Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Voclosporin, a novel calcineurin inhibitor, is approved for the treatment of adults with lupus nephritis in combination with background immunotherapy and was successfully tested in two pivotal trials, AURA-LV (Phase 2) and AURORA 1 (Phase 3). Pooled data from these trials showed that adding voclosporin to mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) and low-dose steroids resulted in significantly more patients achieving urine protein creatinine ratio (UPCR) reductions of ≥50% from baseline at one year; the median time to this endpoint was also significantly shorter in the voclosporin arm.
As reduced proteinuria at one year is the best predictor of improved long-term renal outcomes in lupus nephritis, we have analyzed the impact of voclosporin on the time to proteinuria reduction by biopsy class in pooled data from the AURA-LV and AURORA 1 trials.
Methods: Both trials enrolled patients with biopsy-proven lupus nephritis (Class III, IV, or V ± III/IV), proteinuria ≥1.5 mg/mg (≥2 mg/mg for Class V) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) >45 mL/min/1.73 m2. The pooled analysis included 268 and 266 patients in the voclosporin and control arms, respectively. All patients received MMF (target 2 g/day) and steroids (target dose 2.5 mg/day by Week 16). For this post-hoc analysis, hazard ratios (HR) for the times to UPCR ≤0.5 mg/mg and UPCR reduction ≥50% from baseline were analyzed by biopsy class.
