Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Muscle loss is common in long-standing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. However, less is known about this unfavorable alteration of body composition (BC) and its significances in early RA.
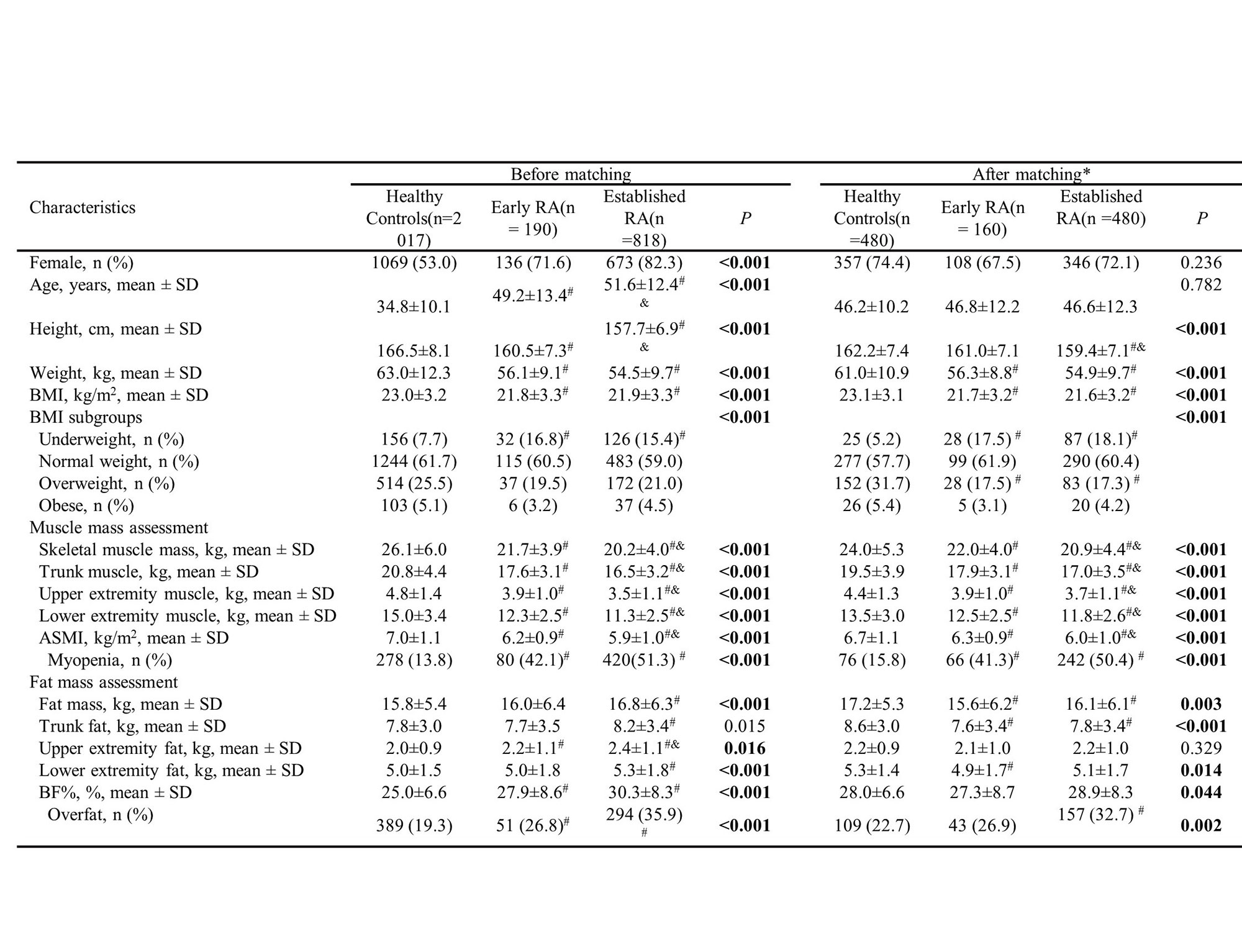
Methods: This cross-sectional study was carried out based on our RA cohort and healthy control. Consecutive RA patients aged ≥16 years who fulfilled the 2010 American College of Rheumatology / European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria for RA were recruited. BC was assessed using bioelectric impedance analysis. Myopenia was defined as an appendicular skeletal muscle mass index (ASMI) ≤ 7.0 kg/m2 (men) and ≤ 5.7 kg/m2 (women), overfat was defined by the percentage of body fat mass (BF%) as ≥ 25% (men) and ≥ 35% for (women). Propensity score matching was performed to balance age and gender difference among early RA (disease duration ≤ 12 months), established RA patients and controls (in 1:3:3 matching).
