Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: Late-Breaking Posters
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
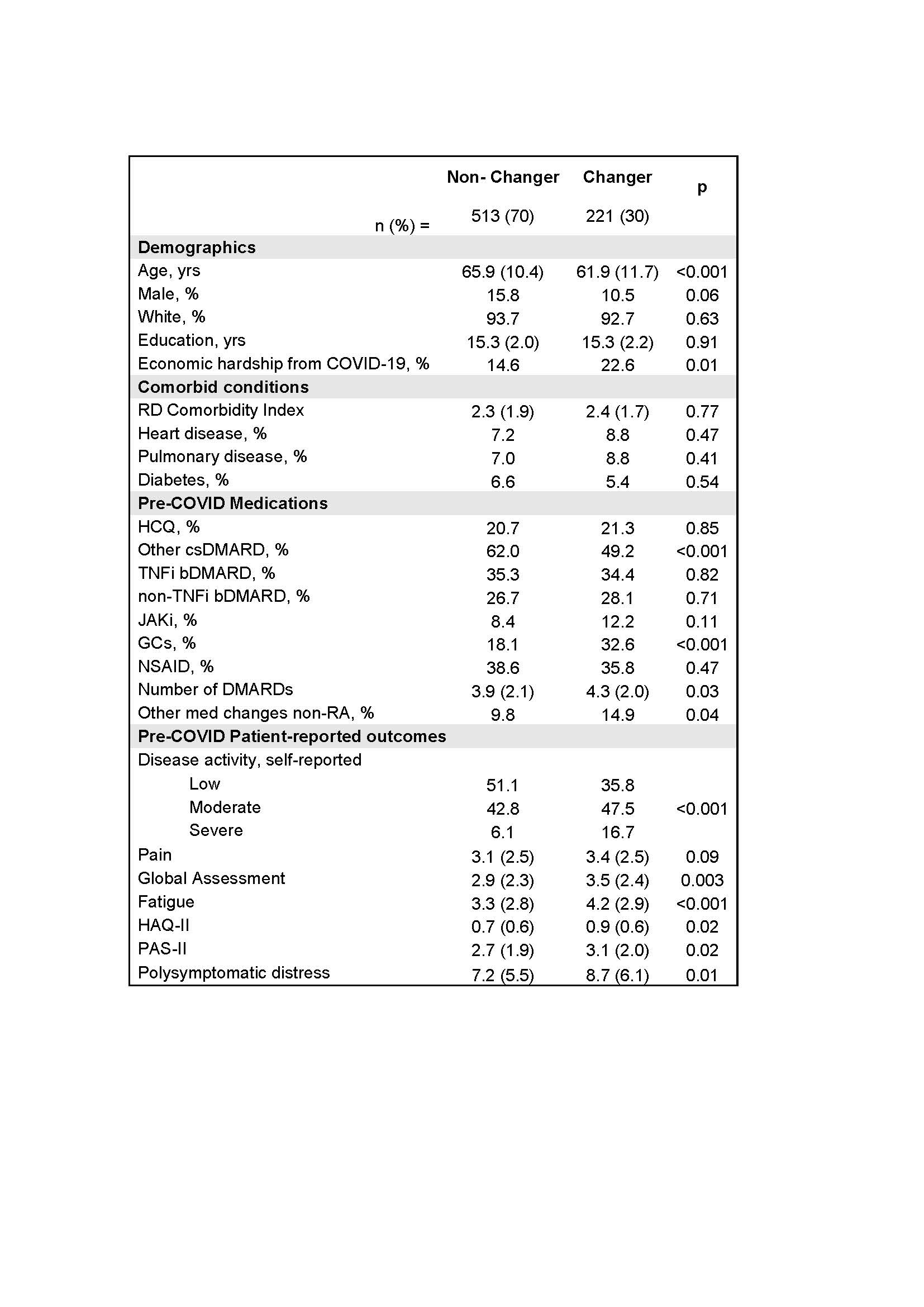
Background/Purpose: To understand medication and clinical care changes by patients with RA during the first 3 months (March through May 2020) of the COVID-19 pandemic in the US.
