Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Two independent studies on genetic risk factors for systemic sclerosis (SSc) identified a polymorphism of Deoxyribonuclease 1-like 3 (DNASE1L3) associated with increased SSc risk. This polymorphism is located in a coding region and results in an amino acid substitution of Arg 206 to Cys (R206C). The mechanisms by which DNASE1L3 R206C polymorphism increase SSc risk are unknown. Based on prior studies indicating that DNASE1L3 is secreted into the circulation and digests DNA in apoptosis-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs), we sought to determine the effect of DNASE1L3 R206C polymorphism on this activity. We tested plasma samples from SSc patients and healthy controls (HCs) with vs. without DNASE1L3 R206C polymorphism for their ability to digest genomic DNA in apoptosis-derived EVs.
Methods: Plasma from SSc patients and HCs were previously collected as part of the Scleroderma Family Registry and DNA Repository based in Houston. Groups of SSc patients and HCs homozygous for the major allele (DNASE1L3 R206 wild-type, or WT), heterozygous, or homozygous for DNASE1L3 R206C were identified and matched for age and sex (with the exception of HCs homozygous for DNASE1L3 R206C, since there were only two HCs with this genotype in the Registry). SSc patients were also matched for disease duration, limited vs diffuse cutaneous subtypes, and SSc-associated autoantibodies (Table 1). DNA-containing EVs were prepared by inducing apoptosis of cultured Jurkat cells with staurosporine, followed by isolation of the apoptosis-derived EVs by centrifugation. EVs were added to plasma samples and incubated for one hour, followed by extraction of the DNA. Each plasma sample was tested in triplicate. The extracted genomic DNA was quantified by qPCR (Figure 1), and the percent of genomic DNA digested in each sample was compared to that of a reference HC with DNASE1L3 R206 WT. The relative DNA digestion in each group was compared by one-way ANOVA.
Results: Plasma from SSc patients and HCs heterozygous for DNASE1L3 R206C polymorphism had less digestion of EV-associated DNA on average than plasma from DNASE1L3 R206 WT SSc patients and HCs. Minimal to no digestion of EV-associated DNA was observed in plasma from individuals homozygous for DNASE1L3 R206C (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Plasma from SSc patients and HCs harboring DNASE1L3 R206C polymorphism has impaired ability to digest EV-associated genomic