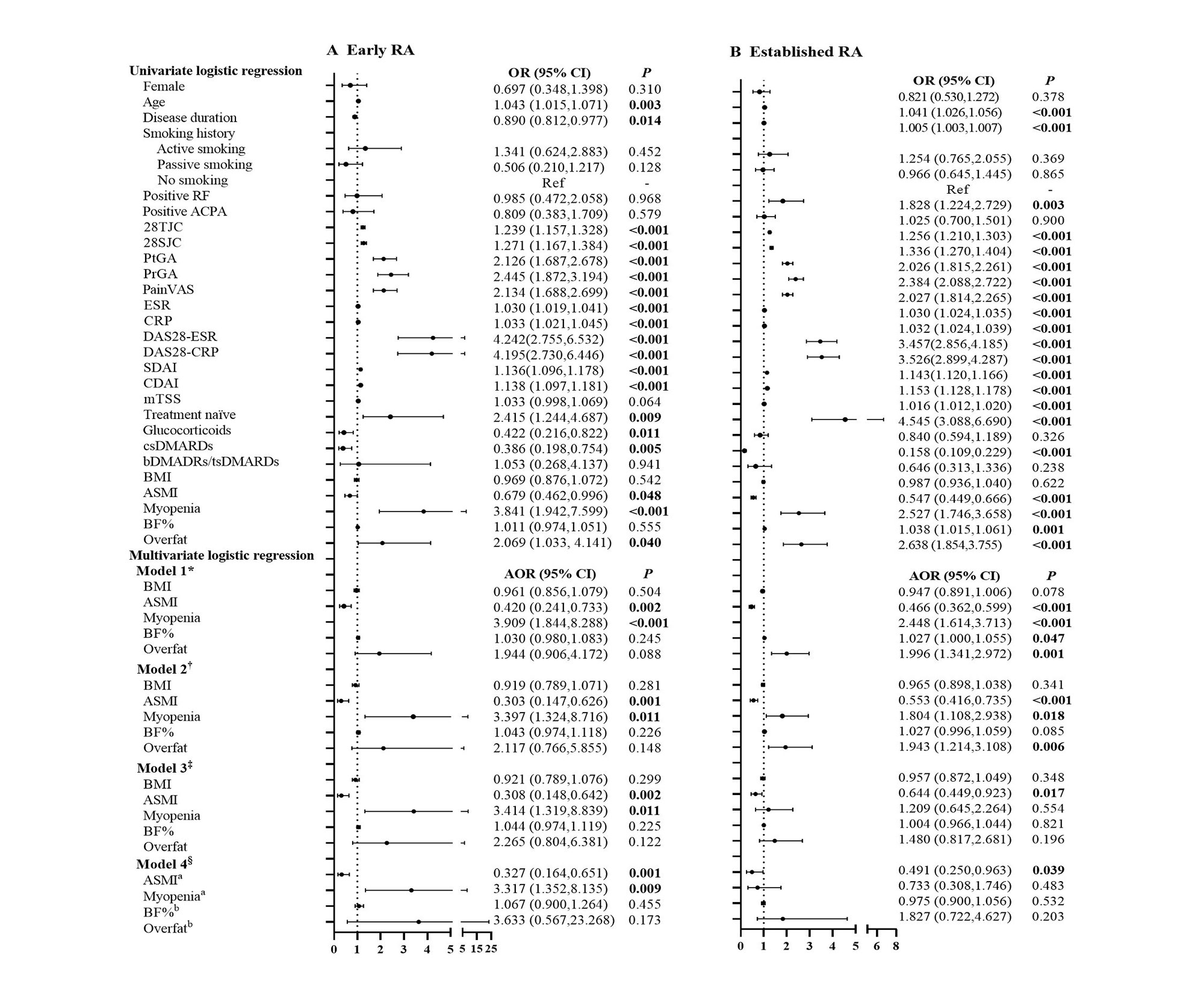
Results: There were 2017 controls and 1008 RA patients recruited, including 190 (18.8%) early RA patients with median disease duration 7(4,11) months. Matched early RA patients (n=160) showed a higher prevalence of myopenia (41.3% vs. 15.8%, P < 0.0167), but no significant difference with matched established patients (41.3% vs. 50.4%, P > 0.0167, Table 1). Compared with established patients, early RA patients exhibited higher disease activity scores (including DAS28-CRP: median 4.76 vs. 3.93, P < 0.001) and more physical dysfunction (26.3% vs. 19.4%, P = 0.035). Higher RA disease activity scores were positively and strongly associated with myopenia in early RA patients, especially DAS28-CRP [AOR 1.680, 95% CI (1.171-2.409)]. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that myopenia [AOR 3.317 (95% CI 1.352-8.135)] was independently associated with physical dysfunction in early RA patients (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Our data indicates early and common muscle involvement in RA. Muscle loss is independently associated with physical dysfunction in early RA patients, which imply the importance of its early detection and further resolution is worth exploring in future.
*Propensity score matching among early and established RA patients and healthy controls in 1:3:3 matching with age and gender
Comparisons among three groups by one-way ANOVA test, or chi-squared test. P value <0.05 was defined as significant difference which was shown in bold.
#Compared early and established RA patients with healthy controls in Bonferroni correction, P < 0.0167
&Compared established RA with early RA patients in Bonferroni correction, P < 0.0167
BC, body composition; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; BMI, body mass index; ASMI, appendicular skeletal muscle mass index; BF%, percentage of body fat mass
*Model 1 Adjusted for age, gender, smoking history, disease duration, RF status, ACPA status, and previous treatment