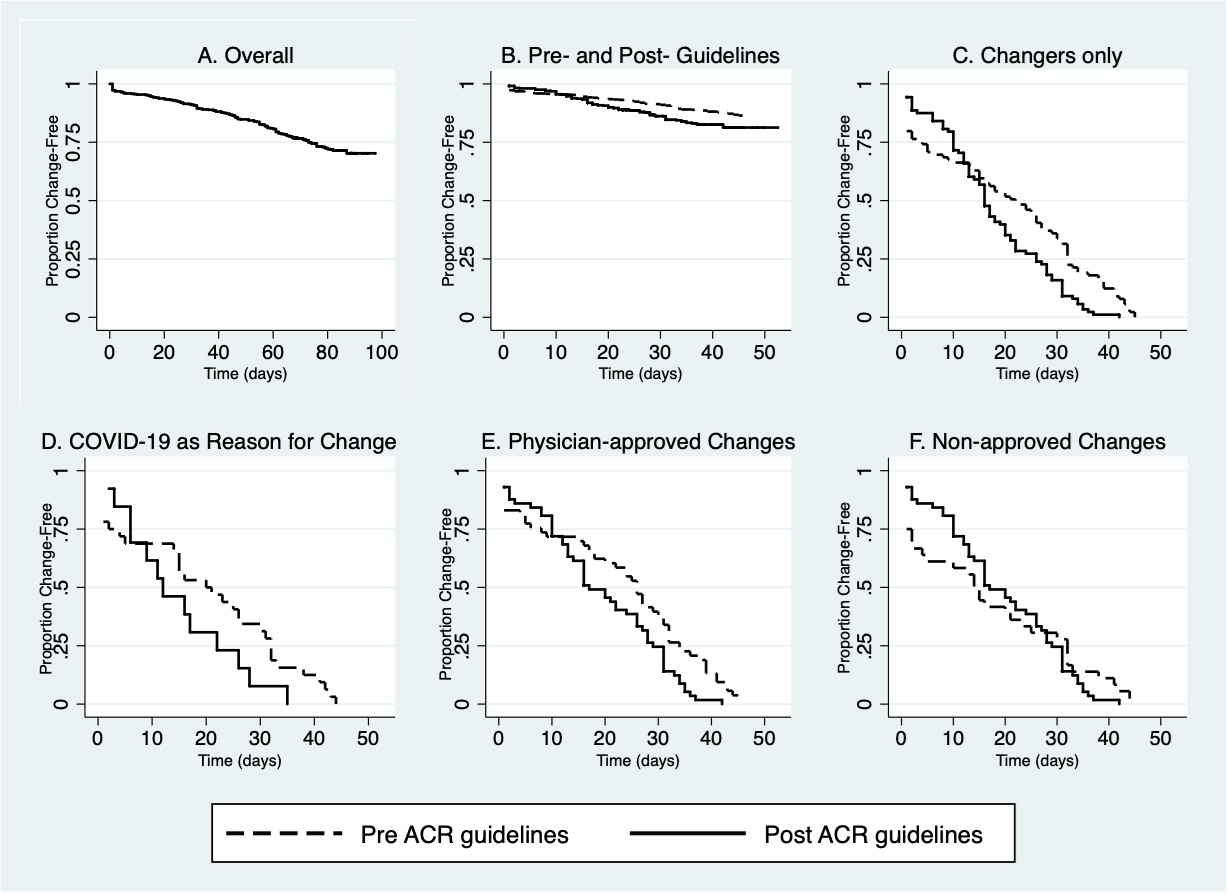
Methods: Data were provided by adults with RA participating in the FORWARD observational registry who answered COVID-19 web-based surveys in May/June 2020 and who previously provided baseline characteristics and medication use for 2019. We compared medication changes by pre-COVID DMARD exposure in logistic models first without adjustment and then adjusting for age, sex, comorbidities including pulmonary and cardiovascular diseases, education, health insurance, RA activity (PAS-II), fatigue, and polysymptomatic distress (PSD). We also examined rates of medication change before and after the first COVID-19 ACR treatment guidelines in April.
Results: Of the 734 respondents, 221 (30%) reported medication changes. Changers were more likely to use glucocorticoids (GCs, 33% vs 18%) and less likely to use non-hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) csDMARDs (49% vs 62%) pre-COVID. While JAKi use was associated (OR 1.9 [95% CI 1.0, 3.4]) with change in bivariate analyses, only GCs remained as a strong factor (OR 3.0 [1.9, 4.9]) in multivariable models. Change in care was most associated with pulmonary disease (OR 2.9 [1.3, 6.5]) and GC use (OR 1.6 [1.0, 2.5]). While the incidence of medication change before and after April 15 was the same, patient-initiated changes due to COVID-19 were twice as likely before April 15, and physician-guided changes were more likely after.
Conclusion: Our findings confirm US patients with RA made substantial changes to their medication use during the first 3 months of the COVID-19 pandemic. Almost half of DMARD decrease or discontinuations were made without physician guidance, and all types of medication changes after ACR recommendations were made with increased physician guidance. While no direct causation was measured, our findings provide evidence of possible implementation of these recommendations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Michaud K, Pedro S, Wipfler K, Agarwal E, Katz P. DMARD Changes for Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in the US During the First Three Months of the COVID-19 Pandemic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dmard-changes-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-the-us-during-the-first-three-months-of-the-covid-19-pandemic/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dmard-changes-for-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-the-us-during-the-first-three-months-of-the-covid-19-pandemic/