Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have an increased risk for cardiovascular diseases. Recent studies found that RA patients present dysfunctional high density lipoproteins (HDL) with low activity of paraoxonase 1 (PON1), which might contribute to the increased cardiovascular risk. Tofacitinib has been associated with an increase in total cholesterol (TC) and low density lipoproteins (LDL-c). The objective of this study was to compare functional markers of HDL at baseline and 3 months after tofacitinib in patients with RA.
Methods: Patients diagnosed with RA (ACR / EULAR 2010 criteria) who started tofacitinib were included from January 2016. Patients with personal history of cardiovascular disease, renal, hepatic or thyroid alterations were excluded. DAS-28, lipid profile and ultrasensitive C-reactive protein (usPCR) values were analyzed by standardized methods at baseline and 3 months after tofacitinib. The activity of PON1 was evaluated on two substrates, paraoxon (PON activity) and phenylacetate (ARE activity). Differences in quantitative variables were analyzed through paired Wilcoxon test and McNemar test was used for qualitative variables. Correlations were analyzed with Spearman test.
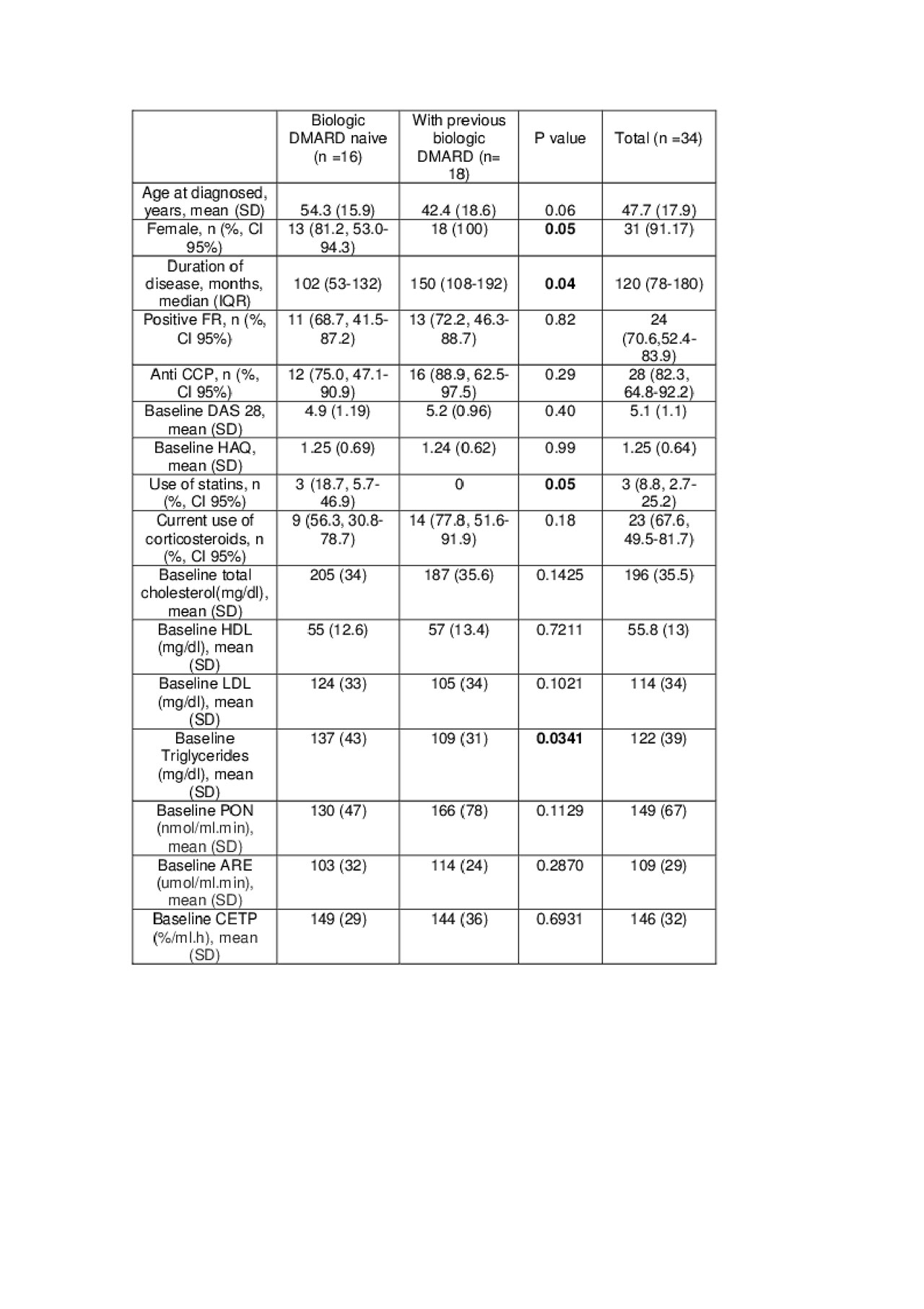
Results: Patients baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. Patients were positive for rheumatoid factor in 70.6% (95% CI 52.4-83.9) and anti-CCP in 82.3% (95% CI 64.8-92.2). Eighteen patients (52.95%) were biologic DMARDs failures and the remaining ones received tofacitinib after conventional DMARDs failure. At three months of follow up, DAS28 decreased significantly (-24%, p < 0.001), and TC, C-LDL, HDL-C and C-non-HDL levels increased significantly (TC: + 8%, p = 0.046, LDL-C: 8%, p = 0.046; HDL-C: + 8%, p = 0.027 and C-non-HDL: + 13%, p = 0.031). No changes were observed in PON or ARE activity associated with tofacitinib use in the whole cohort. Sub analysis on patients not previously treated with biologic DMARDs showed a significant increase in the activity of ARE and PON (Table 2). None of the groups showed significant changes in the cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP).
Conclusion: On biologic DMARD naïve patients, treatment with tofacitinib improved the antioxidant activity of HDL (paroxonase activity), in spite of an increase in the overall lipoprotein levels. This might provide additional protection to the accelerated atherosclerotic process.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Luissi A, Pierini F, Gandino I, Botta E, Brites F, Boero L, Martin M, Meroño T, saez S, Tetzlaff W, Sommerfleck F, Citera G, Rosa J, Sorroche P, Soriano E. Effect of Tofacitinib on the Qualitative Profile of High Density Lipoproteins Molecules in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-tofacitinib-on-the-qualitative-profile-of-high-density-lipoproteins-molecules-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-tofacitinib-on-the-qualitative-profile-of-high-density-lipoproteins-molecules-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/