Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: IL-17F shares structural homology and overlapping biologic function with IL-17A. In vitro studies demonstrate that IL-17F has biologic effector function that can modulate inflammation. Early clinical data support dual neutralization of IL‑17A and IL‑17F as a novel targeting approach in psoriasis, PsA and AS. We report interim results from a Phase 2b study (NCT02969525) assessing the dose response, long-term efficacy and safety of bimekizumab (BKZ), a mAb that potently and selectively neutralizes both IL-17A and IL‑17F, over 48 weeks in patients with active PsA.
Methods: 206 patients with active PsA, ≥3/76 swollen joint count and ≥3/78 tender joint count and fulfilling the CASPAR (score ≥3) criteria, were randomized (1:1:1:1:1) to receive subcutaneous BKZ 16 mg, 160 mg, 160 mg with 320 mg loading dose (160 mg [LD]), 320 mg, or placebo (PBO) Q4W, for 12 weeks (double-blind period). After Week 12, patients receiving PBO or BKZ 16 mg were re-randomized (1:1) to receive BKZ 160 mg or 320 mg; all other patients continued on their previous dose (dose-blind period). The primary endpoint was ACR50 response at Week 12.
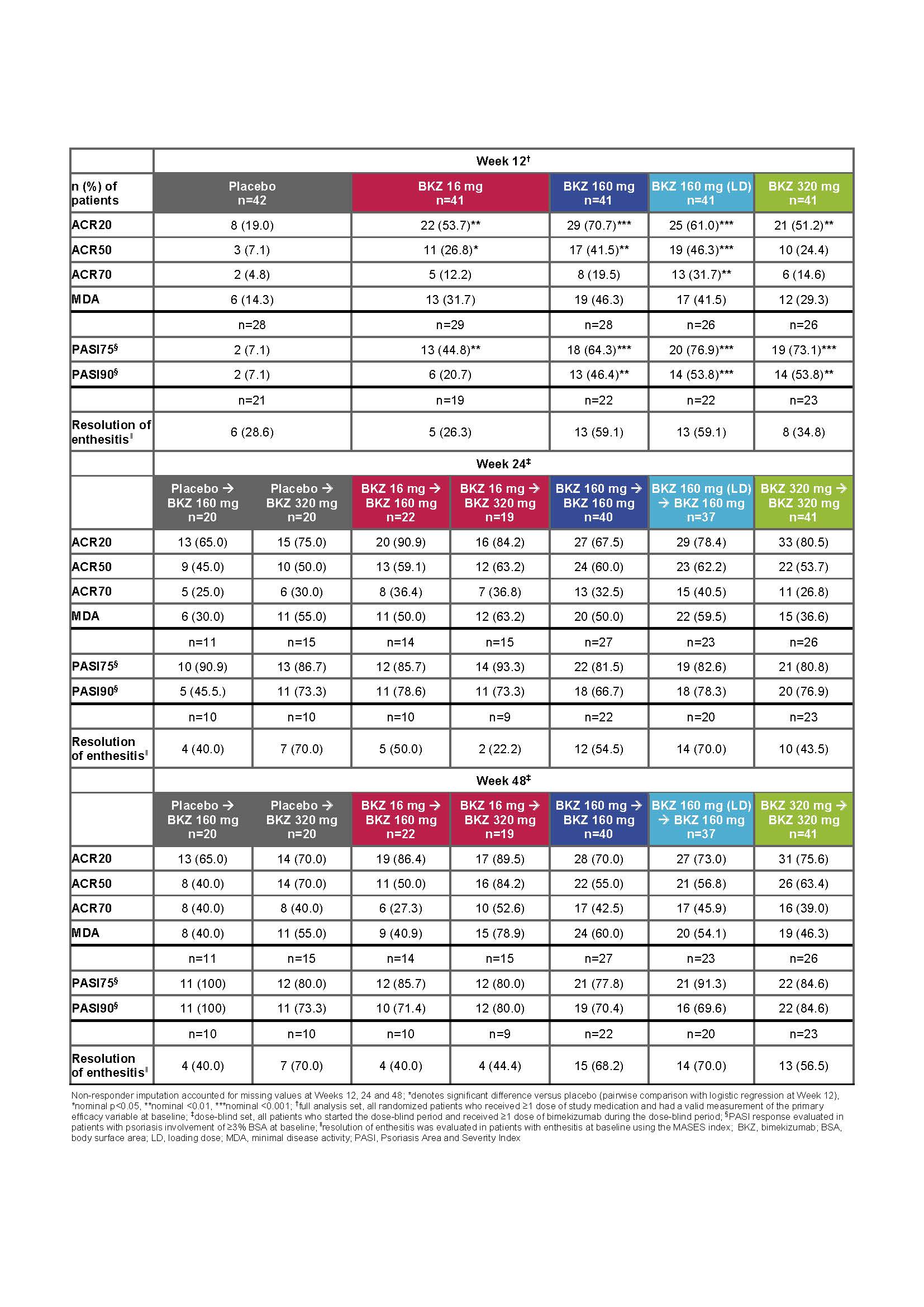
Results: 203/206 and 189/206 patients completed the double- and dose-blind periods, respectively. Overall, demographics and baseline disease characteristics were balanced across groups. 19% of patients had prior exposure to TNF inhibitors. There was a statistically significant (p<0.05) dose-response at Week 12 for ACR50 response rates. At Week 12, significantly more patients receiving BKZ versus PBO achieved ACR50 (primary endpoint: 16–160 mg [LD] doses), ACR20 and PASI90 (in those patients with baseline BSA ≥3%; 160–320 mg doses) (table). ACR20/50/70, PASI75/90, MDA and resolution of enthesitis response rates increased up to Week 24 in those continuing on their initial BKZ dose; responses were maintained through the study and were similar across the three highest dose groups at Week 48. In addition, rapid improvements were observed across all response criteria in patients re‑allocated to BKZ 160 or 320 mg (table). There was no apparent relationship between dose and TEAEs. Serious AEs were reported by 9/206 (4.4%) patients up to Week 48 (8/206 [3.9%] receiving BKZ). The most common TEAE up to Week 48 was nasopharyngitis 25/206 [12.1%]). Oral candidiasis was reported at Week 48 by 10/206 (4.9%) patients (all cases during BKZ treatment). No deaths, or cases of IBD or MACE were reported.
Conclusion: BKZ provided substantial improvements in both musculoskeletal and skin outcomes; response rates continued to increase after Week 12 (primary analysis) and were sustained from Week 24 to 48, with a safety profile consistent with previous BKZ studies. These data provide further support that neutralizing IL‑17F in addition to IL-17A with BKZ is a promising therapeutic approach in patients with active PsA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ritchlin CT, Kavanaugh A, Merola JF, Schett G, Scher JU, Warren RB, Assudani D, Kumke T, Ink B, McInnes IB. Dual Neutralization of IL-17A and IL-17F with Bimekizumab in Patients with Active Psa: Results from a 48-Week Phase 2b, Randomized, Double‑Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Ranging Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dual-neutralization-of-il-17a-and-il-17f-with-bimekizumab-in-patients-with-active-psa-results-from-a-48-week-phase-2b-randomized-double%e2%80%91blind-placebo-controlled-dose-ranging-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dual-neutralization-of-il-17a-and-il-17f-with-bimekizumab-in-patients-with-active-psa-results-from-a-48-week-phase-2b-randomized-double%e2%80%91blind-placebo-controlled-dose-ranging-study/