Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Sustained minimal disease activity (MDA) is only achieved by a small portion of PsA patients (pts). Levels of disease activity consistent with MDA may be achieved less frequently in pt-driven domains1. Here we identified PsA disease domains contributing to MDA non-achievement and associated factors using data from the Phase 3 GO-VIBRANT trial.
Methods: GO-VIBRANT included biologic-naïve pts with active PsA (≥5 swollen [SJC] & ≥5 tender joints [TJC], CRP ≥0.6 mg/dL) despite standard therapies. Pts were randomized 1:1 to intravenous golimumab (IV-GLM) 2 mg/kg at weeks (W) 0, 4, and then Q8W through W52; or IV placebo (PBO) at W0, 4, 12, and 20 followed by crossover to IV-GLM at W24. This post hoc analysis included 241 IV-GLM-treated pts. MDA requires fulfillment of ≥5/7 criteria: TJC ≤1, SJC ≤1, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) ≤1, Pt Pain ≤15mm, Pt Global Assessment (PtGA) ≤20mm, Health Assessment Questionnaire – Disability Index (HAQ-DI) ≤0.5, and ≤1 tender entheses. A trajectory of achieving each MDA criterion through W52 was built using non-responder imputation for missing values. Time to achieving each criterion was assessed with Kaplan-Meier analysis; to account for differences in scales and criteria strictness, a secondary analysis utilized scores normalized to