Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The risk of COVID-19 infection is increased in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and immunosuppressive medications including corticosteroids impact the risk. Furthermore, immunosuppressive medications may reduce the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination. Consensus documents have suggested management strategies on handling immunosuppressive medications to increase vaccine efficacy, but the benefit of such strategies has not been proven.
Methods: We collected information on COVID infection, COVID vaccination history, and COVID antibodies in the Hopkins Lupus Cohort, a longitudinal cohort with structured quarterly visits. A cohort of healthcare workers was used for comparison. SARS-CoV-2 IgG was measured by ELISA (Euroimmun). We included only those receiving either a Pfizer or Moderna vaccination and excluded those with a history of COVID infection. Outcome measures included: SARS-CoV-2 antibody IgG levels after vaccination over time in both cohorts; and effect of immunosuppressive medications on post-vaccine IgG levels in SLE patients.
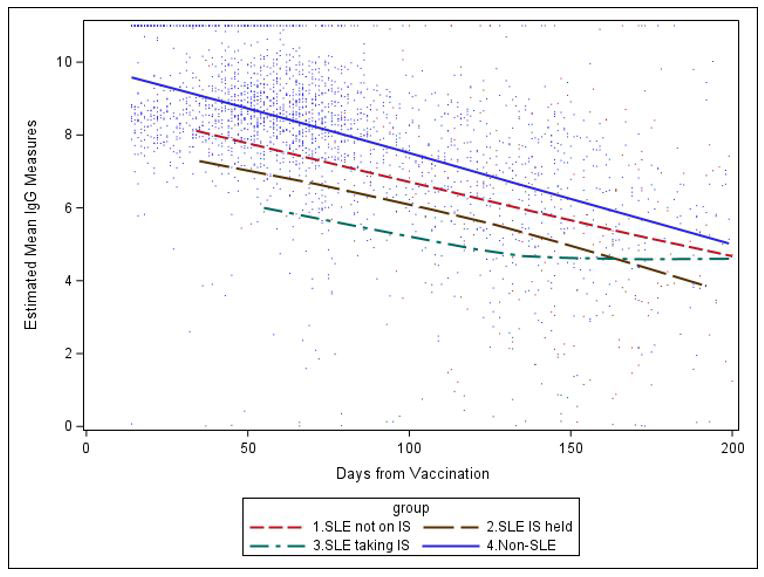
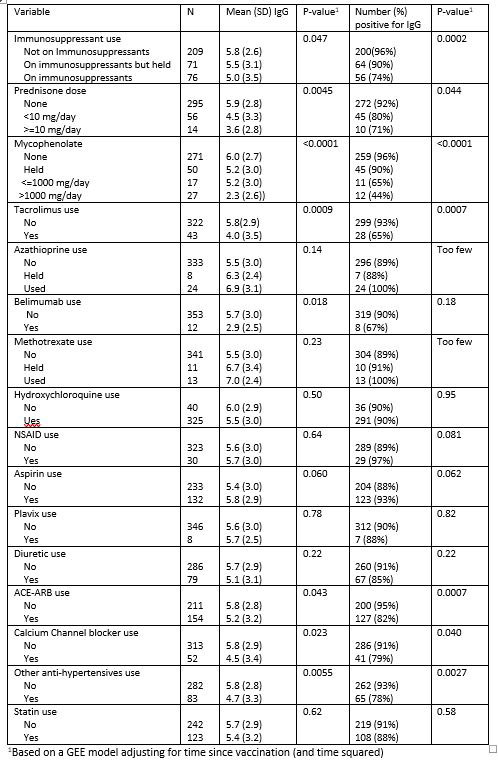
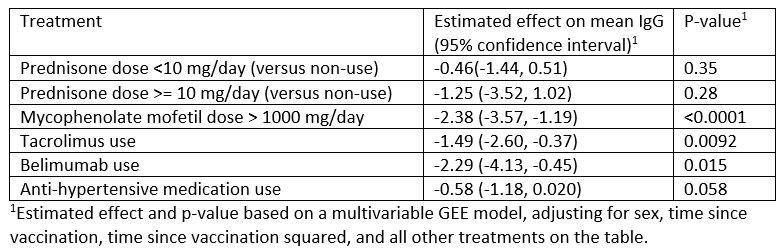
Results: The analysis was based on 334 SLE patients (196 Pfizer, 138 Moderna) and 1887 health care workers (1530 Pfizer and 357 Moderna). SLE patients on immunosuppressive medications had lower post-vaccine IgG levels than SLE patients who were not; but both groups had lower levels than healthcare workers (Figure 1 and Table 1). Holding mycophenolate for one week after vaccine increased post-vaccine IgG levels significantly. In multiple variable models, mycophenolate mofetil, tacrolimus, and belimumab all significantly reduced antibody response to vaccination (Table 2).
Conclusion: SLE patients, regardless of background immunosuppressive therapy, had lower vaccine IgG levels than healthcare workers. Belimumab, tacrolimus and mycophenolate use significantly reduced IgG response to vaccine. Holding mycophenolate for one week improved vaccine efficacy, providing clinical benefit on vaccine response, without leading to clinical flares.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Petri M, Joyce D, Haag K, Fava A, Goldman D, Zhong D, Xiao S, Milstone A, Magder L. Effect of Immunosuppression on COVID Vaccination in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-immunosuppression-on-covid-vaccination-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-immunosuppression-on-covid-vaccination-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/