Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Smoking and obesity are common in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and can lead to higher disease activity and poorer response to treatment with Tumor Necrosis Factor inhibitors (TNFi). Few studies have investigated the impact of these factors on secukinumab (an interleukin 17A inhibitor, IL-17Ai) treatment outcomes. In this study, we investigated secukinumab treatment outcomes in routine care patients with PsA and their association with smoking status and Body Mass Index (BMI) class.
Methods: Patients with PsA, as diagnosed by their treating physician, initiating secukinumab between 2015 and 2020 with available data on smoking status and BMI were identified in eight European registries participating in the European Spondyloarthritis (EuroSpA) research collaboration. Patients were stratified according to smoking status (never, former, current) and BMI class (normal [18.5 kg/m2 ≤ BMI < 25 kg/m2], overweight [25 ≤ BMI < 30], obese [BMI ≥30]) at treatment start (baseline). The 12-month secukinumab retention rates were estimated with Kaplan-Meier curves and compared with Cox regression across smoking status and BMI class, respectively. The proportion of patients achieving Disease Activity index for Psoriatic Arthritis in 28 joints (DAPSA28) low disease activity (LDA) after 6 months of treatment was calculated and compared with logistic regression. All models were adjusted for baseline age, sex, country’s gross domestic product, time since diagnosis, line of treatment with biologic/targeted disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and BMI/smoking status depending on stratification. Missing baseline covariates and DAPSA28 at 6 months were imputed using multiple imputations with chained equations.
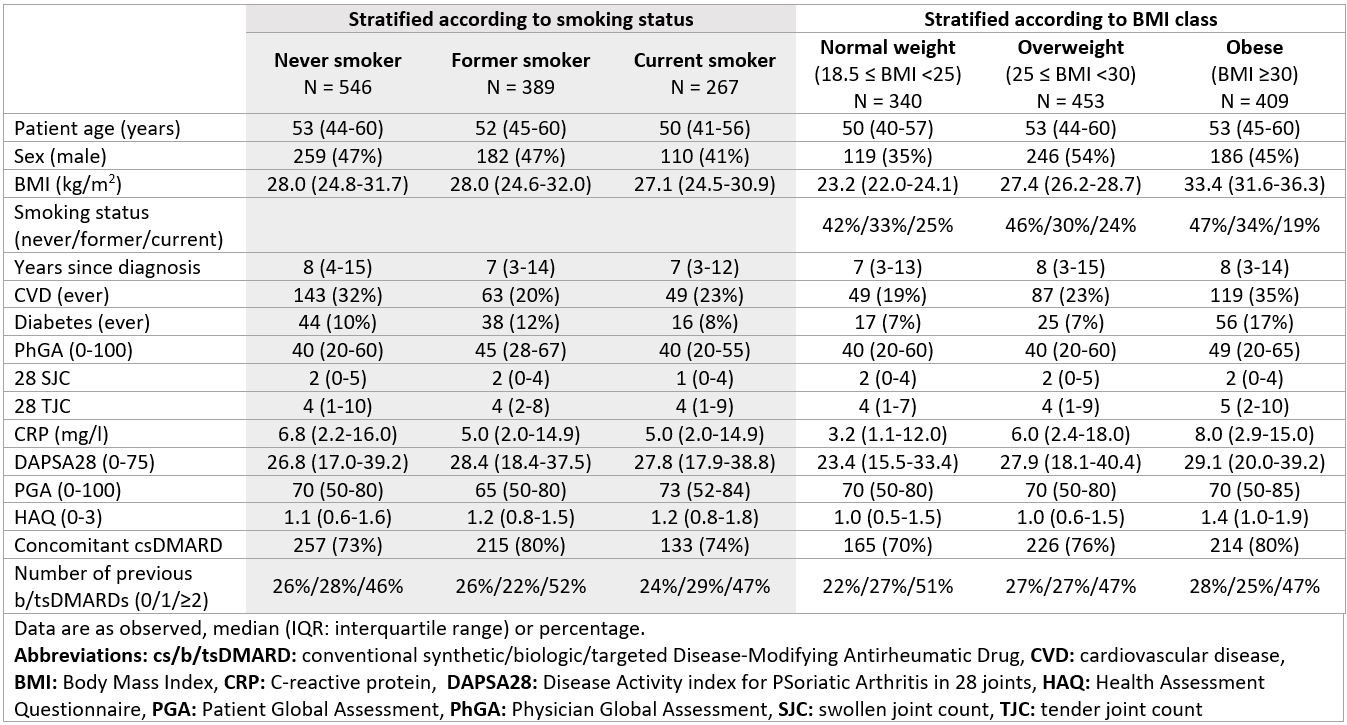
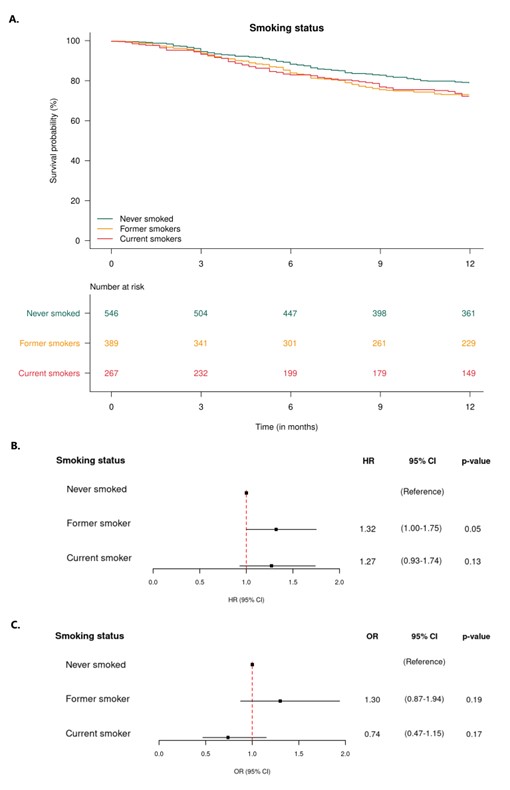
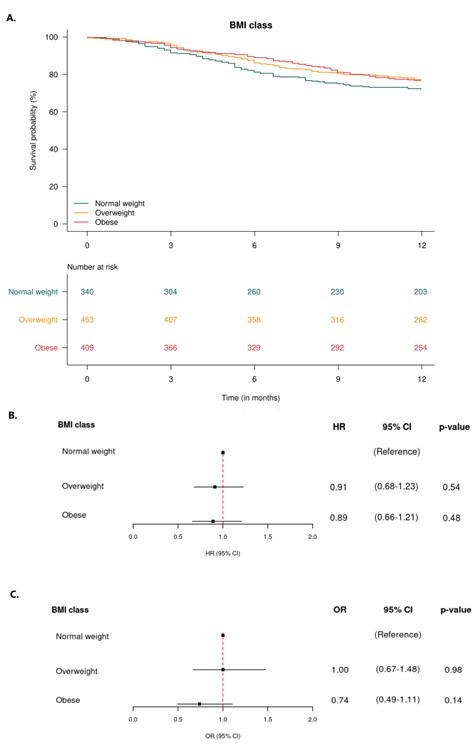
