anyone of the following: 1) A DAS28-ESR increase of ≥1.2 from baseline and minimum score of ≥3.2; 2) increase dose/frequency of treatment due to disease worsening; 3) discontinuation of SB4 or ETN due to disease worsening.
Methods: The study was conducted in 14 sites in Canada and 5 sites in Australia. Patients were ≥18 years old, diagnosed with RA by 2010 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria, with treatment with ETN as their first or second biologic for at least 6 months. Patients needed to have stable disease defined by DAS28-ESR < 3.2 at enrollment with no evidence of flare within the previous 3 months. Use of background disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) was allowed if patients had taken the same combination for ≥12 weeks and the same dose and frequency of each DMARD for the last 6 weeks.
Results: Of the 163 patients enrolled, 109 patients elected to continue to receive ETN and 54 patients transitioned to SB4. Mean (SD) age was 60.4 (12.7) for ETN and 61.1 (13.6) for SB4. 71.3% of ETN and 66.7% of SB4 patients were female. Approximately 90% of both groups were Caucasian. The mean (SD) duration of RA was 17.2 (10.4) and 18.6 (10.8) years for ETN and SB4 respectively. Approximately half of both groups used concomitant methotrexate. Baseline RA Disease Activity (Table 1) was similar for the two groups.
83.5% of ETN patients and 75.9% of SB4 patients completed the study. The majority of patients (94.1% in ETN group and 84.3% in SB4 group) received ≥36 weeks of study treatment.
RA disease activity at Month 12 was similar between groups (Table 2). Occurrence of adverse events was low and similar between groups.
The primary study endpoint of proportion of disease worsening at Month 12 is 17.6% (95% CI [8.4%, 30.9%] ) for SB4 and 22.8% (95% CI [15.5%, 32.2%]) for ETN (Figure 1).
Conclusion: The biosimilar SB4 was shown to have similar efficacy over 12 months compared to originator ETN in this prospective observational study in well-controlled RA patients with stable disease in a real-world setting. There did not seem to be evidence of a nocebo effect as there was no difference in worsening between groups. This study adds to the accumulating evidence that transitioning patients from originator ETN to biosimilar SB4 offers effective treatment in people willing to switch to a biosimilar and may allow for a reduction in costs.
 RA Disease Activity at Baseline (Mean, Standard Deviation)
RA Disease Activity at Baseline (Mean, Standard Deviation)
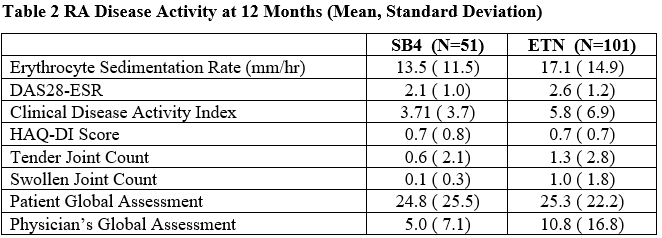 RA Disease Activity at 12 Months (Mean, Standard Deviation)
RA Disease Activity at 12 Months (Mean, Standard Deviation)
 Proportion and 95% CI of Patients Who Experienced Disease Worsening at Month 12
Proportion and 95% CI of Patients Who Experienced Disease Worsening at Month 12
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pope J, Hall S, Bombardier C, Keystone E, Haraoui B, Jones G, Naik L, Wu W, Ramey D, Infante R, Etzel C. Effectiveness After Transition to SB4 (Brenzys, Etanercept Biosimilar) versus Continuation of Etanercept (ETN) Originator (Enbrel) Among Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Patients in Low Disease Activity: A Prospective Multinational Multicenter Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-after-transition-to-sb4-brenzys-etanercept-biosimilar-versus-continuation-of-etanercept-etn-originator-enbrel-among-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patients-in-low-disease-activity-a-p/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effectiveness-after-transition-to-sb4-brenzys-etanercept-biosimilar-versus-continuation-of-etanercept-etn-originator-enbrel-among-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patients-in-low-disease-activity-a-p/
