Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is a rare and severe clinical phenotype of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) with a poor prognosis. Anticoagulation therapy is efficient, but is associated with potentially severe side-effects, especially bleeding episodes. The aim of this study was to retrospectively analysis our single center experience on long-term anticoagulation in APS patients presenting a PVT.
Methods: Data of 26 APS patients with PVT from 2012 to 2019 were enrolled. The diagnosis of PVT was made according to the 2009 American College of Liver Diseases (AASLD) criteria. Regular imaging was performed to monitor the outcome of PVT. The hemorrhagic complications and the recurrence of the PVT after anticoagulation withdrawal were also analyzed.
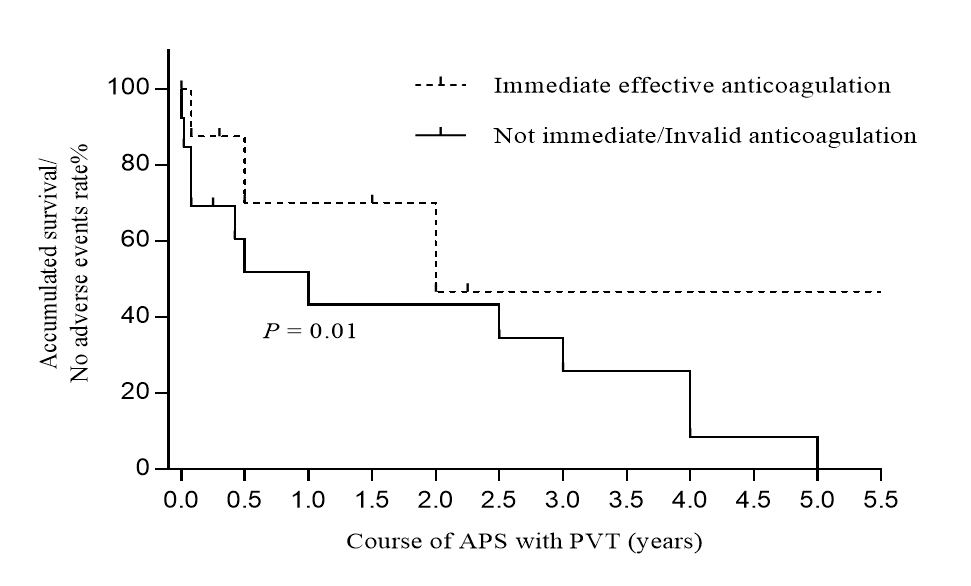
Results: A total of 26 patients with APS-PVT were enrolled, 5 males and 21 females, with an average age of 39±12.65 years, 9 cases (35%) with acute thrombosis, 12 cases (46%) with chronic thrombosis, and 5 cases (19%) with portal vein spongiformity. 14 cases (54%) with portal hypertension, 13 cases (50%) with esophageal varices, 4 cases(15%) with spleen infarction , 6 cases (23%) with gastrointestinal bleeding and 2 cases (8%) with abdominal infection. Triple aPLs positive in 5 cases (19%). 14 cases began anticoagulation therapy immediately after diagnosis of thrombus. 7 patients got thrombus recanalization. 3 patients got recurrence. 5 patients died.
Conclusion: PVT usually had insidious onset with atypical clinical symptoms and easily be misdiagnosed. Early diagnosis and anticoagulation treatment can bring thrombus recanalization thereby significantly improving the prognosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
You H, Zhao J, Tian X, Li M, Zeng X. Early Anticoagulation Improves the Long-term Prognosis in Patients with Antiphospholipid Syndrome Associated Portal Vein Thrombosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-anticoagulation-improves-the-long-term-prognosis-in-patients-with-antiphospholipid-syndrome-associated-portal-vein-thrombosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/early-anticoagulation-improves-the-long-term-prognosis-in-patients-with-antiphospholipid-syndrome-associated-portal-vein-thrombosis/