Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: Plenary II
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
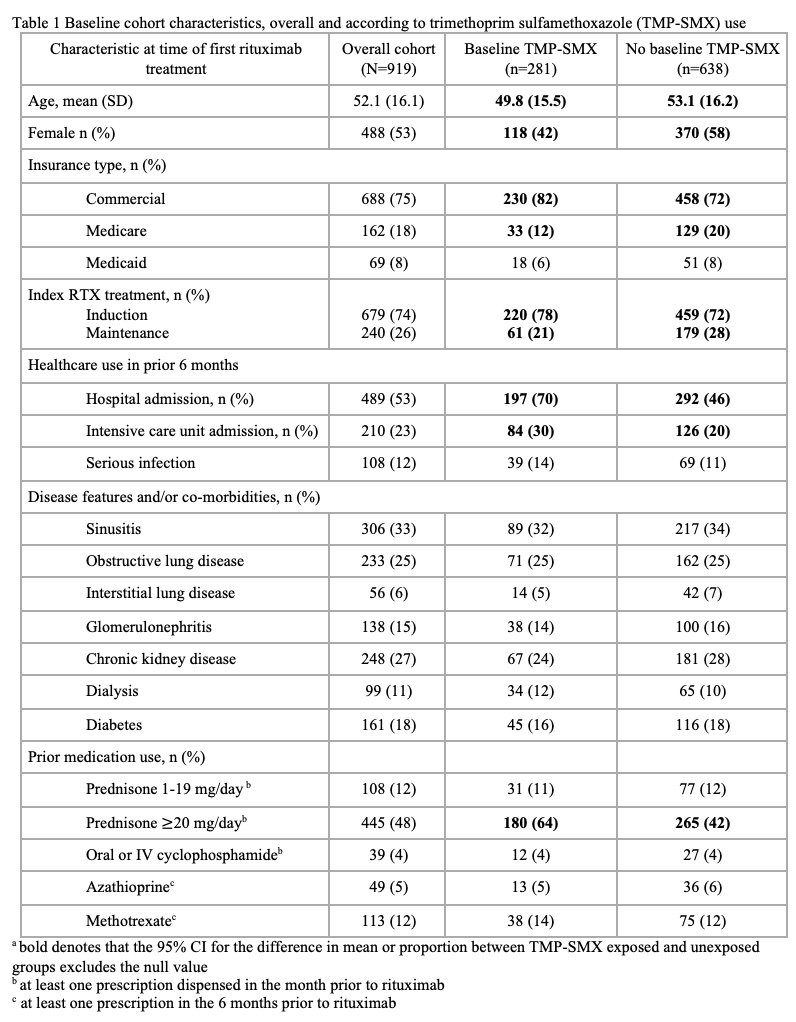
Background/Purpose: Infections during treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) lead to excess mortality. Trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX), recommended for pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) prophylaxis, has broad antimicrobial activity. We assessed associations between TMP-SMX prophylaxis and subsequent infections within a United States population sample of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) treated with rituximab (RTX).
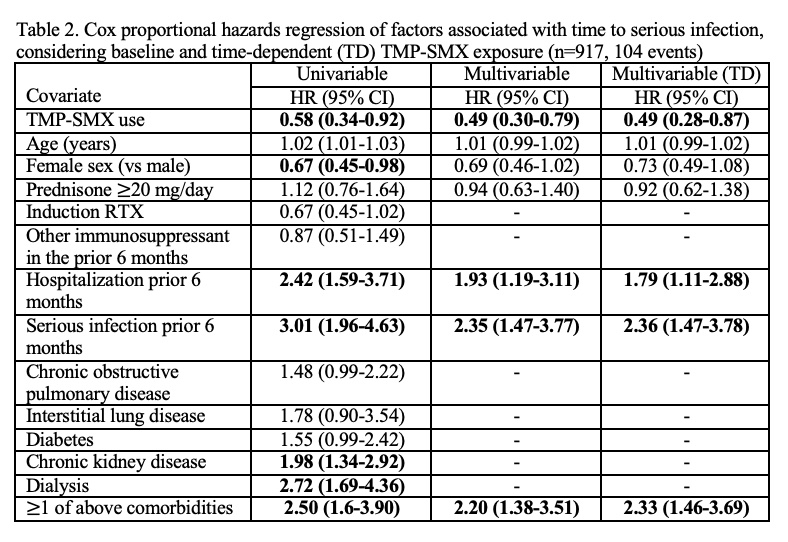
Methods: We included adults with GPA within the Merative™ Marketscan® Research Databases who had a minimum 6 months of insurance enrolment prior to a first (index) RTX treatment (2011-2020). Baseline TMP-SMX prophylaxis was defined as a >=28-day prescription dispensed within 30 days (before/after) RTX initiation. We defined serious infections as an inpatient ICD-9 or -10 primary diagnostic code for infection following the index date (excluding viral and mycobacterial codes). Secondary outcomes were outpatient infections (for the same codes), and PJP. Subjects were followed until end of insurance enrolment or Dec 31, 2020. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression assessed the association of baseline and time-dependent TMP-SMX with serious infection. Models were adjusted for age, sex, prednisone ( >=20 mg/day dispensed < 30 days prior to index RTX), hospitalization and/or serious infection in the 6 months prior to index RTX, and having any of of the following: interstitial or obstructive lung disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or dialysis. As a sensitivity analysis, we assessed the association between TMP-SMX prophylaxis and a “control” infection, herpes zoster (HZ). Finally, we determined rates of adverse events potentially attributable to TMP-SMX during person-time exposed and unexposed to TMP-SMX.
Results: The cohort included 919 RTX-treated individuals with GPA, of which 53% were female, mean age 52 years (SD 16). TMP-SMX was dispensed to 281 (31%) at the time of index RTX (and to 40% on prednisone >=20 mg/day). Over a median (IQR) follow-up of 496 (138, 979) days, the rates of serious infection, outpatient infection, and PJP per 100-person years were 6.1 (95% confidence interval, CI 5-7), 28.7 (95% CI 26-32), and 0.7 (0.4-1.2), respectively. Serious infections were primarily pulmonary (36%) or general sepsis (45%). In multivariable analyses, TMP-SMX was negatively associated with serious infections, considering baseline (adjusted HR 0.5; 95% CI 0.3-0.8) and time-varying TMP-SMX exposure (aHR 0.5; 95% CI 0.3-0.9). Prophylaxis was also negatively associated with outpatient infections (aHR 0.7; 95% CI 0.5-0.9). Thirteen PJP infections occurred, all in TMP-SMX unexposed subjects. TMP-SMX was not associated with reduced HZ (aHR; 1.6, 95% CI 0.6-3.2). Rates for adverse events potentially attributable to TMP-SMX per 100 person-years were 29.6 (95% CI, 22-39) during periods of TMP-SMX exposure and 13.4 (95% CI, 11-16) during periods without TMP-SMX exposure.
Conclusion: TMP-SMX prophylaxis was associated with subsequent reduced serious and overall infections in RTX-treated GPA. Further study is needed to determine how to balance potential benefits and harms from prophylaxis in individual patients, and determine optimal prophylaxis duration.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mendel A, Behlouli H, Vinet E, Curtis J, Bernatsky S. Effect of Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole Prophylaxis on Infections During Treatment of Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis with Rituximab: A Population-Based Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-prophylaxis-on-infections-during-treatment-of-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-with-rituximab-a-population-based-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole-prophylaxis-on-infections-during-treatment-of-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-with-rituximab-a-population-based-study/