Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Several studies have shown an negative association between smoking status and psoriatic arthritis (PsA) clinical outcomes1,2. The German non-interventional study AQUILA provides real-world data on the influence of smoking on therapeutic effectiveness and safety issues under secukinumab (SEC), a fully human monoclonal antibody that selectively inhibits interleukin-17A.
The aim of this interim analysis is to describe selected baseline (BL) demographics, to evaluate SEC effectiveness on disease activity and depressive mood and to report the safety profile depending on smoking status of PsA patients.
Methods: AQUILA is an ongoing, multi-center study including up to 2700 patients with active PsA or ankylosing spondylitis. Patients were observed from BL up to week (w) 52. Real-world data was assessed prospectively and analyzed as observed. In addition to the assessment of C-reactive protein (CRP), data was collected on patient´s disease activity (tender/swollen joint counts, TJC/SJC), skin disease activity (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, PASI) and depressive mood (Beck´s Depression Inventory version II, BDI-II). For calculation of the proportion of patients who experienced (serious) adverse events ((S)AEs), all PsA patients were included who received at least one dose of SEC irrespective of further documentation of any study visit. This interim analysis focuses on subgroups non-smoker (NS) and smoker (S).
Results: At BL, 641 PsA patients were included: 49.8% (n=319) non-smokers (NS) and 24.3% (n=156) smokers (S). 17.5% (n=112) were ex-smoker and 8.4% (n=54) of unknown smoking status. In both, NS and S, the proportion of women was higher (58.0% in NS and 67.3% in S). NS were slightly older than S (mean age: 53.8/49.7 years). There were no significant differences between NS and S in mean CRP within the 52 weeks (Fig. 1A). Both TJC and SJC improved over time and were similar between NS and S (Fig. 1B). Although mean absolute PASI value was worse in S at BL, a similar temporal improvement was seen in both groups (NS: 7.0 at BL to 1.0 at w52; S: 9.2 at BL to 1.0 at w52). BDI-II scores decreased in both groups with overall higher values in S (NS: 10.9 at BL to 9.1 at w52; S: 12.8 at BL and 10.8 at w52). Regarding the occurrence of AEs and SAEs with or without suspected relationship to SEC, NS had percentagewise less events than S (Table 1). In addition, percentage of PsA patients who discontinued SEC treatment due to an AE was lower for NS compared to S.
Conclusion: In a real-world setting, SEC improved disease activity and depressive mood of PsA patients with no obvious differences between NS and S. Overall, this interim analysis shows that SEC is an effective and reliable treatment, irrespective of the PsA patients’ smoking status. Further progress of the AQUILA study as well as long-term data from other real-world observational studies with SEC, such as SERENA, will reveal whether this trend will continue.
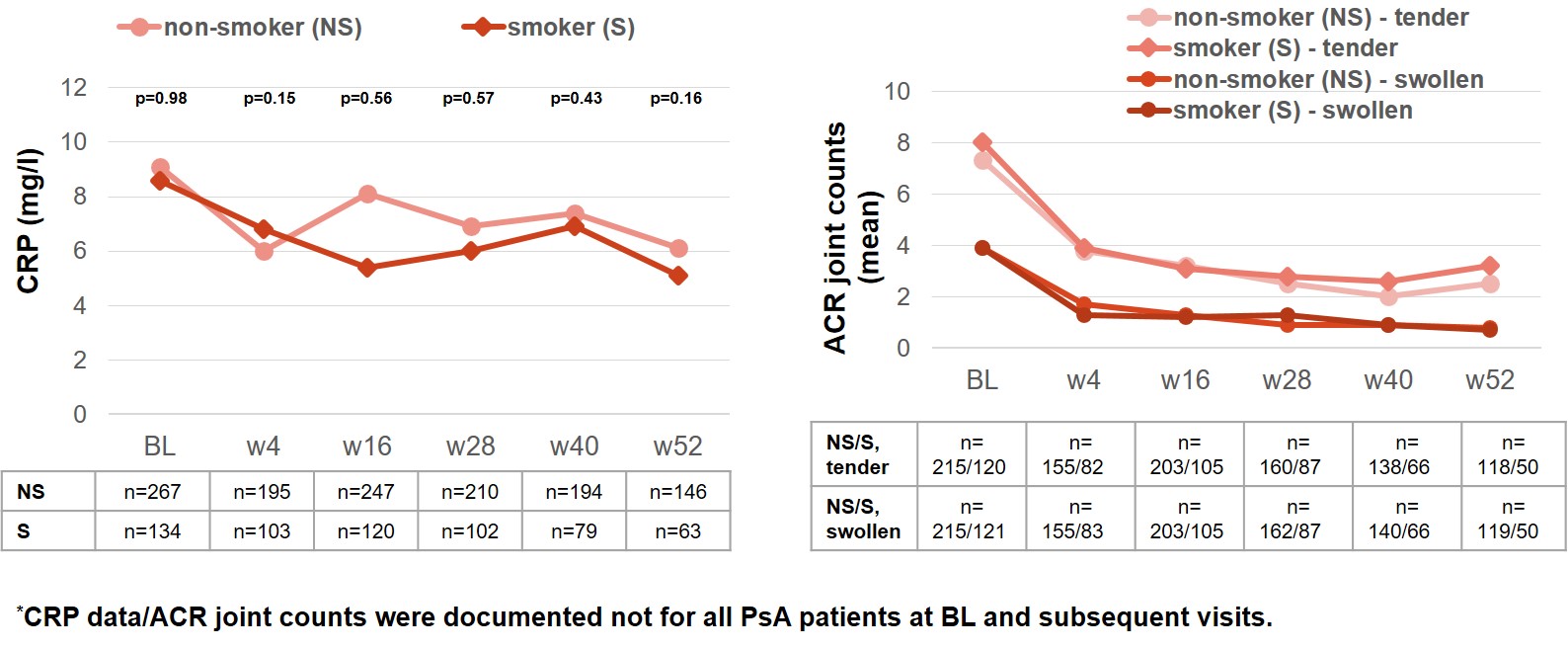 Figure 1: Disease activity in PsA patients treated with SEC depending on the smoking status*
Figure 1: Disease activity in PsA patients treated with SEC depending on the smoking status*
 Table 1: Overview of AEs (and SAEs) under SEC treatment depending on smoking status in PsA patients
Table 1: Overview of AEs (and SAEs) under SEC treatment depending on smoking status in PsA patients
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Riechers E, Kiltz U, Brandt-Jürgens J, Kästner P, Peterlik D, Tony H. Does Smoking Affect Secukinumab Treatment Outcomes and Safety in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis? – Real World Data from German Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-smoking-affect-secukinumab-treatment-outcomes-and-safety-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-real-world-data-from-german-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-smoking-affect-secukinumab-treatment-outcomes-and-safety-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-real-world-data-from-german-observational-study/