DNA. These findings solidify the hypotheses that circulating DNASE1L3 is a major determinant for digestion of DNA in apoptosis-derived EVs and that the R206C polymorphism reduces this activity. Given that the DNASE1L3 R206C polymorphism is a robustly-replicated risk factor for SSc, these results suggest that excess DNA in apoptosis-derived EVs may have a pathogenic role in SSc.
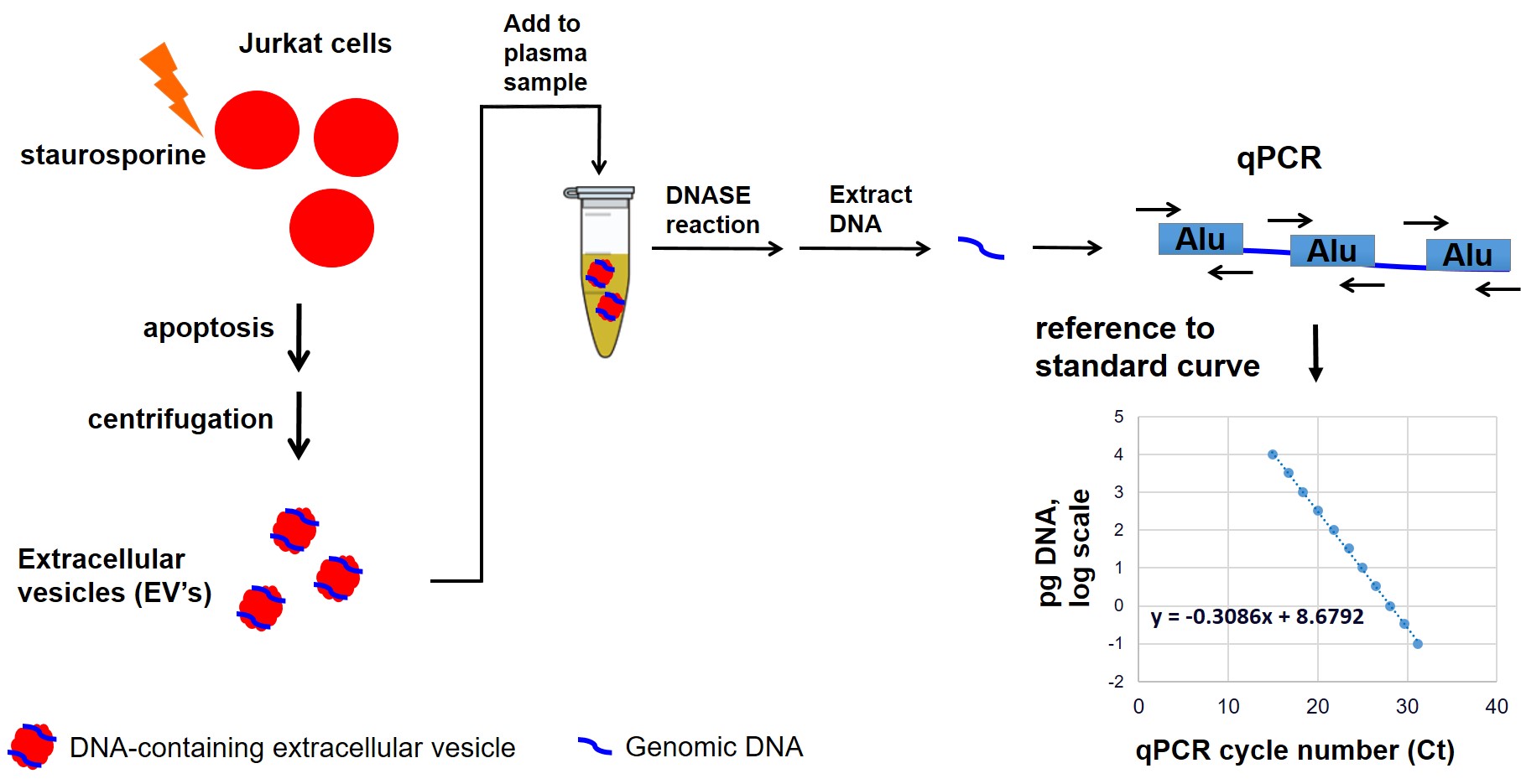 Figure 1: Schematic of assay to measure digestion of genomic DNA in apoptosis-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) by plasma samples
Figure 1: Schematic of assay to measure digestion of genomic DNA in apoptosis-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) by plasma samples
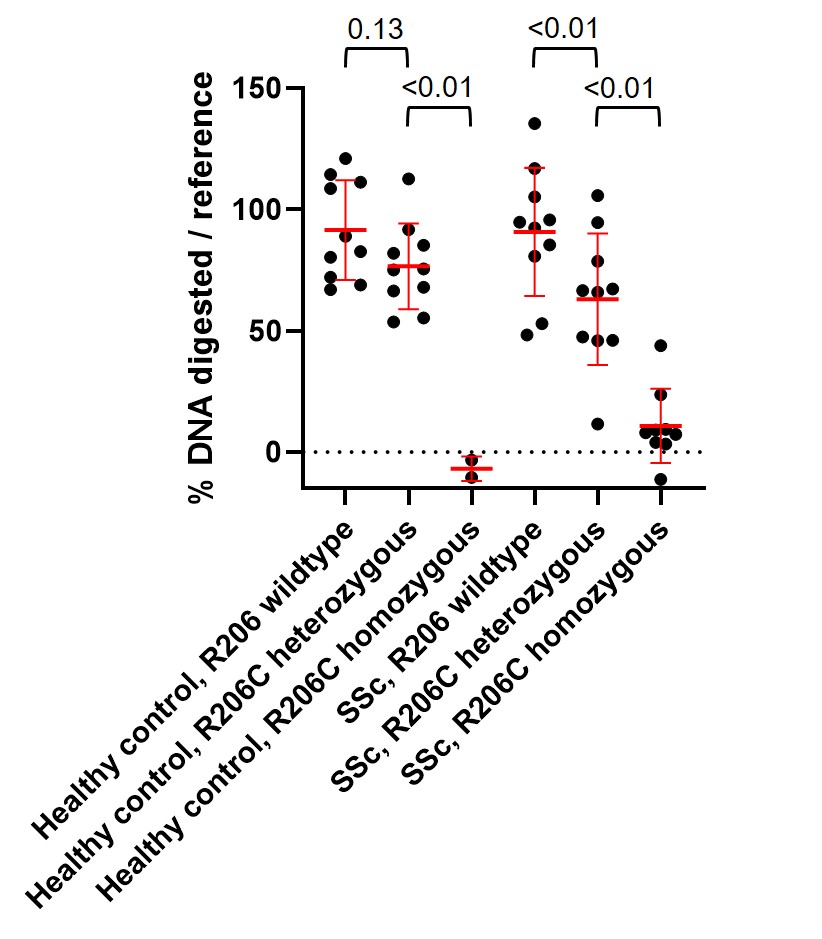 Figure 2: Impaired digestion of EV-associated genomic DNA in plasma from DNASE1L3 R206C SSc patients and healthy controls. Relative percentage of genomic DNA digested in each sample is plotted for each individual based on the mean of triplicates for each plasma sample. Each sample was compared to a reference healthy control with DNASE1L3 R206 WT. Red midlines and error bars indicate the mean and standard deviation for each group, respectively. Groups were compared by one-way ANOVA, with p values shown at top. SSc: systemic sclerosis
Figure 2: Impaired digestion of EV-associated genomic DNA in plasma from DNASE1L3 R206C SSc patients and healthy controls. Relative percentage of genomic DNA digested in each sample is plotted for each individual based on the mean of triplicates for each plasma sample. Each sample was compared to a reference healthy control with DNASE1L3 R206 WT. Red midlines and error bars indicate the mean and standard deviation for each group, respectively. Groups were compared by one-way ANOVA, with p values shown at top. SSc: systemic sclerosis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Skaug B, Charles J, Couturier J, Lewis D, Mayes M, Assassi S. DNASE1L3 R206C Polymorphism, a Systemic Sclerosis Risk Factor, Causes Impaired Digestion of Genomic DNA in Apoptosis-derived Extracellular Vesicles [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dnase1l3-r206c-polymorphism-a-systemic-sclerosis-risk-factor-causes-impaired-digestion-of-genomic-dna-in-apoptosis-derived-extracellular-vesicles/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dnase1l3-r206c-polymorphism-a-systemic-sclerosis-risk-factor-causes-impaired-digestion-of-genomic-dna-in-apoptosis-derived-extracellular-vesicles/

