Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: An unmet need remains in patients with failure and/or inadequate response (IR) to biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD-IR) and/or Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi-IR). The CD40/CD40L (CD154) costimulatory interaction is linked to inflammation and joint destruction in RA via production of autoantibodies and inflammatory mediators. KPL-404 is a humanized IgG4 antibody engineered to bind CD40 without triggering Fc effector functions.
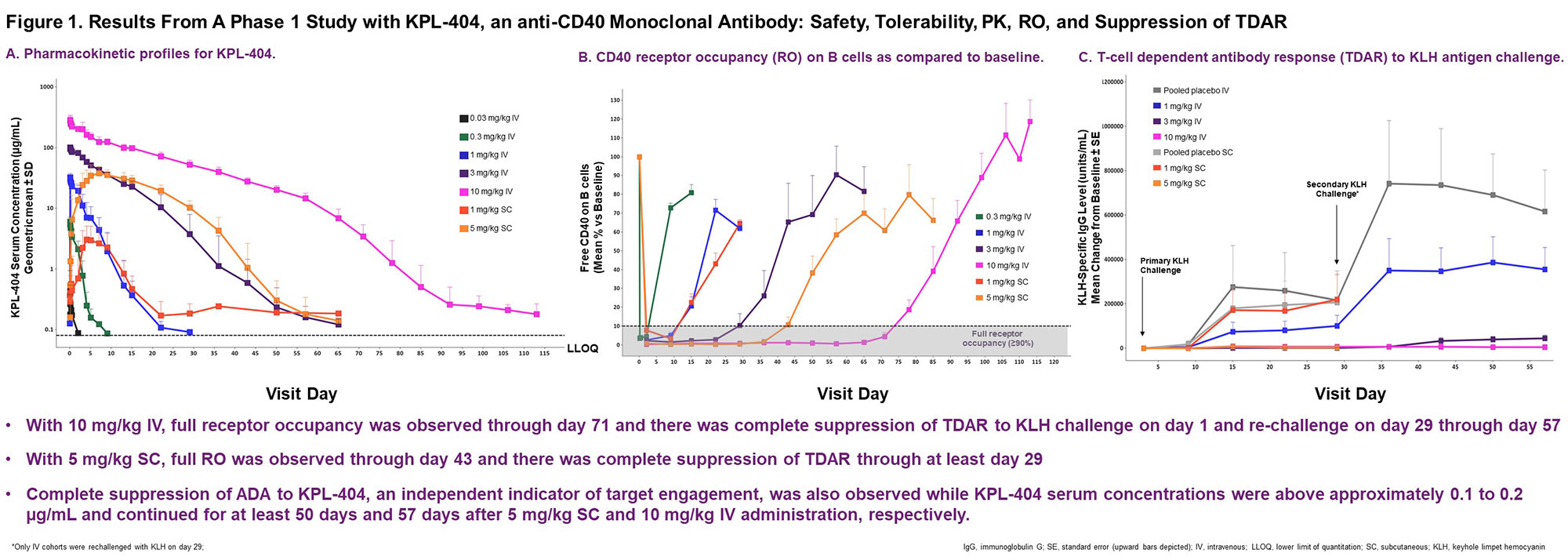
In a first-in-human Phase 1 single ascending dose study, 52 healthy volunteers received single doses of KPL-404 administered either subcutaneously (SC) or intravenously (IV) with no dose-limiting safety findings, infectious episodes, or toxicities. Pharmacodynamic assessments suggested full target engagement and dose-dependent suppression of TDAR for primary and secondary KLH challenge were achieved at pharmacologically relevant concentrations (Figure 1).
Using Phase 1 and nonclinical data, identify chronic dosing regimens anticipated to yield PK in the sub-therapeutic, therapeutic, and supra-therapeutic ranges to be utilized in a Proof of Concept Phase 2 Study.
Methods: A PK model was used to simulate multiple dosing scenarios, including: 2.5, 5, and 10 mg/kg SC qwk, q2wk, and q4wk, as well as 10 mg/kg IV q4wk. The model was used to identify optimal Phase 2 dosing schedules by generating 1000 virtual subjects using the typical parameter estimates with between-subject variability included.
Results: Following SC administration, all subjects were predicted to achieve complete ADA suppression for the full dosing interval at/above 2.5 mg/kg SC q2wk. At 2 mg/kg SC q2wk (starting dose level), simulated steady-state 8-week data predicted PK in a sub-therapeutic range for most subjects and an approximately 31- and 18-fold safety margin relative to preclinical NOAEL dose. At 5 mg/kg SC q2wk, 100% of patients were predicted to be in a therapeutic range, indicating a potential practical efficacious dose level. At 10 mg/kg SC q2wk, 100% of patients were predicted to be in the supratherapeutic range.
