Session Information
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases I: Imaging in Gout, Pediatric, Soft and Connective Tissue Diseases
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) is an advanced imaging method with potential for monitoring urate deposition in patients with gout. The aim of this prospective longitudinal study was to analyse the sensitivity to change of DECT urate volume measurement.
Methods: Seventy-three patients with tophaceous gout attended study visits at baseline and 12 months. All patients had a comprehensive clinical assessment including serum urate (SU) testing and DECT scanning of both feet at both visits. Two readers analysed the DECT scans for the total urate volume in both feet. Paired scans were read in chronological order. The readers were blinded to each other’s measurements and all clinical measures including serum urate concentrations. Analysis included inter-reader intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) and limits of agreement, and calculation of the smallest detectable change (SDC).
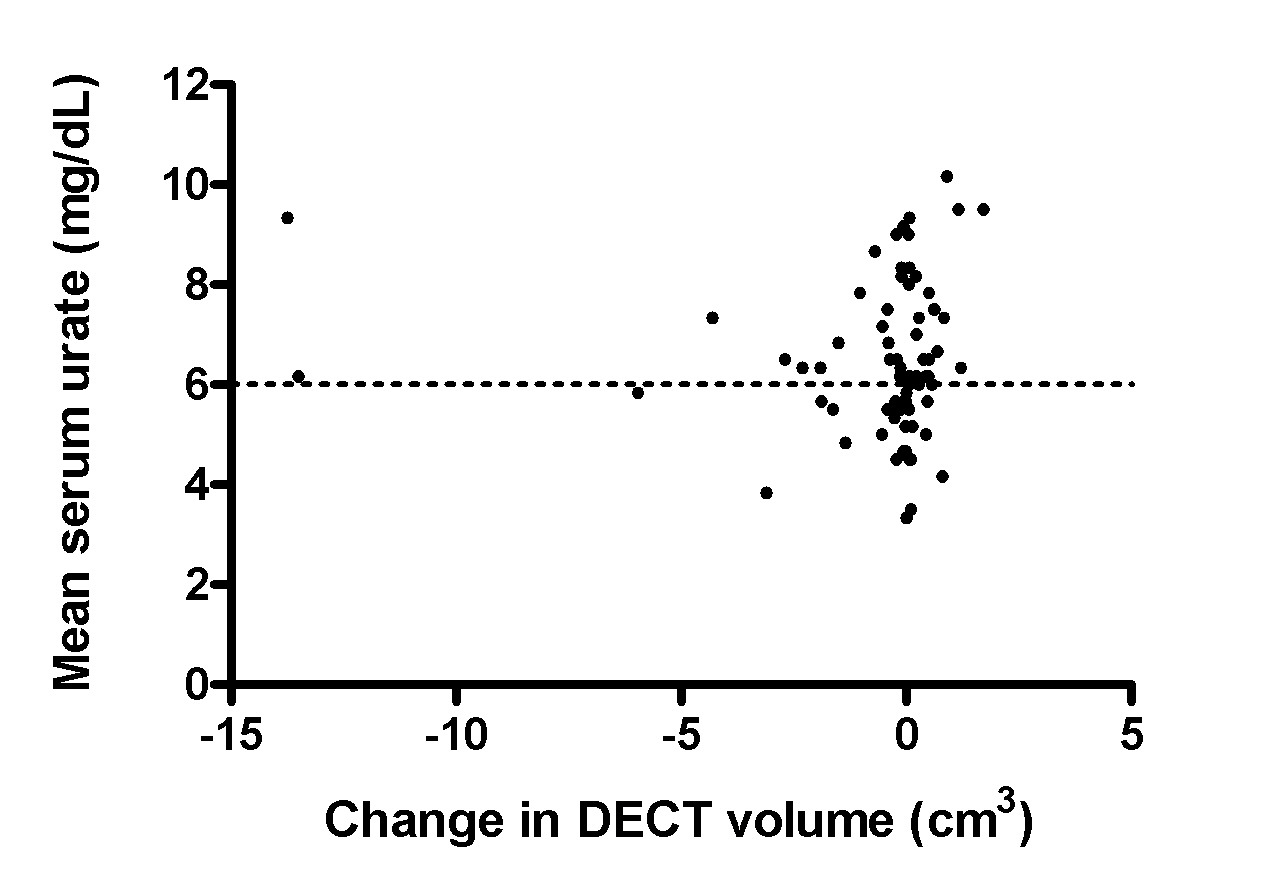
Results: Allopurinol was prescribed in 85% patients during the study period. Mean (SD) SU concentration for both timepoints was 6.3 (1.5) mg/dL. The median (IQR) baseline DECT urate volume was 0.49 (0.16, 2.18) cm3, and change in DECT urate volume was -0.01 (-0.40, 0.28) cm3. Inter-reader ICCs were 1.00 for baseline DECT volumes and 0.93 for change values. Inter-reader bias (SD) for baseline volumes was -0.18 (0.63) cm3 and for change was -0.10 (0.93) cm3. The SDC was 0.91cm3. There were 47 (64%) patients with baseline DECT urate volumes <0.91cm3. Higher mean SU concentrations were observed in patients with increased DECT urate volumes above the SDC (one way ANOVA p=0.006). However, a relationship between changes in DECT urate volumes and mean SU concentrations was not observed in the entire group (Figure).
Conclusion: DECT urate volume measurement has high inter-reader agreement but low sensitivity to change over one year in patients with tophaceous gout receiving conventional urate-lowering therapy. These data raise questions about the role of DECT as an outcome measure for clinical studies of gout.
Figure: Scatter plot showing the relationship between change in DECT urate volumes and mean serum urate concentrations (baseline and Year 1).
Disclosure:
A. Rajan,
None;
O. Aati,
None;
R. Kalluru,
None;
G. Gamble,
None;
A. Horne,
None;
A. Doyle,
None;
F. M. McQueen,
None;
N. Dalbeth,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dual-energy-computed-tomography-for-monitoring-of-urate-deposition-in-tophaceous-gout-a-prospective-longitudinal-study-examining-sensitivity-to-change/