Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 26, 2025
Title: (0554–0592) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Understanding how treatments affect disease-relevant biomarker expression is essential for advancing targeted therapies. Deucravacitinib, an oral, selective, allosteric tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor, has demonstrated superior efficacy in the placebo (PBO)-controlled phase 3 POETYK PsA-1 (NCT04908202) and PsA-2 (NCT04908189) studies. This pooled post hoc analysis of the POETYK PsA studies aimed to identify biomarkers reflecting clinically relevant factors potentially associated with poor prognosis in PsA and to evaluate associations among these biomarkers, deucravacitinib treatment, and clinical responses.
Methods: Spearman correlations between 48 PsA and immune response–related biomarkers and PsA disease activity (PASDAS, DAPSA, PASI) at baseline (BL) and W16 were performed. Pharmacodynamic effects of deucravacitinib on biomarkers were analyzed using a mixed effects model to show covariate-adjusted change from BL for disease activity and Patient Global Assessment of Pain (Pain). Logistic regression was used to assess the relationship between BL biomarkers (eg, CRP, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio [NLR]) and ACR 20 response, minimal disease activity (MDA) response, and modified Sharp-van der Heijde (mSvdH) total score (radiographic progression [defined as change of mSvdH > 0]; evaluated in POETYK PsA-1 only); covariates included BL BMI and prior MTX use. mSvdH nonprogression was evaluated using a stratified Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test with BL csDMARD use as the stratification factor.
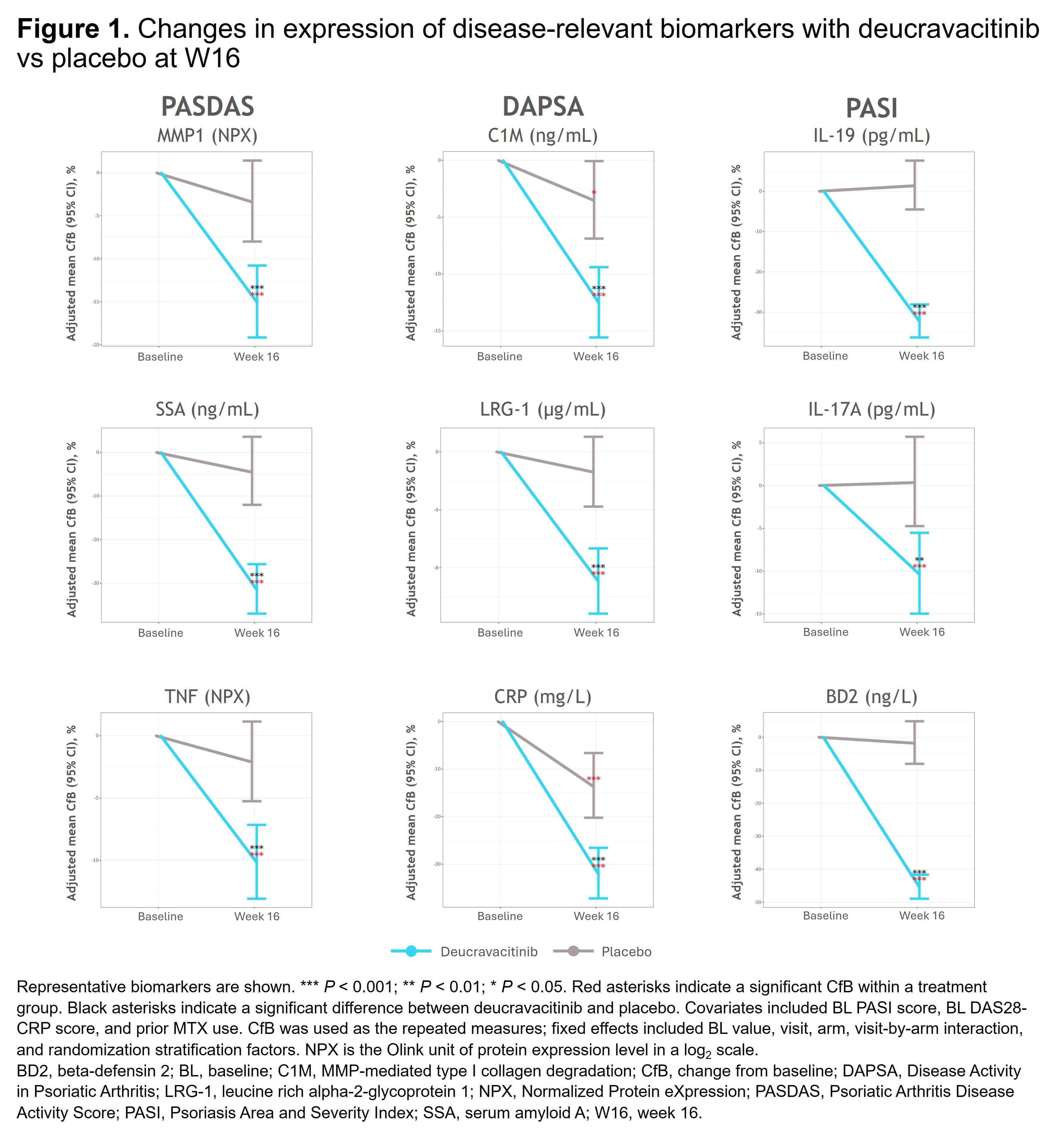
Results: Deucravacitinib significantly reduced disease activity–associated biomarkers, including those impacting skin (eg, IL-19, IL-17A, BD2) and joint (eg, CRP, C1M, LRG-1, MMP1, SAA, TNF) manifestations vs PBO (Figure 1). Patients treated with deucravacitinib were more likely to achieve ACR 20 and MDA response vs PBO at W16 in those with high (≥ median) BL NLR, IL-19, IL-17A, CRP, BD2, and SAA (Figure 2A,C). Response rates for ACR 20 and MDA were higher with deucravacitinib vs PBO at W16, with significant differences observed in patients with high (≥ median) BL IL-19, IL-17A, and BD2 for ACR 20 (Figure 2B) and high BL NLR (≥ 2.81) or high BD2 levels (≥ 7185 ng/L) for MDA (Figure 2D). Deucravacitinib reduced pain-associated biomarkers (eg, CRP, C1M, MMP3, TNF, ICAM-1) vs PBO at W16. Given the clinical relevance of CRP, additional analyses in patients with high BL CRP (≥ 3 mg/L) showed that deucravacitinib significantly reduced Pain score vs PBO as early as W4 (P < 0.01) with sustained reduction at W16 (P < 0.001), provided a greater reduction in mSvdH total score (PBO corrected) vs those with normal BL CRP, and led to reduced radiographic progression vs PBO at W16 (21.1% vs 30.6%; P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Deucravacitinib significantly reduced PsA disease–associated biomarkers in patients with elevated BL biomarkers (eg, CRP, NLR), which may be indicative of severe disease and poor prognosis, and improved efficacy outcomes for multiple disease domains, including radiographic progression. These data provide biological evidence for deucravacitinib as a potential new oral PsA therapy that may benefit patients with severe and difficult-to-treat disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chandran V, FitzGerald O, Mease P, Eder L, Scher J, Ritchlin C, Gladman D, Maksymowych W, Gilvary C, Bal A, Vritzali E, Liu J. Effect of Deucravacitinib Treatment on Disease Activity–Associated Plasma Biomarkers in Patients With Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Results From 2 Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-deucravacitinib-treatment-on-disease-activity-associated-plasma-biomarkers-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-2-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-deucravacitinib-treatment-on-disease-activity-associated-plasma-biomarkers-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-2-phase-3-studies/

.jpg)