Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0283–0307) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Anti-SSa and Ro52 are commonly present in IIM. We previously reported an association of a more severe early course of IIM-ILD with positive Ro52. The aim of this study was to evaluate if presence of anti-SSa and/or Ro52 is associated with more severe radiological and functional evolution of IIM-ILD over time.
Methods: This is a longitudinal analysis of the Northwell Myositis cohort. All patients met 2017 EULAR/ACR IIM classification criteria. ILD diagnosis was validated by manual chart review. Three groups were analyzed: anti-SSa /Ro52 double positive (DP), anti-SSa/ or Ro52 single positive (SP), and both anti-SSa and Ro52 negative (DN). HRCT was scored as improved, stable or worsened on the last available scan compared to baseline. Serial FVC, FEV1, and DLCO comparisons from baseline to most recent PFT were performed, percent change with annualized relative percent change were calculated. Improvement or worsening on PFTs was defined as an increase or decrease of > 10% in 1 PFT parameter with no > 5% decrease or increase in other parameters respectively. Descriptive statistics, T-tests, ANOVA tests, Fisher’s exact and Spearman’s correlation tests were used for statistical analysis.
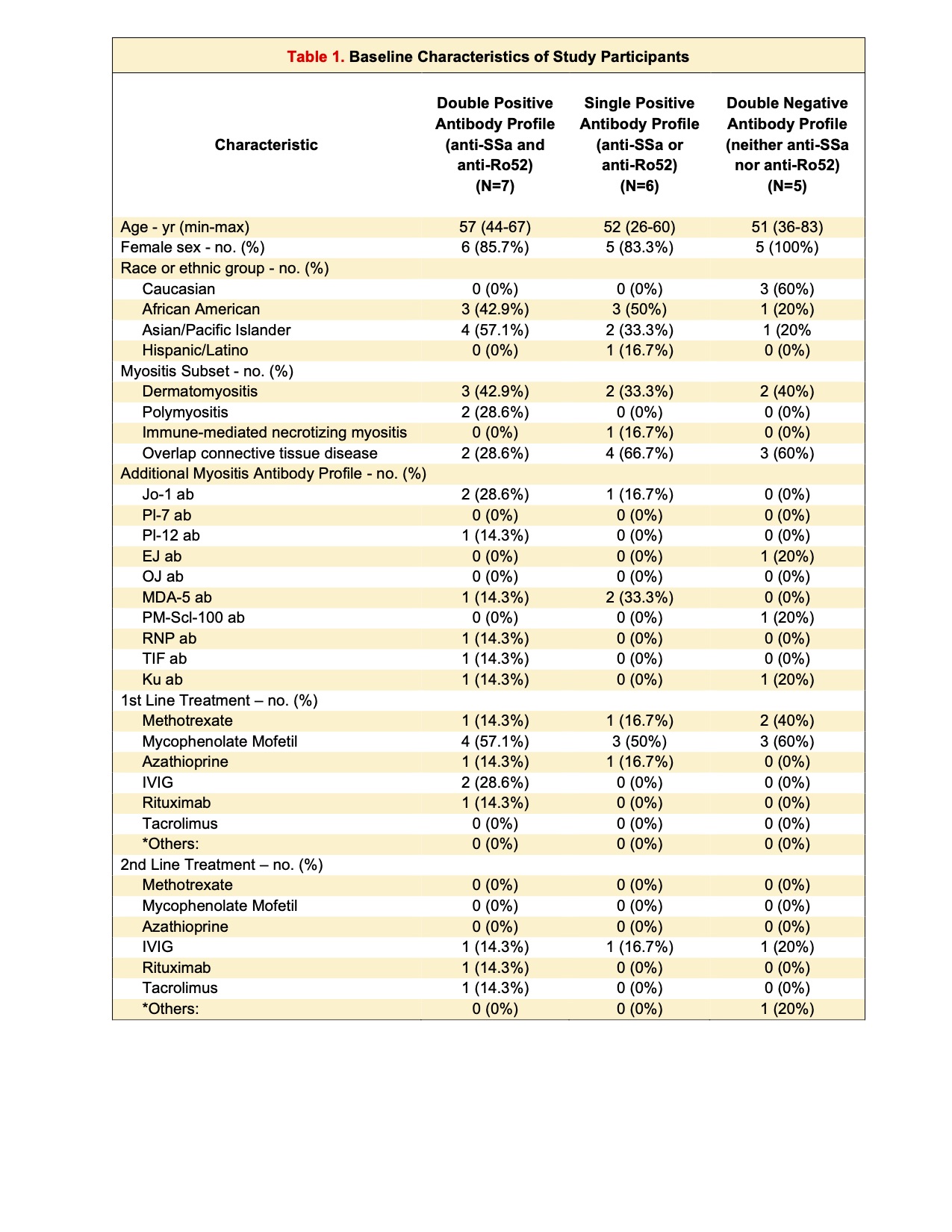
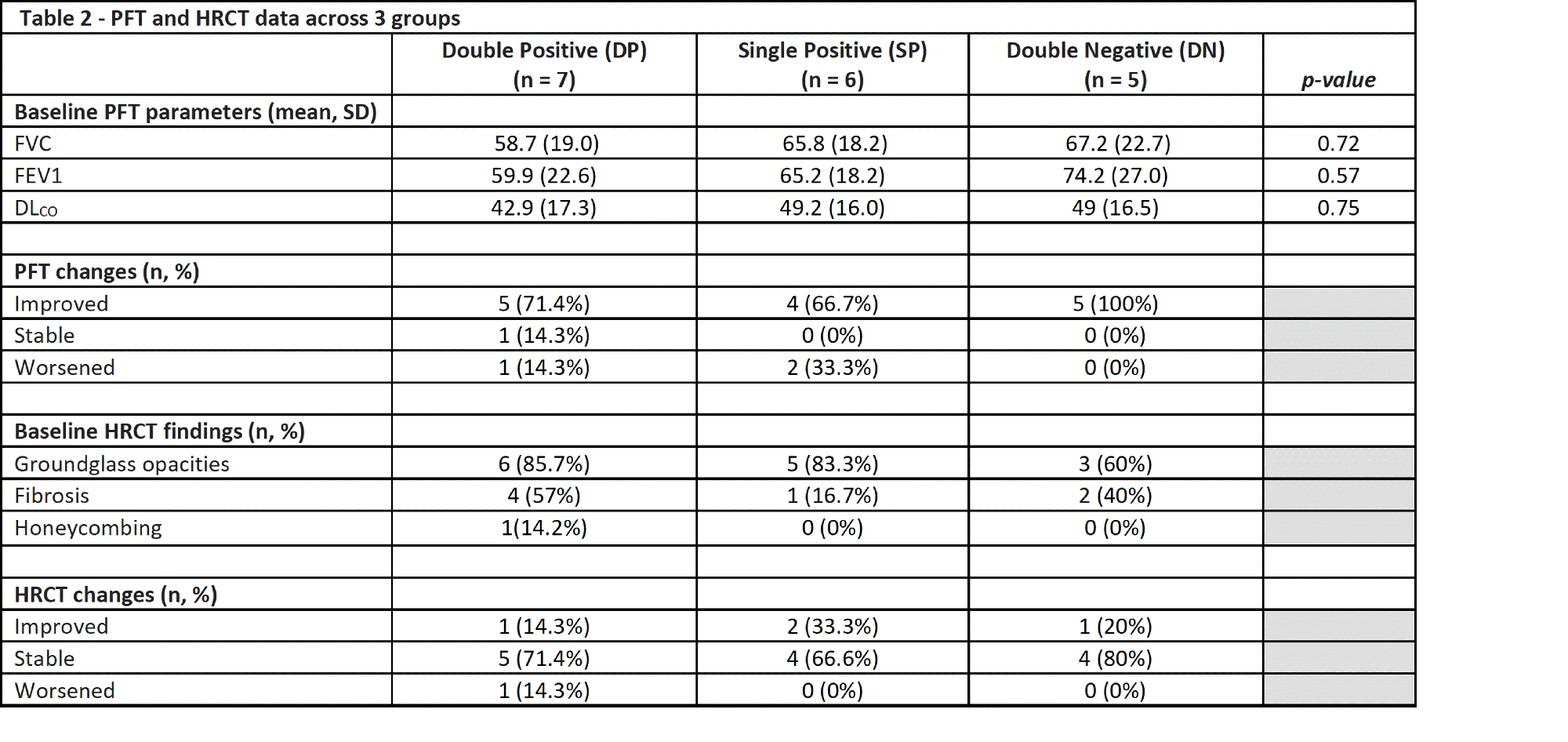
Results: Baseline demographics and clinical characteristics are reported in Table 1. Eighteen patients met inclusion criteria and had > 2 serial HRCT/ PFT of which 7/18 (38.9 %) were DP, 6/18 (33.3%) SP and 5/18 (27.8%) DN. Median follow up was 5 years (range: 1-13).At baseline, PFTs were similar between the groups (Table 2). On baseline HRCT, most observed pattern across all groups was groundglass opacities followed by fibrosis (Table 2).