†Model 2 Adjusted for model 1+ DAS28-CRP (which was the most significantly associated with myopenia and overfat)
‡Model 3 Adjusted for model 2+ mTSS
§Model 4 Adjusted for model 3+BMI+ aBF%/ bASMI
OR, odds ratio in logistic regression; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval; AOR, adjusted OR
RA, rheumatoid arthritis; RF, rheumatoid factor; ACPA, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody; 28TJC, 28-joint tender joint counts; 28SJC, 28-joint swollen joint counts; PtGA, patient global assessment of disease activity; PrGA, provider global assessment of disease activity; Pain VAS, pain visual analogue scale; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, C-reactive protein; DAS28-ESR, Disease Activity Score in 28 joints with four variables including erythrocyte sedimentation rate; DAS28-CRP, Disease Activity Score in 28 joints with four variables including C-reactive protein; SDAI, Simplified Disease Activity Index; CDAI, Clinical Disease Activity Index; mTSS, modified total Sharp score; csDMARDs, conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; bDMARDs, biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; tsDMARDs, target synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; BMI, body mass index; ASMI, appendicular skeletal muscle mass index; BF%, percentage of body fat mass
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pan J, Zou Y, Zhu Y, Ma J, Lin J, Wu T, Yang Z, Zhang X, Zhang Q, Zheng H, He X, Cheng W, Dai L. Early Muscle Involvement in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Large-Scale Cross-Sectional Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-muscle-involvement-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-large-scale-cross-sectional-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-muscle-involvement-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-large-scale-cross-sectional-study/