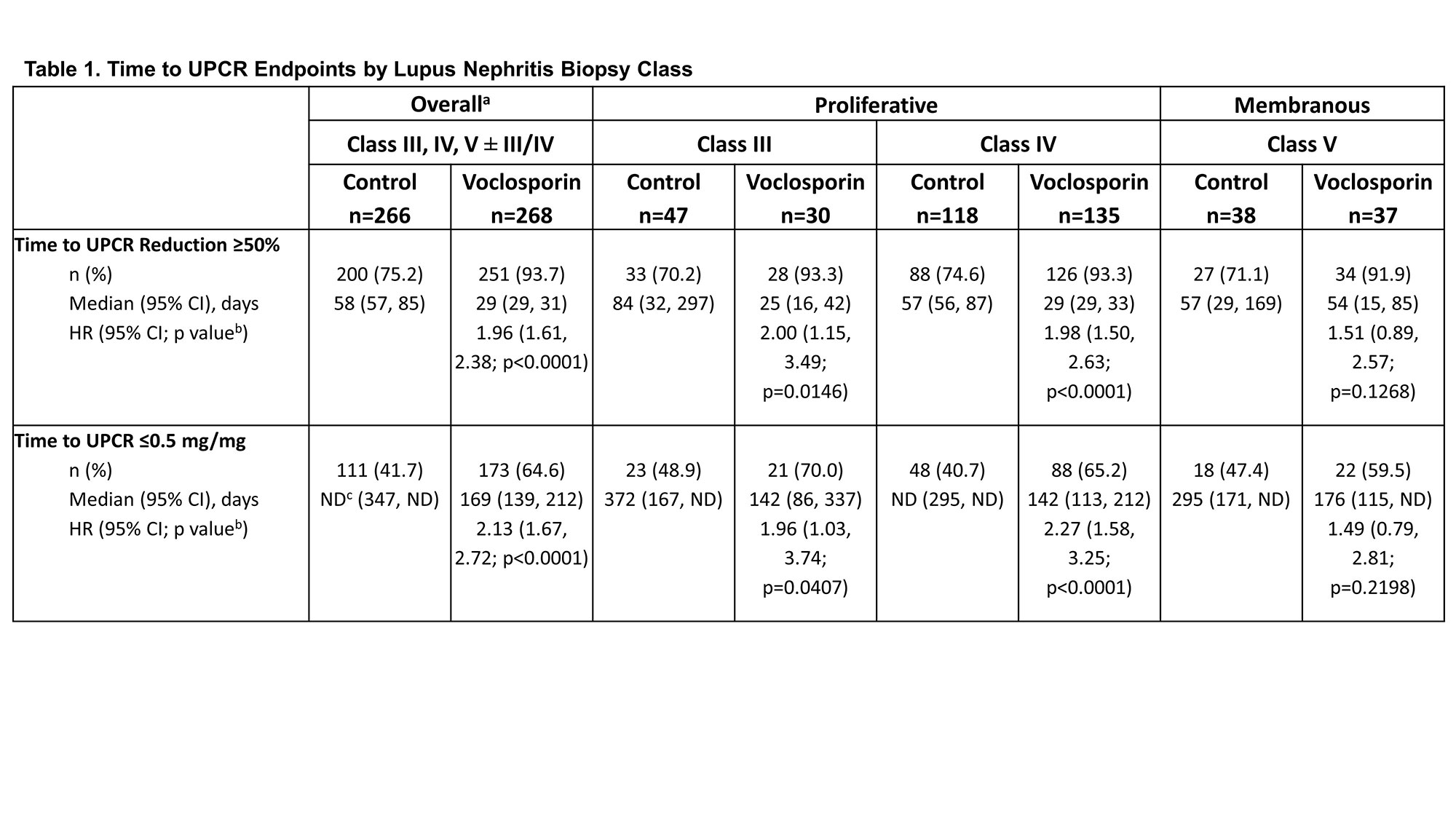
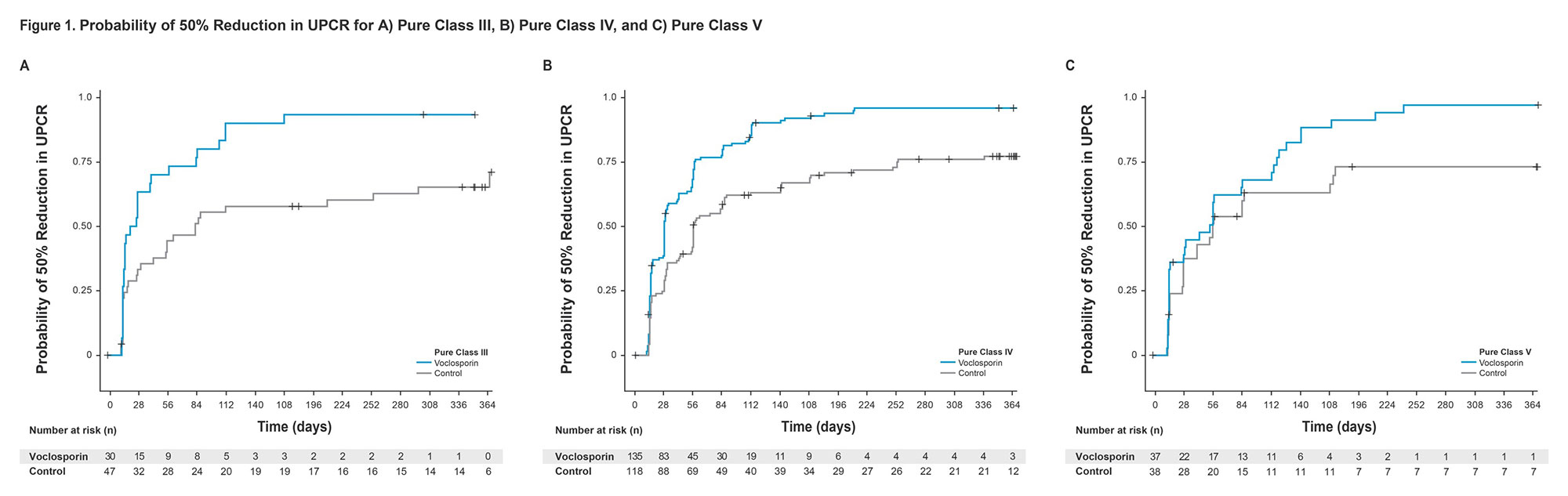
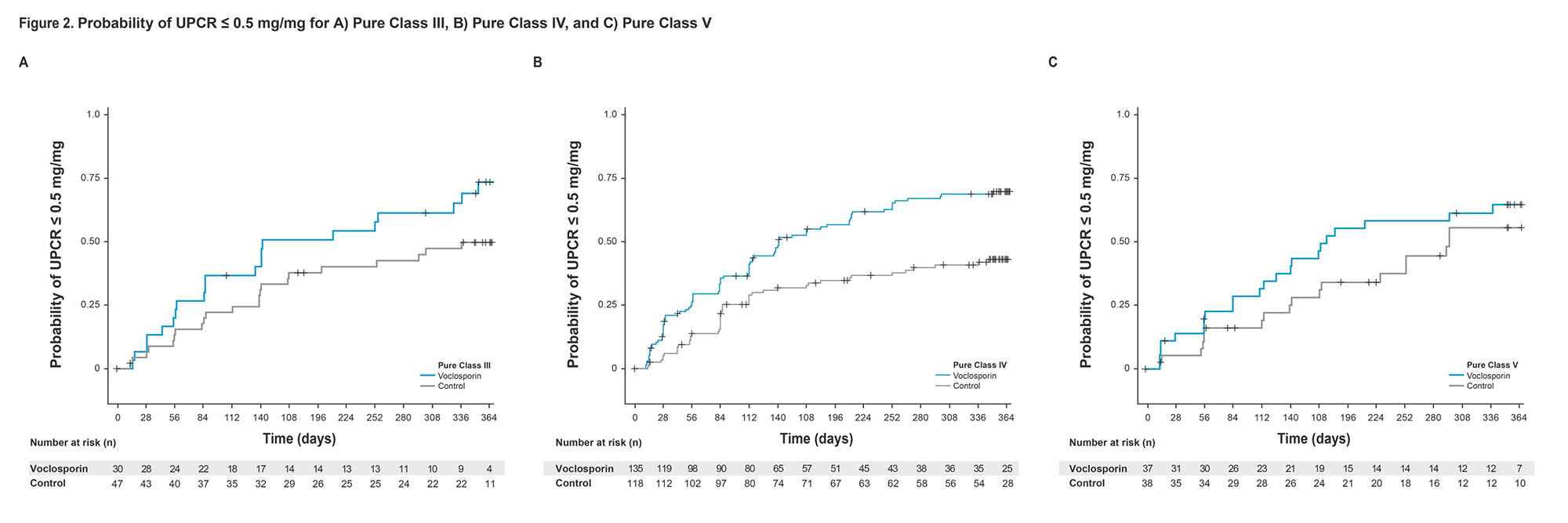
Results: Voclosporin resulted in faster times to both UPCR ≤0.5 mg/mg and UPCR reduction ≥50% from baseline in the overall study population and across individual biopsy classes (HR >1; Table 1). Median times to UPCR ≤0.5 mg/mg and UPCR reduction ≥50% from baseline for patients with pure Class III disease were significantly shorter for voclosporin-treated patients than control: 142 vs 372 days and 25 vs 84 days, respectively. The median time to UPCR reduction ≥50% was faster in pure Class IV patients treated with voclosporin as well (29 vs 57 days); voclosporin-treated patients achieved a UPCR ≤0.5 mg/mg in a median of 142 days while in the control arm, more than 50% of patients did not achieve this endpoint during the one-year study. Differences between voclosporin and control arms for Class III and Class IV were apparent within the first month of treatment and sustained at one year (Figures 1, 2). Patients with pure Class V disease took the longest to achieve both endpoints; the difference between arms was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: The addition of voclosporin to MMF and low-dose steroids resulted in earlier reductions in proteinuria across all biopsy classes. This analysis supports the efficacy results observed in the individual AURA-LV and AURORA 1 trials, indicating faster time to response, when voclosporin is added to standard of care agents MMF and steroids.
a) Includes all biopsy classes in AURORA 1 and AURA-LV.
b) p-value vs control.
c) Values not determinable due to either the endpoint not being met by 50% of the cohort within the study period or limited additional patients achieving the endpoint after the median timepoint but before the end of the study.
CI, confidence interval; HR, hazard ratio; ND, not determinable; UPCR, urine protein creatinine ratio.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Askanase A, Hodge L, Birardi V, Leher H. Early Reductions in Proteinuria with Voclosporin Treatment Across Lupus Nephritis Biopsy Classes: Pooled Data from the AURA-LV and AURORA 1 Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-reductions-in-proteinuria-with-voclosporin-treatment-across-lupus-nephritis-biopsy-classes-pooled-data-from-the-aura-lv-and-aurora-1-trials/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-reductions-in-proteinuria-with-voclosporin-treatment-across-lupus-nephritis-biopsy-classes-pooled-data-from-the-aura-lv-and-aurora-1-trials/