Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-2:15PM
Background/Purpose: People with rheumatic diseases are at risk for acute and post-acute COVID-19 outcomes in part due to immunosuppressive medications. Those on B-cell depleting therapies (BCD) tend to have worse outcomes, and some uncontrolled retrospective case reports and case series showed prolonged viral shedding. Recent data suggest that tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) have less impact on COVID-19 severity. We aimed to prospectively investigate duration of SARS-CoV-2 viral shedding in rheumatic patients using BCD or TNFi
Methods: We conducted a matched cohort study among participants in POSITIVES, a prospective study enrolling outpatients with acute COVID-19 infection within 5 days of diagnosis. Anterior nasal swabs were self-collected three times weekly over 2 weeks and then weekly until two negative PCR results. Viral PCR and culture were performed on each sample. In this analysis, we evaluated people who were on BCD or TNFi at COVID-19 onset. For each case, immunocompetent comparators with acute COVID-19 were matched (1:2) using propensity scores based on age, sex, race, ethnicity, number of prior COVID-19 vaccinations, calendar time, and use of antivirals. We used Cox regression and linear mixed-effects models to compare each immunocompromised group with their immunocompetent comparator for time to negative PCR (primary), time to negative viral culture, and viral load trajectories.
Results: We analyzed 30 TNFi and 16 BCD users, each matched to 53 and 33 immunocompetent comparators, respectively. The most common rheumatic disease was RA (53% among TNFi; 30% among BCD). More than 60% were using an antiviral and the mean number of COVID-19 vaccinations was 4.3 (Table 1). The median time to undetectable viral load was similar between TNFi users and comparators (HR 0.77, 95%CI 0.48 to 1.23, p=0.27; Figure 1). In contrast, there was a significant difference in the median (IQR) days to undetectable viral load between BCD users 15 (7, 23) vs. their comparators 7 (3, 13; HR 0.43, 95%CI 0.22 to 0.86; p=0.017). Results were similar when examining time to negative viral culture. When analyzing the difference in viral decay trajectories, the BCD group had significantly different trajectory than their immunocompetent comparators (p=0.008), while TNFi and their comparators had similar trajectory (p=0.19, Figure 2).
Conclusion: In this prospective study of viral shedding during acute COVID-19, BCD users had longer SARS-CoV-2 viral persistence than immunocompetent comparators. While BCD users had about 8 days longer median duration of viral shedding, nearly all had negative PCR after one month of follow-up. Studies are ongoing to evaluate whether BCD may be associated with in-host viral evolution and the impact of prolonged viral shedding on patient outcomes.
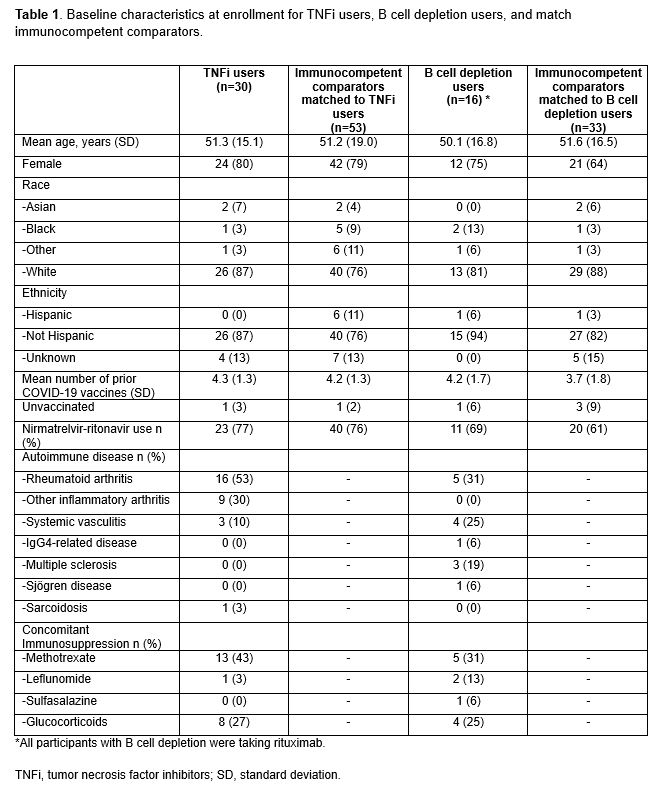 Table 1. Baseline characteristics at enrollment for TNFi users, B cell depletion users, and matched immunocompetent comparators.
Table 1. Baseline characteristics at enrollment for TNFi users, B cell depletion users, and matched immunocompetent comparators.
.jpg) Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier curves and hazard ratios for undetectable viral load for A) TNFi users and their immunocompetent comparators, B) B cell depletion users and their immunocompetent comparators.
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier curves and hazard ratios for undetectable viral load for A) TNFi users and their immunocompetent comparators, B) B cell depletion users and their immunocompetent comparators.
.jpg) Figure 2. Virologic decay over time for A) TNFi users and their immunocompetent comparators, B) B cell depletion users and their immunocompetent comparators.
Figure 2. Virologic decay over time for A) TNFi users and their immunocompetent comparators, B) B cell depletion users and their immunocompetent comparators.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Getachew L, Wang X, Wallace Z, Patel N, O'Keeffe L, Negron M, Qian G, Saavedra A, Mueller K, Davis N, Li Y, Choudhary M, Boucau J, Leeman B, Edelstein G, Glover O, Kawano Y, Deo R, Marino C, Reynolds Z, Su K, Mandell C, Passell E, Barry M, Alexandrescu A, Ghimire D, Mandal M, Vyas T, Hammond S, Vyas J, Lemieux J, Siedner M, Barczak A, Li J, Sparks J. Duration of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Shedding After Acute Infection in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases Using B Cell Depletion or Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/duration-of-sars-cov-2-viral-shedding-after-acute-infection-in-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-using-b-cell-depletion-or-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/duration-of-sars-cov-2-viral-shedding-after-acute-infection-in-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-using-b-cell-depletion-or-tumor-necrosis-factor-inhibitors/
