Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) often leads to structural damage with resultant disability and reduced quality of life. Biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs), including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL), phosphodiesterase type 4(PDE-4) and Janus kinase (JAK) antagonists have shown clinical efficacy in PsA.
The aims of this study are to determine the efficacy of the following drug combinations in preventing radiographic progression in peripheral joints of PsA patients, namely 1) bDMARDs versus placebo 2) concomitant methotrexate (MTX) versus bDMARD monotherapy 3) IL blockers in anti-TNF-naïve patients versus anti-TNF-failure patients.
Methods:
Systematically review of articles published up to May 2018 in Medline and Web of Science, and abstracts from the two last EUropean League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) and American College of Rheumatology (ACR) meetings. Primary endpoint was the proportion of patients without radiographic progression (non-progressors) at week 24. Secondary endpoint was the mean change in total radiographic score [modified total Sharp score (mTSS) or modified van der Heijde–Sharp score (mvdH-SS)]at week 24. Odds ratio (OR) and standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% CIs across studies were synthesized. Subgroup analyses were performed on pre-specified study-level characteristics. We assessed the quality of evidence using the GRADEpro. This study was registered with PROSPERO, number CRD42018095272.
Results:
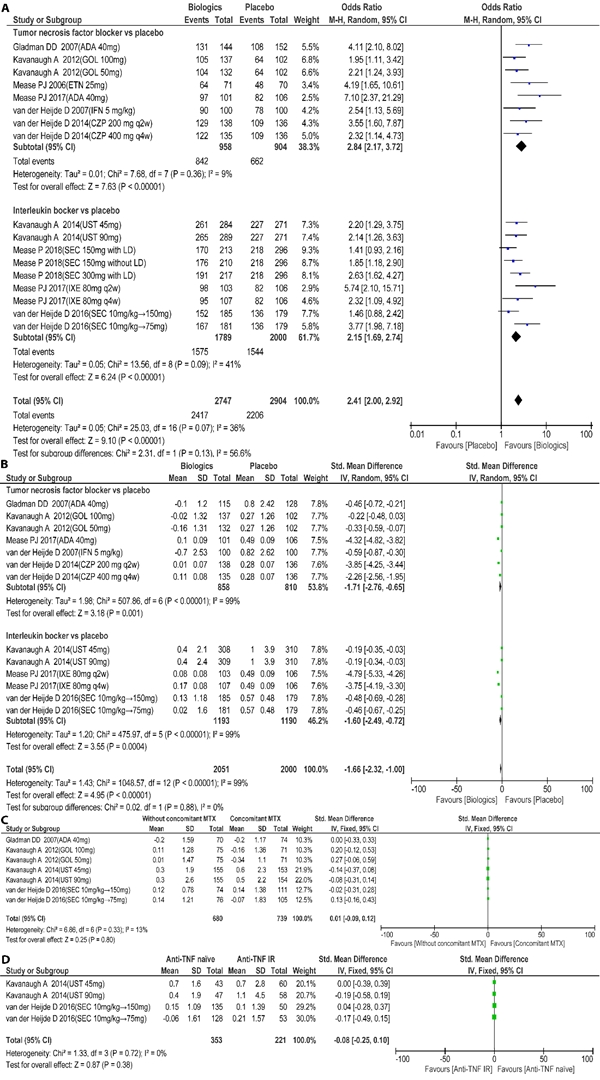
Nine studies (10 RCTs, 4,478 patients), 8 drugs (adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, secukinumab, ustekinumab, ixekizumab) and 16 treatments were evaluated. Tofacitinib and apremilast were not included as complete radiographic data was not available. (1) Patients treated with bDMARDs were more likely to achieve radiographic non-progression compared with placebo (OR for pooled:2.41, 95%CI:2.00, 2.92; OR for TNF blocker:2.84, 95%CI: 2.17, 3.72; OR for IL blocker: 2.15, 95%CI:1.69, 2.74; Figure 1A), and have significantly lower radiographic progression (SMD for pooled: -1.66, 95%CI: -2.32, -1.00; SMD for TNF blocker: -1.71, 95%CI: -2.76, -0.65; SMD for IL blocker: -1.60, 95%CI:-2.49, -0.72; Figure 1B). (2) In patients receiving bDMARDs, concomitant MTX use was not superior to monotherapy (SMD: 0.01, 95%CI: -0.09, 0.12; Figure 1C). (3) The effect of IL blockers (ustekinuamb, secukinuamb) on radiographic progression were not influenced by prior anti–TNF therapy (SMD: -0.08, 95 %CI: -0.25,0.10; Figure 1D).
Conclusion:
Biologic DMARDs can retard radiographic progression in PsA compared with placebo. Concomitant MTX treatment does not improve this effect. Prior anti-TNF therapy does not influence the radiographic efficacy of IL blockers.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wu D, Wong P, Griffith JF, Yue J, Tam LS. Effect of Biologics on Radiographic Progression of Peripheral Joints in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-biologics-on-radiographic-progression-of-peripheral-joints-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-of-randomized-controlled-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-biologics-on-radiographic-progression-of-peripheral-joints-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-of-randomized-controlled-trials/