Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), qualitative alterations of low and high density lipoproteins (LDL and HDL, respectively) might partially explain their increased cardiovascular risk. Tocilizumab has been associated with increase in lipids, including triglycerides (TG) and cholesterol levels, in all its lipoprotein fractions. The aim of this study was to compare, in patients with RA, the effect of tocilizumab on HDL and LDL characteristics at baseline and 3 months after the start of treatment.
Methods: patients diagnosed with RA (ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria) who received tocilizumab were included from November 2016. Patients with personal history of cardiovascular disease, renal, hepatic or thyroid alterations were excluded. Clinical assessment (Health assessment questionnaire -HAQ-, DAS28) lipid profile, and ultrasensitive C reactive protein (usCRP) by standardized methods were collected in all patients at baseline and after three months of follow up. Lipoproteins characteristics were measured with the activity of paraoxonase (PON1) evaluated through the activity of arylesterase (ARE), and by the ability to promote the efflux of cholesterol from foam cells generated in vitro, and by levels of oxidized LDL (LDLox). Changes were evaluated by paired means difference tests and correlations between lipoproteins characteristics and acute phase reactants were analyzed by Spearman tests.
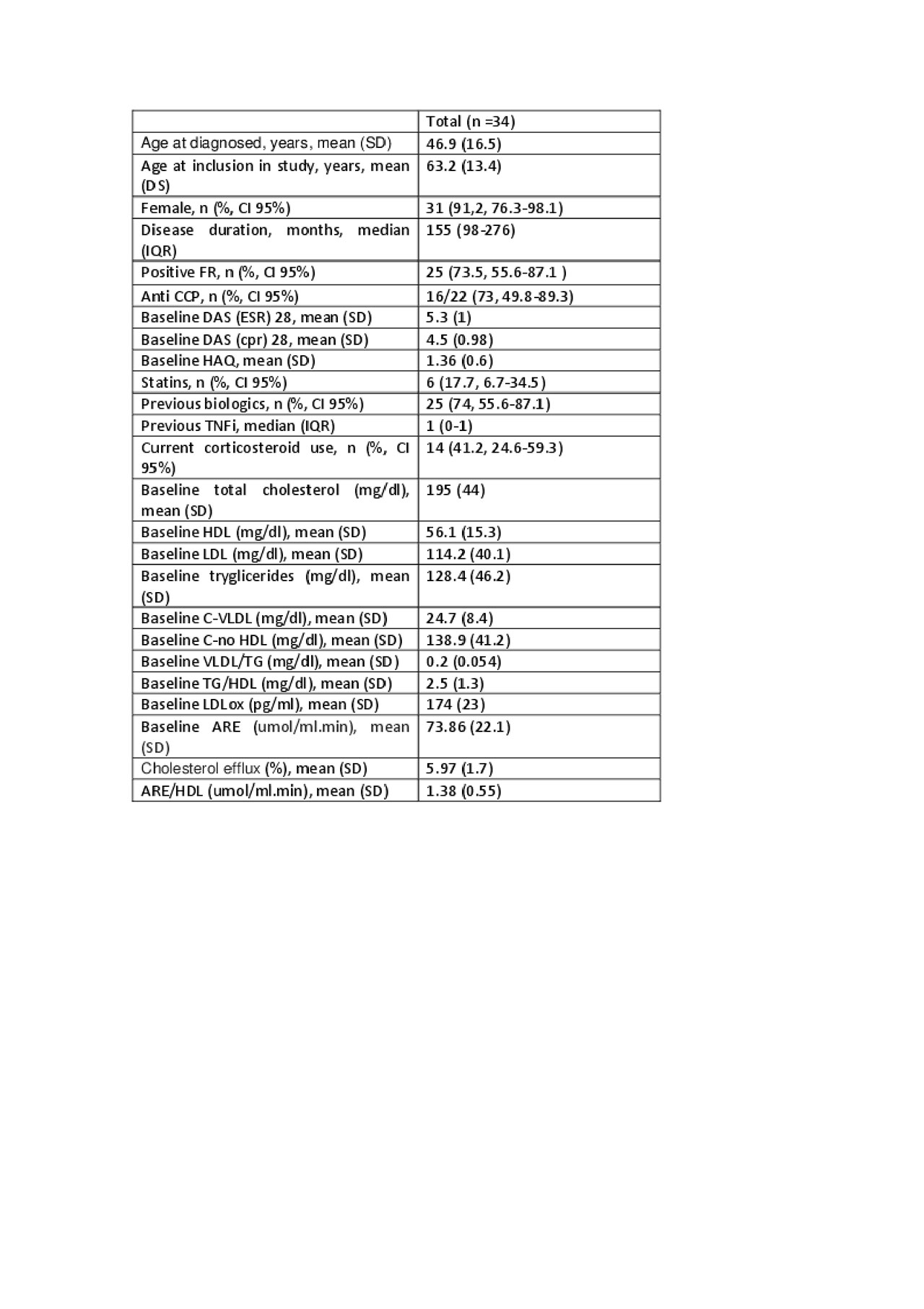
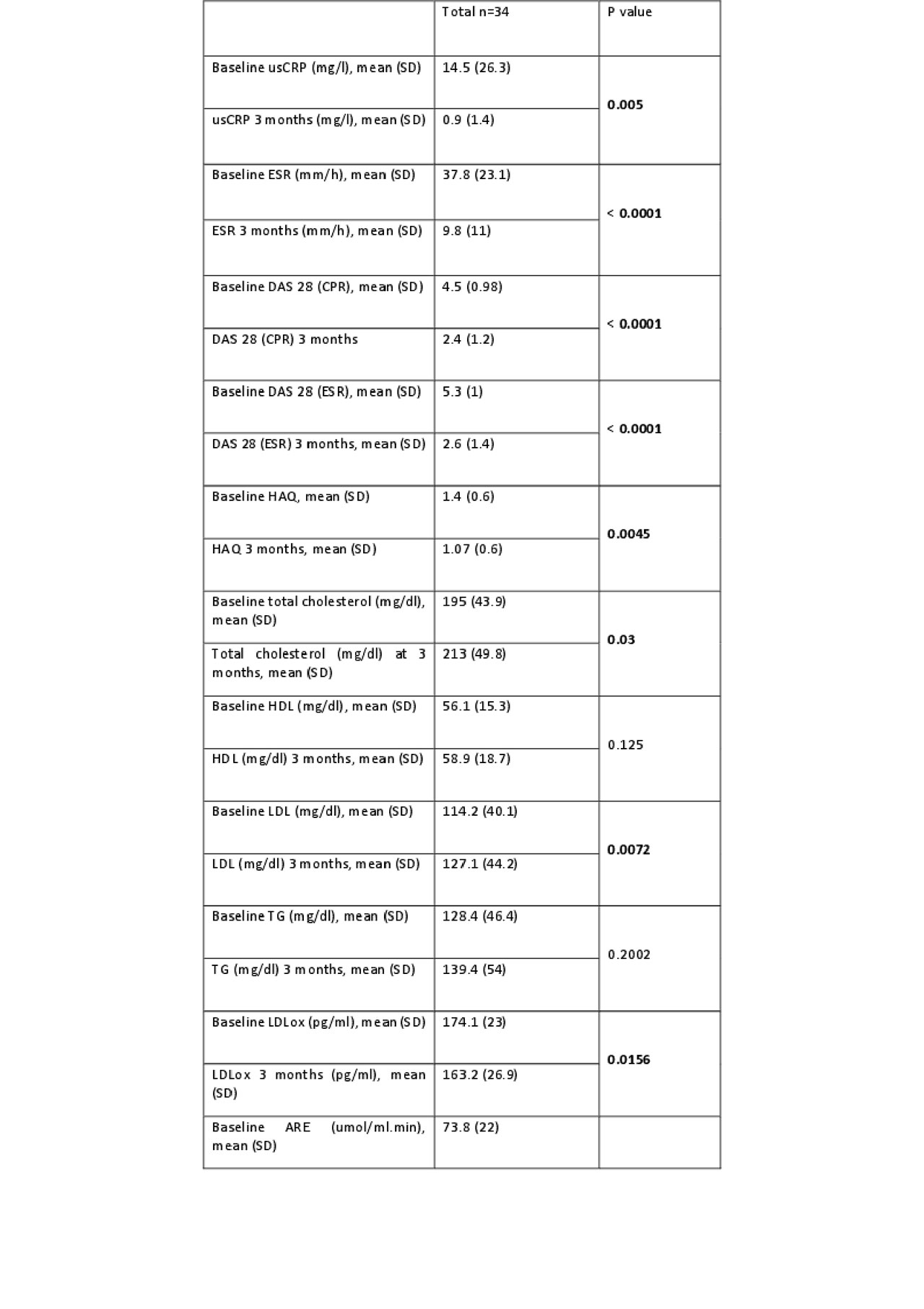
