Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Clinical Manifestations
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Disease activity, damage and quality of life (QOL) are core outcomes in Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). ER visits and hospital admissions (non-routine health care utilization, HCU) can be surrogates for higher disease related morbidity. Quality of care (QOC) measured by validated quality measures (QM) is associated with decreased accrual of damage in SLE. We aimed to study the association between high QOC and QOL and non-routine HCU in SLE.
Methods: Data was obtained from 814 participants from Lupus Outcomes Study Sample (LOS), a large observational cohort of individuals with ACR criteria confirmed SLE at University of California, San Francisco. Data on socio-demographics, disease status, medications and healthcare variables were collected through annual interviews beginning in 2003. QOC was available on self-report of 13 QMs. Baseline QOC for this study was measured in Year 10 interviews and follow up QOL and non-routine HCU in Years 11 and 12. We considered a performance on QMs of ≥67% (top quartile) as high QOC. QOL was measured by the Short Form (SF)-36 (Physician Component Summary PCS, mental component summary MCS score). Patient-reported disease activity and damage were measured with the Systemic Lupus Activity Questionnaire (SLAQ) and Brief Index of Lupus Damage (BILD). Chi square and T tests identified co-variates of high QOC at baseline. Univariate and multivariate regression analyses evaluated high QOC at baseline as predictor of minimal clinically important difference (MCID) improvements in SF-36 summary scores, ER visits and hospitalizations at follow up.
Results: Mean age was 53 years, 93% were women. Income below poverty and use of steroids were inversely associated with high QOC while presence of diabetes, lupus nephritis, fibromyalgia, hydroxychloroquine use, a primary care provider, and higher disease activity were directly associated with high QOC. High QOC was associated with worse QOL at baseline (PCS). High QOC at baseline was predictive of MCID based improvements in SF-36 PCS and MCS, and higher non-routine HCU (ER visits and Hospitalizations) at follow up on univariate analyses (Table 1). However, after adjusting for baseline covariates (income below poverty line, disease activity, damage, quality of life, and fibromyalgia), high QOC did not remain an independent predictor of improvement in QOL or non-routine HCU.
Conclusion: High QOC was predictive of subsequent clinically meaningful improvements in QOL. However high QOC did not remain an independent predictor of subsequent QOL or non-routine HCU on adjusting for other baseline covariates, suggesting that the effects may be mediated through one or more of the covariates (such as disease activity).
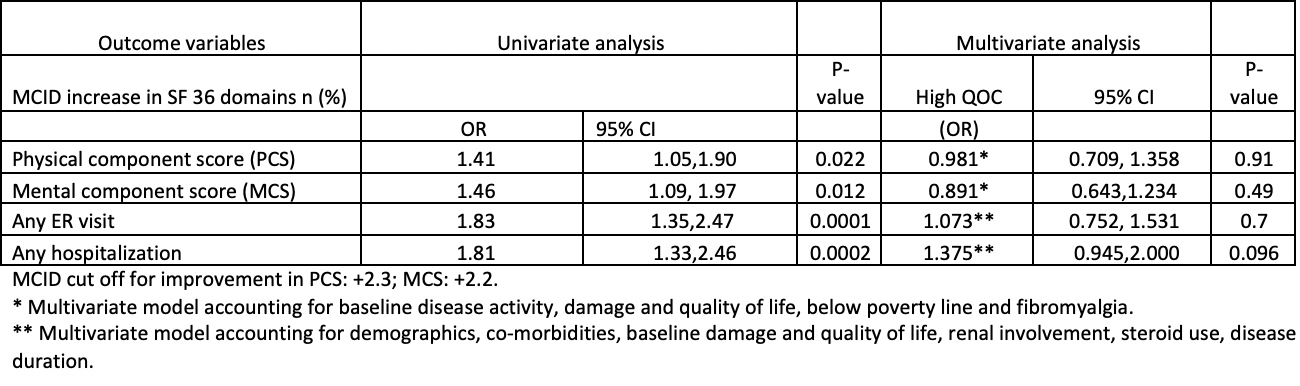 Table 1 Relationship between high QOC (at baseline) and (MCID) increase in QOL and non-routine HCU at follow up in Lupus Outcomes Study sample
Table 1 Relationship between high QOC (at baseline) and (MCID) increase in QOL and non-routine HCU at follow up in Lupus Outcomes Study sample
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Arora S, Katz P, Yazdany J, Block J, Yelin E, Jolly M. Does Higher Quality of Care in SLE Improve Quality of Life? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-higher-quality-of-care-in-sle-improve-quality-of-life/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/does-higher-quality-of-care-in-sle-improve-quality-of-life/
