Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tumour necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) are efficacious in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), but still some patients switch to a different TNFi because of adverse effects (AE) or lack of effect (LOE). The EuroSpA Collaboration has previously demonstrated a 1-year retention rate of 79% and 6 months LUNDEX adjusted BASDAI< 4 of 59%1 in patients initiating the first TNFi treatment. Little is known about the effectiveness of switching to a second and third TNFi in patients with axSpA.
We aim to investigate retention and response rates at 6, 12 and 24 months in patients with axSpA initiating the 2nd and 3rd TNFi in clinical practice across Europe. Secondly, to investigate whether the outcomes were associated with the reason for withdrawal (AE or LOE) from the previous treatment.
Methods: Prospectively collected data on axSpA patients in routine care from 12 European registries were pooled. Kaplan-Meier estimation was used to investigate TNFi retention rates. LUNDEX adjusted2 response rates were calculated for BASDAI< 4 and ASDAS inactive disease (ASDAS< 1.3). Group comparisons were performed by Chi-square test.
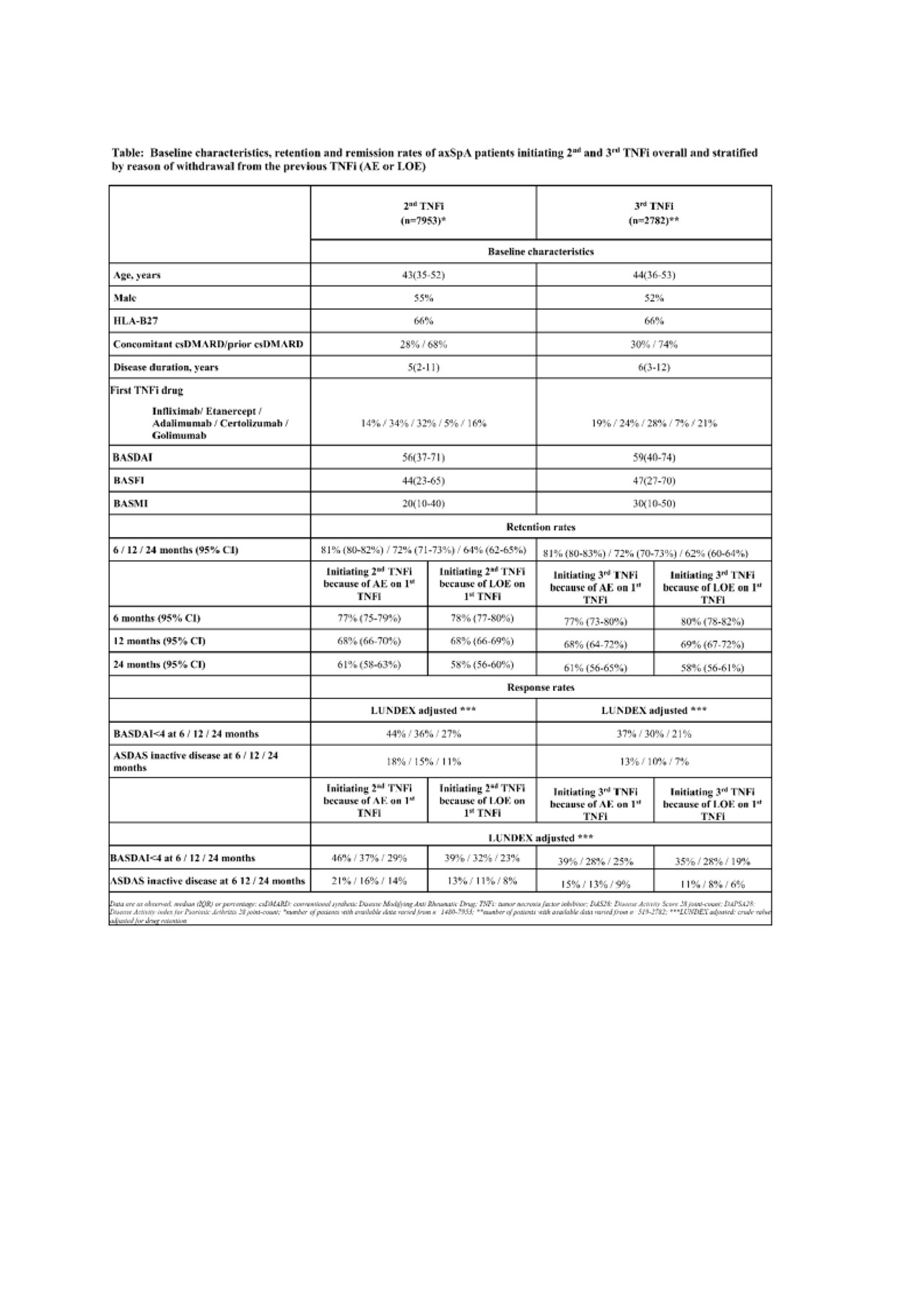
Results: A total of 7953 patients initiating their 2nd TNFi and 2782 patients initiating 3rd TNFi were included. Baseline characteristics are shown in the Table.
