Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Defective clearance of apoptotic cells (AC) and complement deficiency are important contributors to the pathogenesis of systemic lupus. Dead (sunburn) cells and complement activation are also observed in patients with cutaneous lupus. ACs are opsonized by several proteins including C1q, C3 and MFG-E8. MFG-E8 is a soluble milk protein that binds to phosphatidylserine on AC and facilitates their removal through its interaction with avb3 and avb5 integrins on phagocytes. In its absence, AC debris accumulates in germinal centers. In MFG-E8-/- B6 mice, we observed a C1q dependent increase of C3/IgG deposition on MZ B cell and FDCs, suggesting excessive self antigens can activate the classical pathway and be presented as antigen/immune complexes to autoreactive B cells in spleen. In this study, we determined how the interaction between AC and complement contribute to autoantibody production, nephritis and photosensitivity in lupus.
Methods: We introduced MFG-E8-/-, C1q-/- and C3-/- into SLE 1 congenic mice. We created MFG-E8-/-C1q-/- and MFG-E8-/-C3-/- double knock-out in the SLE1 background. We analyzed the titers of anti-chromatin and anti-dsDNA (n =15-20 in each group) by ELISA and confirmed the results by Crithidia luciliae staining. We examined T and B cell phenotypes by flow cytometry. Kidney damage was evaluated by blood urea nitrogen, immuno-fluorescence and PAS staining. We exposed respective strains to repeated UVB irradiation and followed development of nephritis and skin lesions.
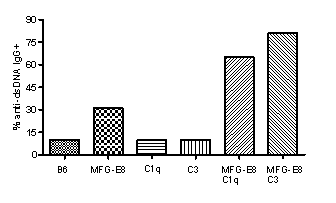 Results: In 7 month old female B6.SLE1 mice, 10% of mice developed anti-dsDNA IgG. Neither C1q nor C3 deficiency alone changed the percentages of anti-dsDNA IgG+ mice. MFG-E8-/- SLE1 mice had a significantly higher number of germinal center B cells and 30% of females became anti-dsDNA IgG+. Combining MFG-E8-/- with either C1q-/- or C3-/- significantly accelerated the production of anti-dsDNA IgG and increased the percentage of anti-dsDNA IgG+ mice to 65% and 80%, respectively (Figure). Furthermore, 50% MFG-E8-/-C1q-/- but 0% FG-E8-/-C3-/- SLE1 mice showed early mortality due to spontaneous lupus nephritis. When exposed to UVB irradiation, 90% (8 out 9) MFG-E8-/-C3-/- developed either acute nephritis or persistent skin lesions. On the contrary, none of MFG-E8-/-C1q-/- mice (0 out 15) experienced similar symptoms.
Results: In 7 month old female B6.SLE1 mice, 10% of mice developed anti-dsDNA IgG. Neither C1q nor C3 deficiency alone changed the percentages of anti-dsDNA IgG+ mice. MFG-E8-/- SLE1 mice had a significantly higher number of germinal center B cells and 30% of females became anti-dsDNA IgG+. Combining MFG-E8-/- with either C1q-/- or C3-/- significantly accelerated the production of anti-dsDNA IgG and increased the percentage of anti-dsDNA IgG+ mice to 65% and 80%, respectively (Figure). Furthermore, 50% MFG-E8-/-C1q-/- but 0% FG-E8-/-C3-/- SLE1 mice showed early mortality due to spontaneous lupus nephritis. When exposed to UVB irradiation, 90% (8 out 9) MFG-E8-/-C3-/- developed either acute nephritis or persistent skin lesions. On the contrary, none of MFG-E8-/-C1q-/- mice (0 out 15) experienced similar symptoms.
Conclusion: Both C1q and C3 are essential
in reducing the immunogenicity of
apoptotic cells in lupus. The protective mechanisms they provide depend on availability of other opsonins and environmental factors such as sunlight exposure.
Disclosure:
C. Sontheimer,
None;
Y. Nguyen,
None;
K. B. Elkon,
None;
Y. Peng,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/distinct-contributions-of-c1q-and-c3-in-preventing-immunogenicity-of-apoptotic-cells-in-lupus/
