Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Almost all protein-based biotherapeutics can induce immunogenicity, which may result in loss of efficacy and/or increased risk of adverse reactions. Despite all the efforts of protein engineering to reduce drug immunogenicity, recent assays still show unexpectedly high immunogenicity rates, even in fully human products. Pre-existing endogenous antibodies (Pre-Abs) (before first biotherapeutic administration) may be a contributing factor to these findings, leading to new challenges in assessing immunogenicity and its clinical relevance. We aim to assess if the levels of anti-drug antibodies (ADA) and drug concentrations influence response to first Tumor Necrosis Factor inhibitor (TNFi), Adalimumab (ADL).
Methods: Patients from the BioEfficacySpa study (Biomarkers identification of anti-TNF alfa agents efficacy in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) patients using a transcriptome analysis and mass spectrometry) were included. Data and blood samples (including ADA levels and serum ADL concentrations) were collected at bl (before first ADL infusion) and at w14 post-treatment with ADL. To be considered responders, patients had to achieve both ASAS 20 and ASDAS clinically important improvement responses. Association between ADA titer/drug concentrations, at both bl and/or w14, and response to TNFi was assessed through logistic regression models, adjusted for relevant confounders.
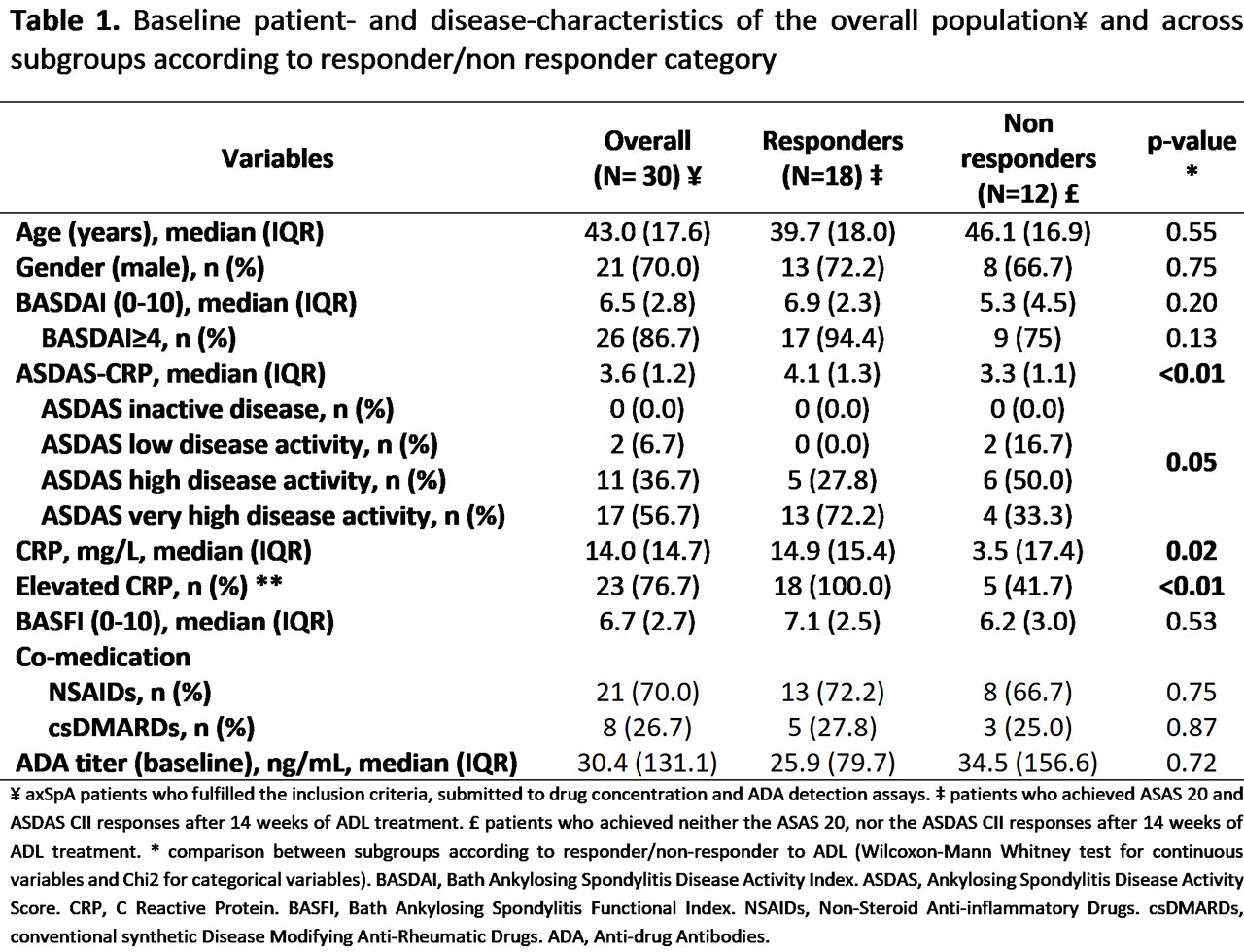
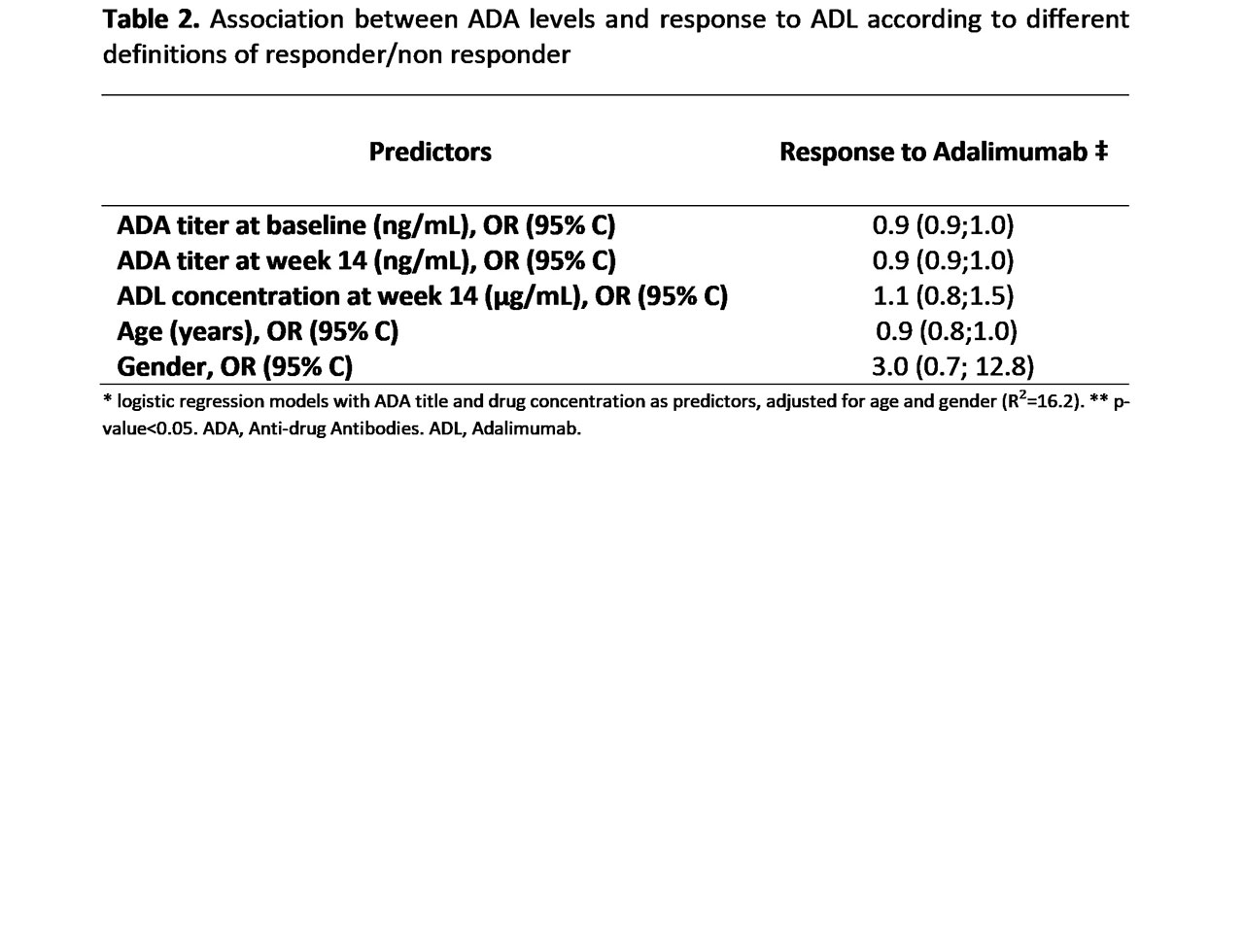