Honeycombing was reported in 14.2 % of DP but not seen in SP or DN groups.
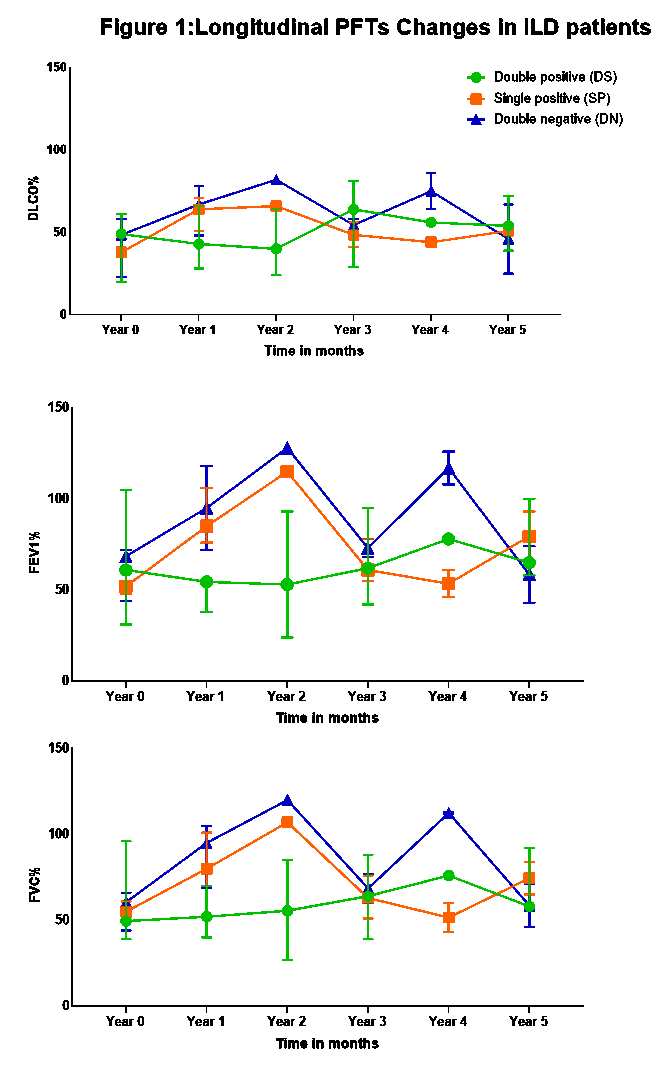
HRCT showed improvement in four patients (1 DP, 2 SP and 1 DN), but mostly recorded stability (DP: 71.4%,5/7and SP: 66.6%, 4/6). Nine patients (DP: 71.4%,5/7 and SP: 66.7%, 4/6) improved by PFT criteria while no DN patients improved (p=0.28). Four patients worsened: one by HRCT and 3 by PFT, all were seropositive (2 from SP and 2 from DP), no patients in DN group worsened. FVC or FEV 1 did not improve in seropositive groups, but in DN mean FEV1 improved from baseline 74.2 % to 90.4% (p= 0.04). Mean annualized % change of PFT was not different between groups. Overall DLCO improved in DN group (49% to 63%, p=0.03) and no improvement was seen in DP or SP groups, but weak improvement trend was observed when positive groups were combined (p=0.05). DP group had overall stability across all PFT parameters over the 5 years follow up. In contrast DN and SP groups appeared to have a modest improvement during the first 2 years that was lost by the 5th year follow up. At year 5 the change of all PFT parameters from baseline was not significant in all 3 groups (Figure 1).
Conclusion: While we previously reported the patients with diagnosis of IIM associated ILD with Ro52 positive antibodies may have worse outcomes, this study demonstrates that after initial decline of PFT during first 2 years, pulmonary function stabilizes over time irrespective of serological cluster. At the same time patients with negative of SSA/ Ro52 antibodies are more likely to improve over the years as determined by FEV1 and DLCO. HRCT was not sensitive to changes and mostly reported stability.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Narain S, Hu C, Liu M, Shargani K, Marder G. Does Presence of Anti-SSa and Ro52 Influence the Progression of Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies (IIM) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-presence-of-anti-ssa-and-ro52-influence-the-progression-of-interstitial-lung-disease-ild-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-iim/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-presence-of-anti-ssa-and-ro52-influence-the-progression-of-interstitial-lung-disease-ild-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies-iim/