Results: A total of 1,202 patients were included, the baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. The 12-month secukinumab retention rates were 79%/73%/72% in never/former/current smokers and 72%/77%/77% in normal-weight/overweight/obese patients, respectively, Figures 1A and 2A. Former and current smokers had a ≈30% increased risk of treatment withdrawal compared with never smokers, while overweight and obese patients had a ≈10% decreased risk compared to normal weight, Figures 1B and 2B. However, no significant differences in hazard ratios were found. The 6-month LDA rates were 56%/64%/51% in never/former/current smokers and 60%/60%/51% in normal-weight/overweight/obese patients, respectively. The odds of achieving DAPSA28 LDA after 6 months were ≈30% higher in former smokers and ≈25% lower in current smokers compared with never smokers, while the odds were equal in overweight and ≈25% lower in obese patients compared with normal-weight. However, no significant differences were found in the odds ratios, Figures 1C and 2C.
Conclusion: In PsA, former and current smokers appeared to have approximately 30% increased risk of withdrawing from secukinumab treatment within 12 months compared with never smokers, whereas, we found no evidence of an impact of BMI class. Neither smoking status nor BMI class were associated with the odds of achieving DAPSA28 LDA after six months. Our findings suggest that smoking impacts the retention of IL-17Ai, similar to what has been demonstrated for TNFi.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ahmadzay Z, Georgiadis S, Ostergaard M, Glintborg B, Møller-Bisgaard S, Pons M, Heberg J, Christiansen S, Rasmussen S, Loft A, Castrejon I, Otero-Varela L, Závada J, Pavelka K, Rutanen J, Kuusalo L, Nissen M, Rotar Z, Perdan-Pikmajer K, Bernardes M, Gudbjornsson B, Gröndal G, van der Horst-Bruinsma I, Laas K, Michelsen B, Codreanu C, DiGuiseppe D, Moeller B, Kenar G, Hetland M, Oernbjerg L. Do Smoking and Obesity Impact Secukinumab Treatment Outcomes? Real-world Data from 1,202 European Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/do-smoking-and-obesity-impact-secukinumab-treatment-outcomes-real-world-data-from-1202-european-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/do-smoking-and-obesity-impact-secukinumab-treatment-outcomes-real-world-data-from-1202-european-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/