Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: MicroRNAs are markers and mediators of disease and drug response. Prior studies have proposed several miRNAs for prediction of drug response or monitoring drug effect in patients with RA. Our objective was to determine if baseline or change in concentrations of these plasma miRNAs are associated with clinical response to several key disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDS): methotrexate, adalimumab and tocilizumab.
Methods: We developed a list of candidate miRNAs which are associated with response to a DMARD based on literature: let-7a-5p, let-7b-5p, miR-126-3p, miR-132-3p, miR-146a-5p, miR-16-5p, miR-22-3p, miR-223a-3p, miR-23a-3p, miR-24-3p, and miR-27-3p. Candidate miRNAs were measured in plasma from 70 patients with RA in the TETRAD repository before and 6-months after starting a new DMARD by qPCR. The miRNA concentration was determined from a standard dilution curve of a known DNA mimic concentration. MiRNAs were log2 transformed due to skewness. The relationship between change in miRNA concentration and DAS28-ESR before versus after DMARD was assessed by Spearman correlation and using a two-step linear regression with 6-month DAS28-ESR as the outcome and baseline DAS28-ESR and the log2-transformed residualized miRNA as predictors. The residualized miRNA reflects the baseline adjusted miRNA at 6-months, thus enabling adjustment for both baseline miRNA and DAS28-ESR in the final analysis. The predictive capacity of the baseline concentrations of miRNAs adjusted for baseline DAS28-ESR to predict DAS28-ESR at 6 months was assessed by linear regression. Pathway analysis of the miRNA predicted targets was performed using MSigDB Reactome gene sets.
Results: The 70 patients with RA had a median age of 54 years; 80% were Caucasian, 81% were female, median baseline DAS28-ESR was 4.91 units; after 6-months 73% had a moderate to good EULAR response (Table 1). Increasing plasma concentrations between baseline and 6-months of six of the miRNAs (let-7a-5p, let-7b-5p, miR-126-3p, miR-146a-5p, miR-16-5p, and miR-22-3p) were significantly associated with decreasing DAS28-ESR after 6-months of new DMARD treatment in the residualized miRNA