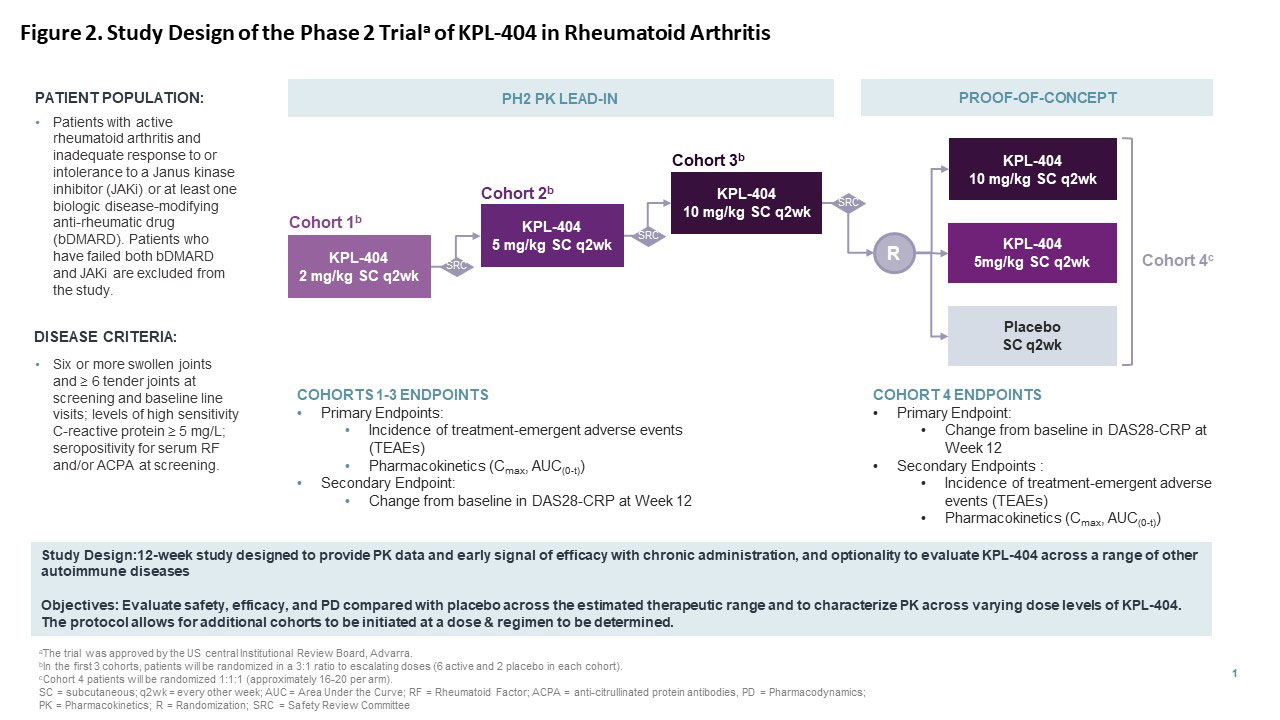
These results support a Phase 2 study design, with Multiple Ascending Dose (MAD) PK lead-in (Cohorts 1-3) and a Proof-of-Concept Cohort (Cohort 4) (Figure 2). The ongoing study will evaluate efficacy (Disease Activity of 28 joints using C-reactive protein [DAS28-CRP]), safety, PK, and pharmacodynamics (PD) of escalating dose levels of KPL-404 compared with placebo in patients with moderate to severe RA (bDMARD-IR or JAKi-IR). The study also allows the flexibility of optional cohorts including additional dosing regimens and/or subpopulations identified based on clinical response and biomarkers.
Conclusion: Inhibition of the CD40-CD154 co-stimulatory interaction holds promise for the management of a spectrum of autoimmune diseases. KPL-404 demonstrated prolonged absorption/excretion capable of suppressing TDAR for extended periods allowing for use of extended dosing intervals irrespective of IV or SC dosing. These analyses supported the design of the ongoing Phase 2 study assessing the efficacy and safety KPL-404 in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pupim L, Burmester G, Fang F, Kivitz A, Njenga M, Pitzalis C, Chatfield J, Papandrikopoulou A, Samant M, Schmitz S, Spiers M, Tessari E, Ziemniak J, Paolini J. Dose-dependent Suppression of T Cell-Dependent Antibody Response in Healthy Volunteers by KPL-404, an Anti-CD40 Monoclonal Antibody, Supports Phase 2 Study in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dose-dependent-suppression-of-t-cell-dependent-antibody-response-in-healthy-volunteers-by-kpl-404-an-anti-cd40-monoclonal-antibody-supports-phase-2-study-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dose-dependent-suppression-of-t-cell-dependent-antibody-response-in-healthy-volunteers-by-kpl-404-an-anti-cd40-monoclonal-antibody-supports-phase-2-study-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/