Results: baseline characteristics of the 34 patients included are shown in Table 1. Most of the patients were seropositive (table 1). Twenty-five patients (74%) had been previously treated with other biologics disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) while 9 (26%) received tocilizumab after conventional DMARDs failure. 59% of patients used monotherapy tocilizumab and 41% used concomitant conventional DMARD (methotrexate: 71.4%). At three months, DAS28 (-51%, p < 0.001), HAQ (-23.57%, p = 0.0045) and usCRP decreased significantly. Total cholesterol and LDL-C levels increased significantly after 3 months of treatment (CT: 9.2%, p = 0.03 and LDL-C: 11.29%, p = 0.0072). A decrease in LDLox was observed after 3 months of treatment (11.29%, p = 0.0156). No changes were observed in arylesterase activity or HDL capacity to promote cholesterol efflux (p > 0.05) in the whole group (Table 2). Changes in HDL efflux correlated positively with ARE activity (r = 0.58, p = 0.03), and with CRP levels reduction (r = -0.77, p = 0.021).
Conclusion: treatment with tocilizumab decreased LDLox levels, (a classic risk factor for cardiovascular disease) in spite an increase in total cholesterol and LDL-C levels. Decreases in usCRP levels significantly correlated with an improvement of HDL anti atherogenic capacities.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pierini F, Gandino I, Botta E, Brites F, Meroño T, Cerda O, Citera G, Rosa J, Sorroche P, Boero L, Martin M, saez S, Tetzlaff W, Soriano E. Effect of Tocilizumab on HDL and LDL Characteristics in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Preliminary Results [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-tocilizumab-on-hdl-and-ldl-characteristics-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-preliminary-results/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-tocilizumab-on-hdl-and-ldl-characteristics-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-preliminary-results/