analyses (Table 2, all p< 0.05), although mean miRNA concentrations did not significantly change before versus after treatment. There was no significant interaction based on the DMARD initiated (all p >0.2), and baseline miRNA concentrations did not predict drug response (all p >0.05). Pathway analysis demonstrated that the six miRNAs which are associated with change in DAS28-ESR are predicted to target pertinent functions like cytokine signaling, and signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases (Figure), which could contribute to drug response.
Conclusion: Increasing concentrations of six of the eleven miRNAs were significantly associated with greater improvement in RA disease activity 6-months after starting a new DMARD. Pathway analysis demonstrates that these miRNAs, while being markers of drug response may play a direct role in resolution of inflammation. Further studies will be needed to confirm this.
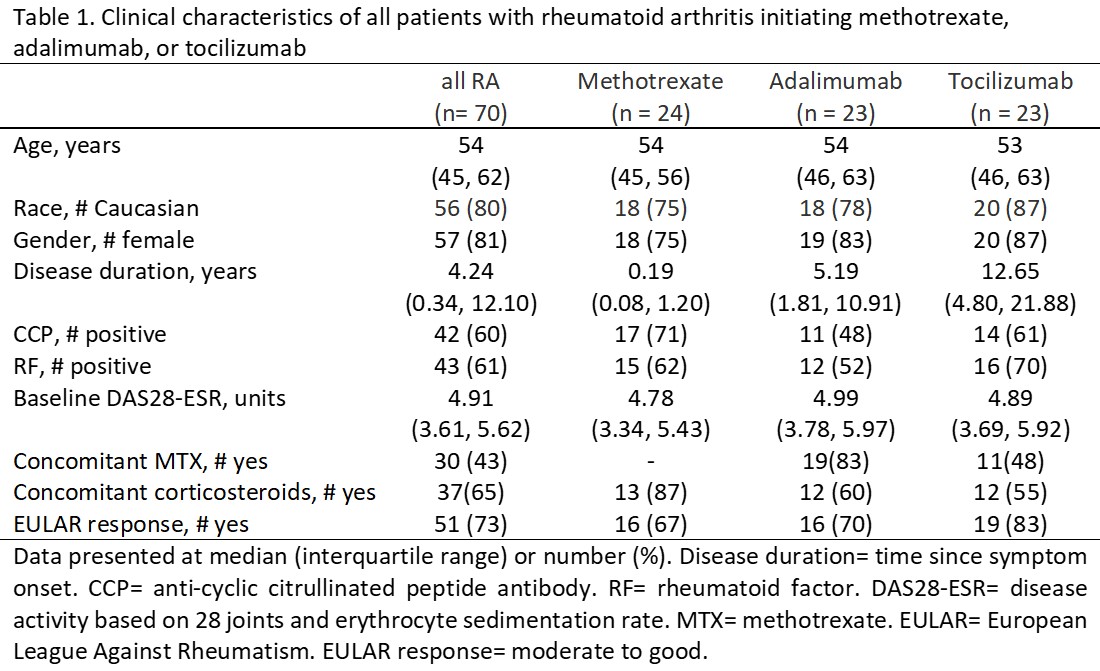 Table 1. Clinical characteristics of all patients with rheumatoid arthritis initiating methotrexate, adalimumab, or tocilizumab
Table 1. Clinical characteristics of all patients with rheumatoid arthritis initiating methotrexate, adalimumab, or tocilizumab
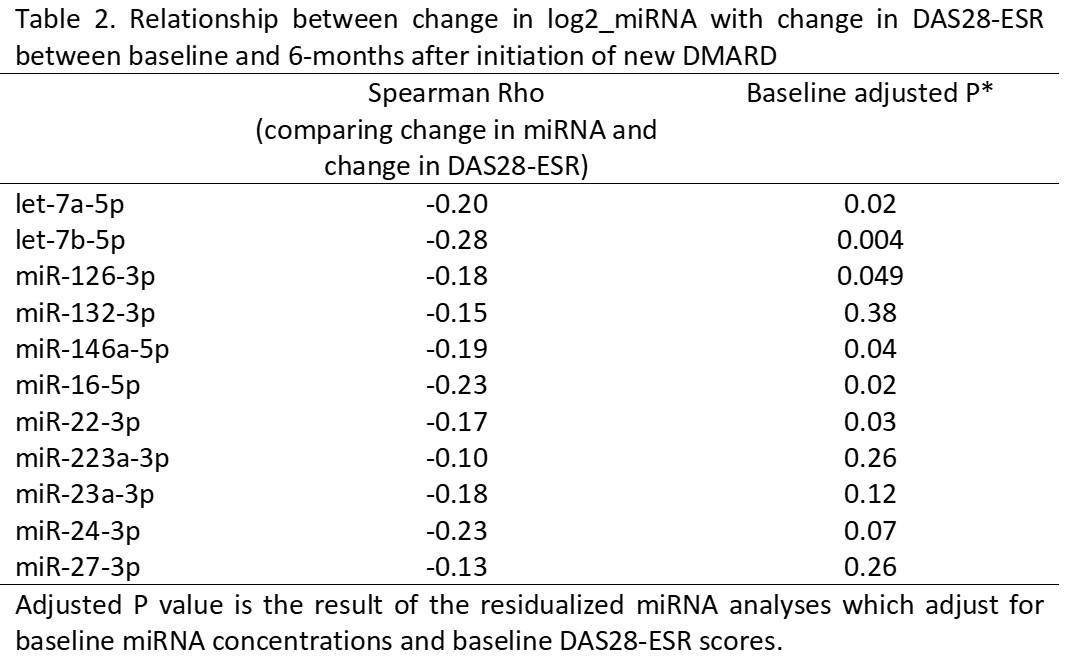 Table 2. Relationship between change in log2_miRNA with change in DAS28-ESR between baseline and 6-months after initiation of new DMARD
Table 2. Relationship between change in log2_miRNA with change in DAS28-ESR between baseline and 6-months after initiation of new DMARD
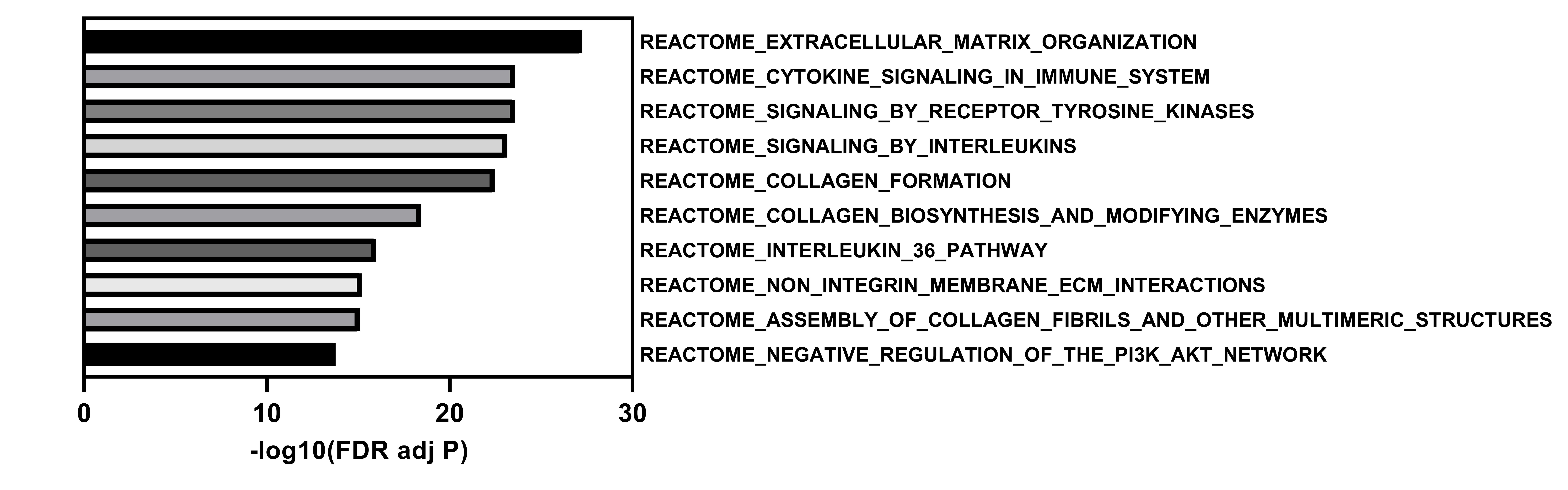 Figure. Reactome pathways which are significantly enriched among miRNA predicted targets.
Figure. Reactome pathways which are significantly enriched among miRNA predicted targets.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wu Q, Chen S, Ye F, Solus J, Bridges, Jr. S, Curtis J, Stein C, Ormseth M. Drug Response Is Associated with Changes in Specific MicroRNAs in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-response-is-associated-with-changes-in-specific-micrornas-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-response-is-associated-with-changes-in-specific-micrornas-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/
