Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (bari) is an oral selective inhibitor of Janus kinase (JAK) 1 and JAK2. In the phase 3 study RA-BUILD (NCT01721057), once-daily bari yielded significant clinical benefit in patients (pts) with active RA who had inadequate response or intolerance to conventional synthetic DMARDs compared to placebo (PBO).1 Changes in serum biomarkers2 associated with joint tissue remodeling, including synovial remodeling and inflammation (C1M, C3M, and C4M [matrix metalloproteinase-derived fragments of type I, lll, and IV collagen, respectively] and ProC3 [N-terminal pro-peptide type III collagen]), cartilage degradation (C2M [derived from type ll collagen]), and bone remodeling (CTX-I [C terminal telopeptide of type I collagen] and osteocalcin) were analyzed in a subset (N=240) of these pts.
Methods: Circulating levels of biomarkers from eighty patients per arm (PBO, bari 2- or 4-mg [added to stable background therapy]) were analyzed at baseline (BL), week (Wk) 4, and Wk 12, using a Mixed Model Repeated Measure method to identify markers that are affected by bari longitudinally. Secondly, an analysis of variance was performed to evaluate the relationship between the observed changes in biomarkers at Wks 4 and 12 (grouped as reduction or increase from BL) and the Hybrid ACR response measure (a hybrid of ordinal and continuous versions of ACR scores)3 at the primary endpoint of Wk 12.
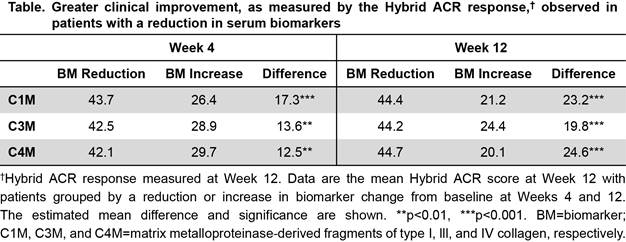
Results: Baseline concentrations of biomarkers tested were similar between all three groups. At Wk 4, C1M was reduced by 21% from BL by bari 4-mg compared to PBO (p<0.01); suppression was sustained at Wk 12 (27%, p<0.001). Similarly, at Wk 4, C3M and C4M were reduced by 14% and 12% from BL by bari 4-mg compared to PBO (p<0.001), respectively, and remained reduced by 16% or 11% from BL at Wk 12 (p<0.001). Similar results were observed with bari 2-mg. Bari treatment did not result in appreciable changes compared to PBO for the other biomarkers tested. We further determined the relationship between changes in biomarkers in RA pts and clinical response, as measured by the Hybrid ACR score (Table). In a pooled analysis with all three treatment arms, a reduction in C1M, C3M, and C4M by Wks 4 and 12 was associated with significantly greater clinical improvement in the Hybrid ACR response at Wk 12 compared to pts with RA having increased levels of these biomarkers.
Conclusion: A reduction in circulating biomarkers associated with tissue destruction and synovial inflammation in RA pts was observed in bari-treated RA pts, suggesting that bari inhibits key pathological processes at the site of inflammation in RA. Moreover, the decrease in these biomarkers was associated with clinical improvement.
1Dougados M et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:88-95.
2Bay-Jensen A et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43:470-478.
3Felson D. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57:193-202.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Thudium CS, Bay-Jensen AC, Cahya S, Dow ER, Karsdal MA, Koch AE, Zhang W, Benschop RJ. Effect of Baricitinib on Joint-Related Biomarkers in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-baricitinib-on-joint-related-biomarkers-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-baricitinib-on-joint-related-biomarkers-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/