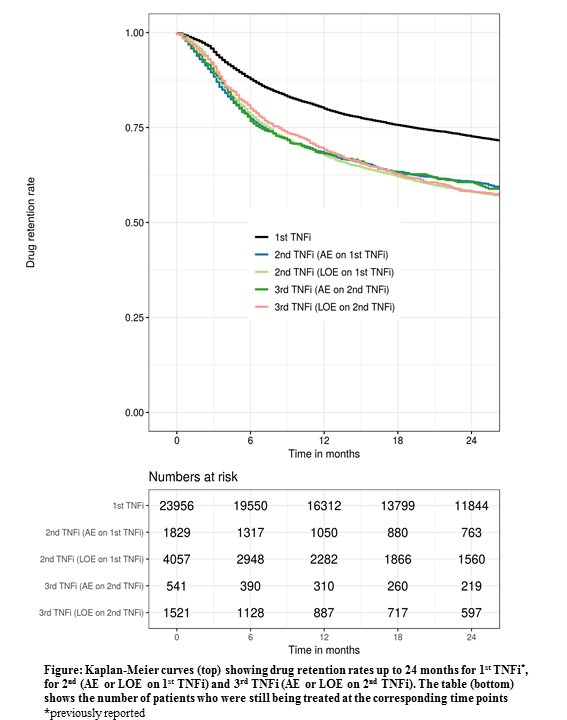
The overall retention rates for both 2nd and 3rd TNFi at 12 months were 72 % (Figure). Corresponding retention rates for the individual registries ranged from 52-90% and 54-89%, respectively. In both patients who stopped 1st TNFi due to AE or LOE, 12-month retention rate for the 2nd TNFi treatment was 68 %. In patients who stopped the 2nd TNFi due to AE or LOE, 12-month retention rates for the 3rd TNFi treatment were 68 % and 69%, respectively.
For the 2nd and 3rd TNFi, 6 months LUNDEX adjusted BASDAI< 4 were 44% and 37% (p< 0.001), respectively, and for ASDAS inactive disease 18% and 13% (p=0.003) (Table).
Conclusion: Data from 12 European countries demonstrated decreasing response rates with increasing number of previous TNFi, although with only minor difference between 2nd and 3rd. Patients who had withdrawn from the previous TNFi due to LOE had retention rates and remission rates similar to those who had withdrawn due to AE.
Acknowledgement
Novartis Pharma AG and IQVIA for supporting the EuroSpA collaboration.
References
1 Brahe et al. ACR 2018
2Arthritis Rheum, 2006, 54(2), p:600-6
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Midtbøll Ørnbjerg L, Brahe C, Loft A, Askling J, Ciurea A, Mann H, Akar S, Kristianslund E, Nordström D, Santos M, Codreanu C, Pombo-Suarez M, Rotar Z, Gudbjornsson B, DiGuiseppe D, Nissen M, Pavelka K, Senel S, Sexton J, Eklund K, Barcelos A, IONESCU R, Sánchez-Piedra C, Tomsic M, Geirsson A, van der Horst-Bruinsma I, Macfarlane G, Iannone F, Michelsen B, Hyldstrup L, Krogh N, Lund Hetland M, Østergaard M. Does Retention and Remission Rates to 2nd and 3rd TNF Inhibitors in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis Depend on the Reason from Withdrawal to the Previous Treatment? – Real World Data from 12 European Countries in the EuroSpA Research Collaboration [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-retention-and-remission-rates-to-2nd-and-3rd-tnf-inhibitors-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-depend-on-the-reason-from-withdrawal-to-the-previous-treatment-real-world-data-from/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-retention-and-remission-rates-to-2nd-and-3rd-tnf-inhibitors-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-depend-on-the-reason-from-withdrawal-to-the-previous-treatment-real-world-data-from/