Results: In total, 30 patients were included (70% males with median age of 43 (IQR: 17.6) years at bl) (Table 1). The majority (n=18; 60%) fulfilled the predefinition of responder at w14. Anti-TNFi antibodies titer at bl was much higher than ADA titer at w14 (median ΔADA level = -45ng/mL) with only a few being of the neutralizing type (n=1; 4% vs n=3; 11.5%, at bl and w14 respectively). There were no statistically significant associations between ADA titer (at bl or w14) and drug concentrations at w14 and response to ADL (Table 2).
Conclusion: Our results show that even though assays used to detect drug concentration and ADA titer may be influenced by an individual/endogenous immune profile (previous to drug administration), response to ADL does not seem to be significantly affected by ADA titers or ADL concentration.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Marona J, Rodrigues-Manica S, Lagoas Gomes J, Lopes C, Iria I, Bernardes M, Santos H, Tavares-Costa J, Madruga-Dias J, Pinto P, Bernardo A, Maia S, Branco J, Gonçalves J, Pimentel-Santos F. Drug Concentrations and Anti-drug Antibodies Influence in Response to Adalimumab: Results from the BioEfficacySpA Clinical Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-concentrations-and-anti-drug-antibodies-influence-in-response-to-adalimumab-results-from-the-bioefficacyspa-clinical-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-concentrations-and-anti-drug-antibodies-influence-in-response-to-adalimumab-results-from-the-bioefficacyspa-clinical-trial/