Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Background: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a frequent complication in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) where it represents the most common extra-articular involvement (with a prevalence of about 10-60%) and the second cause of mortality (after cardiovascular diseases). Spondyloarthritides (SpA) are chronic arthritides that share with RA both a similar disease burden and similar therapeutical approaches. ILD evaluation is challenging, given the low sensitivity of X-ray and pulmonary function tests, and radiation linked to repetitive HRCT. Lung Ultrasound (LUS) has shown potential in the evaluation of ILD in autoimmune diseases. The aim of this study was to assess the prevalence of ILD in a cohort of SpA patients (pts) using LUS with respect to healthy controls (HC).
Methods: Consecutive SpA out-pts were examined by LUS, applying the definition for pleural line irregularity (PLI) recently provided by the OMERACT taskforce for LUS in systemic sclerosis (1). Seventy-one intercostal spaces were studied (14 in the anterior chest, 27 lateral and 30 posterior) in all the pts/HC using an Esaote MyLab25 Gold US machine with a linear 7.5-10 MHz probe. The scoring system by Pinal-Fernandez et al (2) was applied and a total pleural score was calculated. Each patient answered to Italian-validated PROs on respiratory function (Leicester and Saint-George), global health (SF-36) and dyspnea (mMRC scale). Clinical data on disease-duration, disease-onset, disease-activity (at the moment of the examination) and MTX/biologics treatment were collected from the medical records.
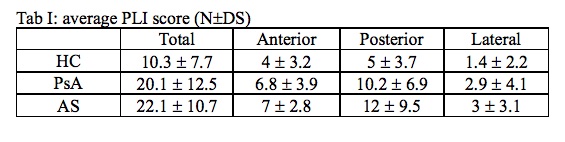
Results: Fifty-six SpA pts (35 psoriatic arthritis -PsA- and 21 ankylosing spondylitis -AS-) and 56 HC were studied. No significant differences were demonstrated between groups (SpA vs HC and PsA vs AS) for age, sex, BMI and smoking habits. The total pleural score was significantly higher in SpA pts than in HC (20.9+-11.8 vs 10.3+-7.7; p< 0.001). A positive correlation was found between total PLI score and PLI score from anterior, posterior and lateral chest. The posterior part of the chest showed a higher PLI score than the anterior and lateral one (with the latter resulting to be significantly lower than the posterior PLI score). Higher differences in the PLI average value between SpA pts and HC were registered for posterior and anterior part of the chest. No differences were found between PsA and AS (with a not statistically significant difference in the posterior PLI score, which was slightly higher in AS pts) (Tab.I).
Conclusion: LUS examination shows a higher amount of PLI in SpA with respect to HC. References: 1- Delle Sedie A et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78(Suppl 2):A834 2- Pinal-Fernandez I et al. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2015;33(4 Suppl 91):S136-41
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Delle Sedie A, Calabresi E, Romagnoli I, Carli L, Mosca M. Does Interstitial Lung Disease Represent a Real Comorbidity in Spondyloarthritis Patients? Results from an Ultrasound, Monocentric, Pilot Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-interstitial-lung-disease-represent-a-real-comorbidity-in-spondyloarthritis-patients-results-from-an-ultrasound-monocentric-pilot-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-interstitial-lung-disease-represent-a-real-comorbidity-in-spondyloarthritis-patients-results-from-an-ultrasound-monocentric-pilot-study/