the SJC (0-66) scale and set targets to ≤1. MDA predictors were assessed with multivariate regression for time to achievement (Cox proportional hazards) and W52 achievement (logistic). Presence of a proxy for central pain sensitization/fibromyalgia (pFM) was defined as TJC minus SJC ≥72.
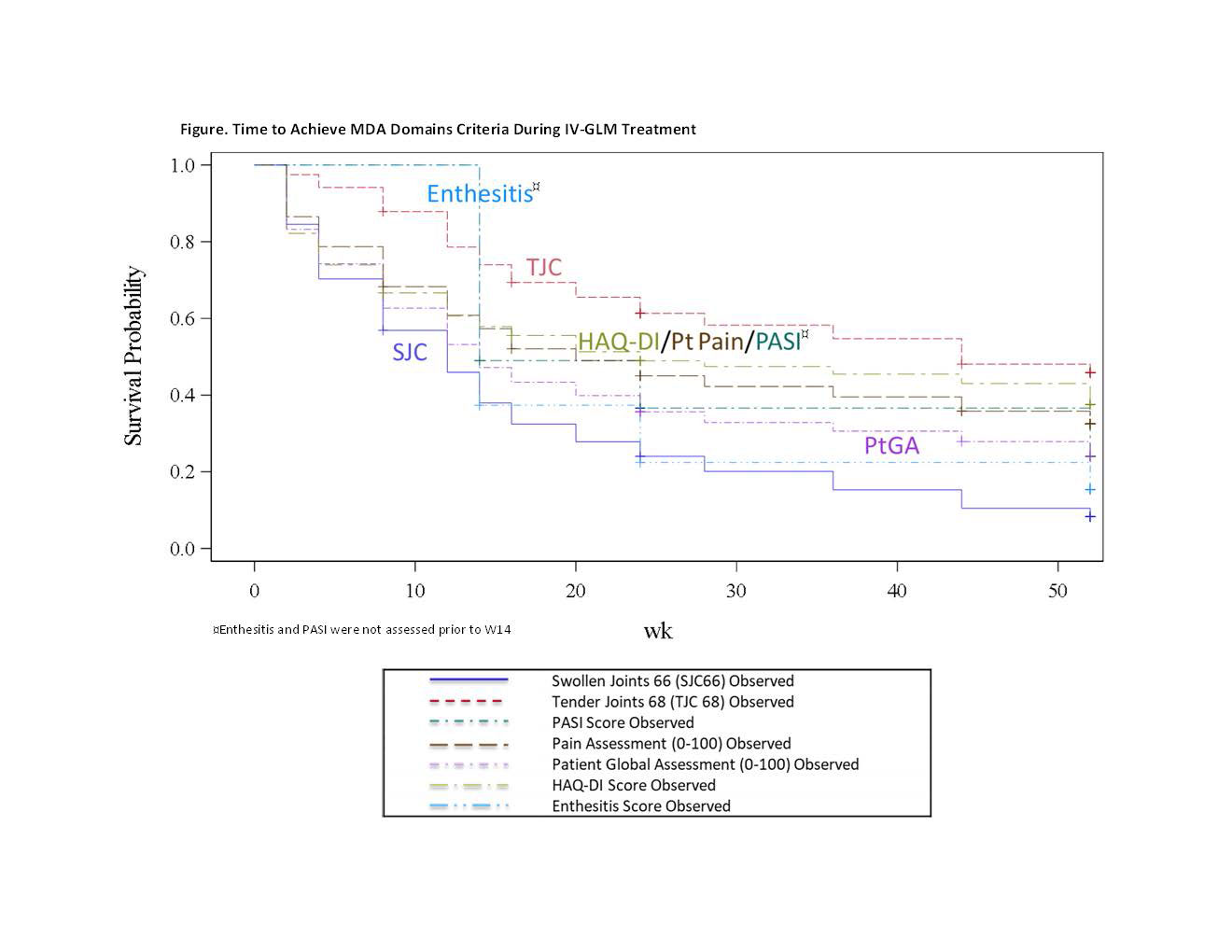
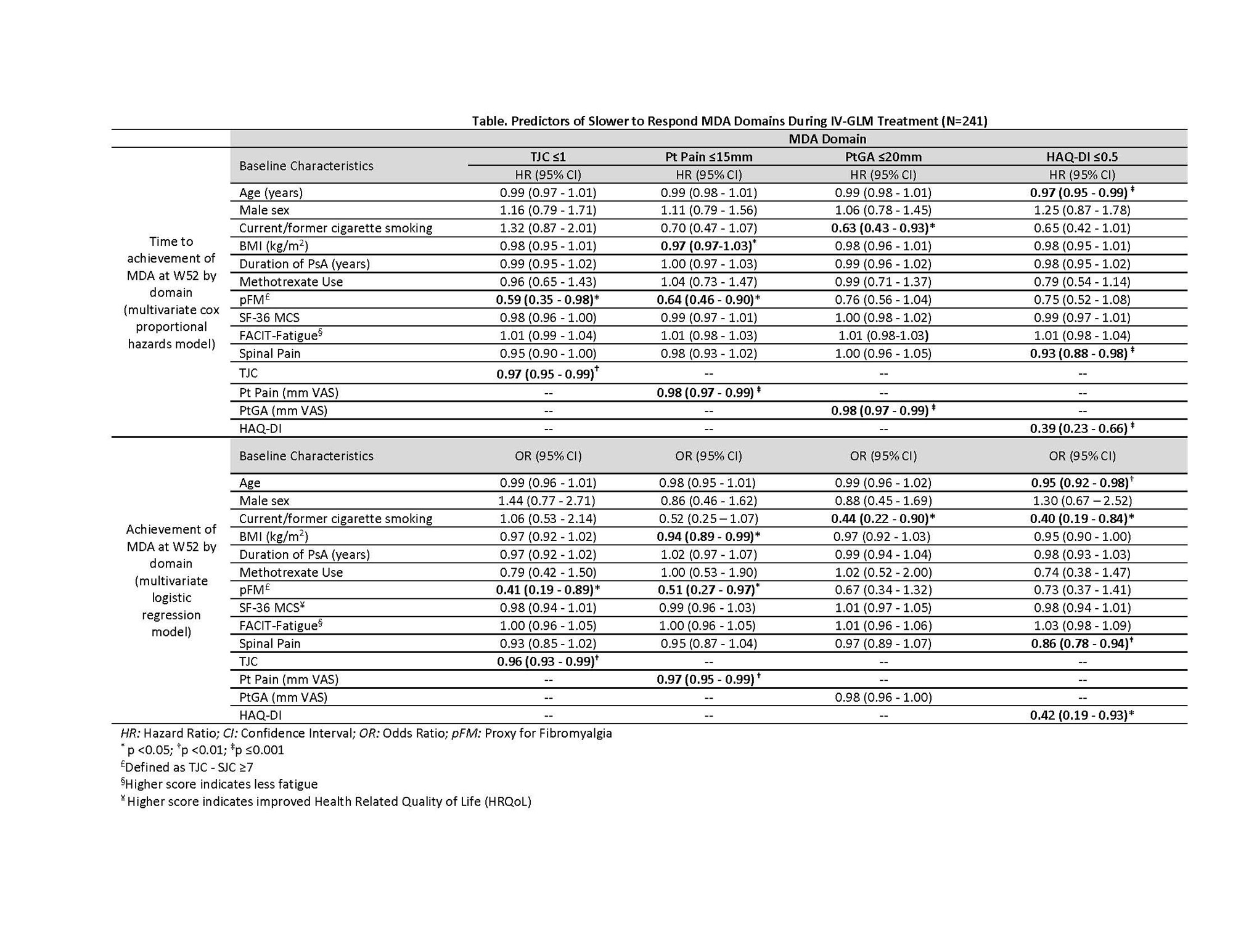
Results: IV-GLM treatment was associated with improvement in all MDA domains, with W24 & W52 response rates of: SJC (53.5% & 61.8%), TJC (22.8% & 32.4%), PASI (53.6% & 59.7%), Pt Pain (37.3% & 43.6%), PtGA (44.8% & 45.2%), HAQ-DI (37.8% & 44.9%), entheseal points (68.4% & 64.6%). Time to achieve minimal SJC and enthesitis was significantly faster than TJC, HAQ-DI, and Pt Pain for native-scale scores (Fig). When normalized, TJC, HAQ-DI, and Pt Pain, as well as PtGA, were slower to respond. Higher baseline (BL) TJC and pFM were significant predictors of longer time to achieve TJC ≤1 and of not meeting TJC ≤1 at W52 (Table). Significant BL predictors of longer time to achieve HAQ-DI ≤0.5 were higher age, HAQ-DI score, and spinal pain; these as well as smoking were associated with lower odds of HAQ-DI ≤0.5 at W52. Worse BL pain, pFM, and higher BMI were significant predictors of longer time to achieve Pt Pain ≤15 mm and non-achievement at W52. Worse BL PtGA (only for time to achievement) and smoking status were negative predictors of PtGA ≤20mm.
Conclusion: IV-GLM provided improvement in each MDA domain through W52. Although IV-GLM was effective across most variables assessed, BL domain score, pFM presence, older age, and modifiable lifestyle factors (smoking, higher BMI) were negative determinants of MDA in the slower to respond pt-driven domains. Addressing these modifiable factors may optimize MDA achievement in PsA.
References:
1. Rahman et al. BMJ Open 2017; 7 (8): e016619.
2. Pollard et al. Rheumatology. 2010 May;49(5):924-8.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kavanaugh A, Lam G, Tam L, Shiff N, Lee Y, Bravo Perdomo A, Shawi M, Hsia E, Rampakakis E, Toro Gutiérrez C. Domains Contributing to Minimal Disease Activity Non-Achievement in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Receiving Golimumab: Post Hoc Analysis of a Phase 3, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/domains-contributing-to-minimal-disease-activity-non-achievement-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-receiving-golimumab-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/domains-contributing-to-minimal-disease-activity-non-achievement-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-receiving-golimumab-post-hoc-analysis-of-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled/