Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Prior research has shown that differences exist in disease activity and clinical outcomes for RA across racial and ethnic groups in the US.1 This study provides an updated analysis examining differences in disease burden and change in clinical outcomes over time across racial and ethnic groups.
Methods: This study used data from CorEvitas’ RA Registry, which consists of over 56,000 RA patients across 42 US states. We included patients with a visit during two time periods (visit 1: 2013–2015; visit 2: 2018–2020) and selected the first visit in the first time period and the last visit in the second time period for each patient. Patients self-reported race and ethnicity at enrollment; Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) score was obtained at both visits.
Patient characteristics at visits 1 and 2 by race/ethnicity (white [non-Hispanic], Black [non-Hispanic], Hispanic, or Asian) are summarized. The primary outcome was CDAI at visits 1 and 2. Secondary outcomes included the proportion of patients in low disease activity (LDA; CDAI ≤ 10) or remission (CDAI ≤ 2.8), and HAQ-disability index (DI) at each visit. We evaluated mean change in CDAI and HAQ-DI from visit 1 to 2 and probability of achieving LDA and remission at visit 2.
Linear regression models were adjusted for demographics, clinical characteristics, and site as a random effect variable. From these models, marginal means or mean change for each outcome were computed; overall and pairwise tests were used to detect differences in outcomes between races.
Results: Of 9363 eligible patients (8142 White, 527 Black, 545 Hispanic, 149 Asian), a majority (76–85%) were female. Mean age at visit 1 ranged from 55.1 to 60.7 years, and mean disease duration ranged from 9.8 to 11.8 years (Table 1). Many patients had history of serious infections (50–61%) and hypertension (22–41%).
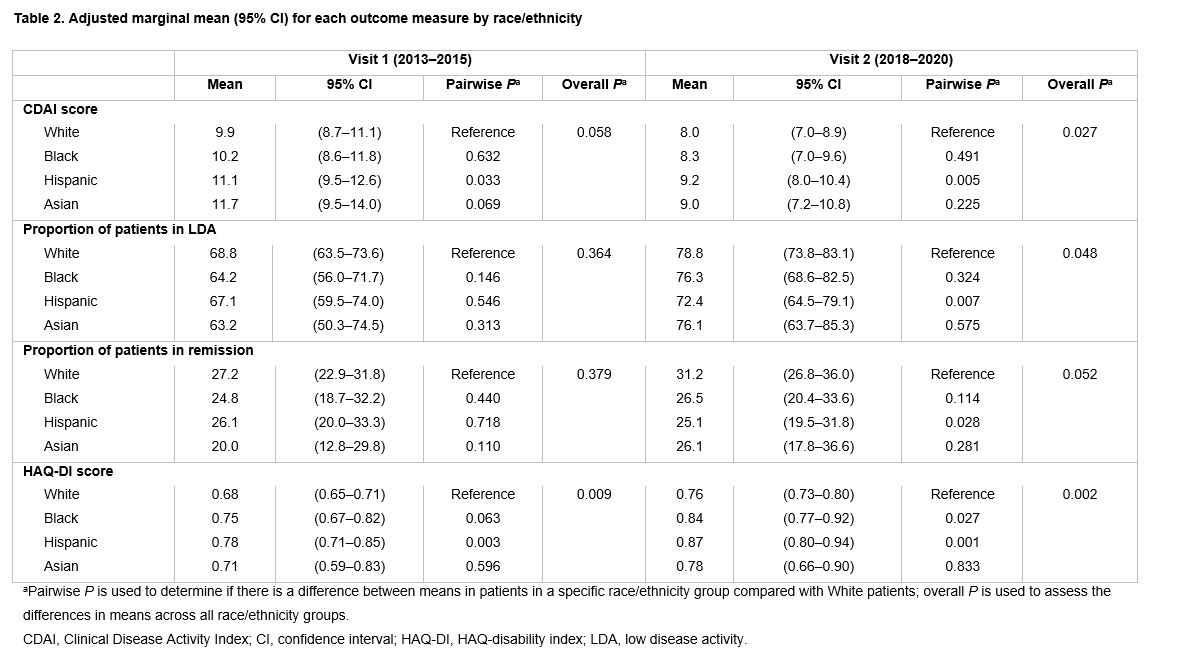
In adjusted analyses, we estimated higher CDAI scores for Hispanic vs White patients at both visits 1 and 2 (Table 2). Proportions of patients in LDA and remission were similar across groups at visit 1; at visit 2, a significantly lower proportion of Hispanic patients were in LDA and remission compared with White patients.
Functional status declined over time for all groups, indicated by greater mean HAQ-DI scores at visit 2 vs visit 1. Compared with White patients, Hispanic patients had significantly higher mean HAQ-DI scores at visit 1, and both Black and Hispanic patients had significantly higher mean HAQ-DI scores at visit 2 (Table 2).
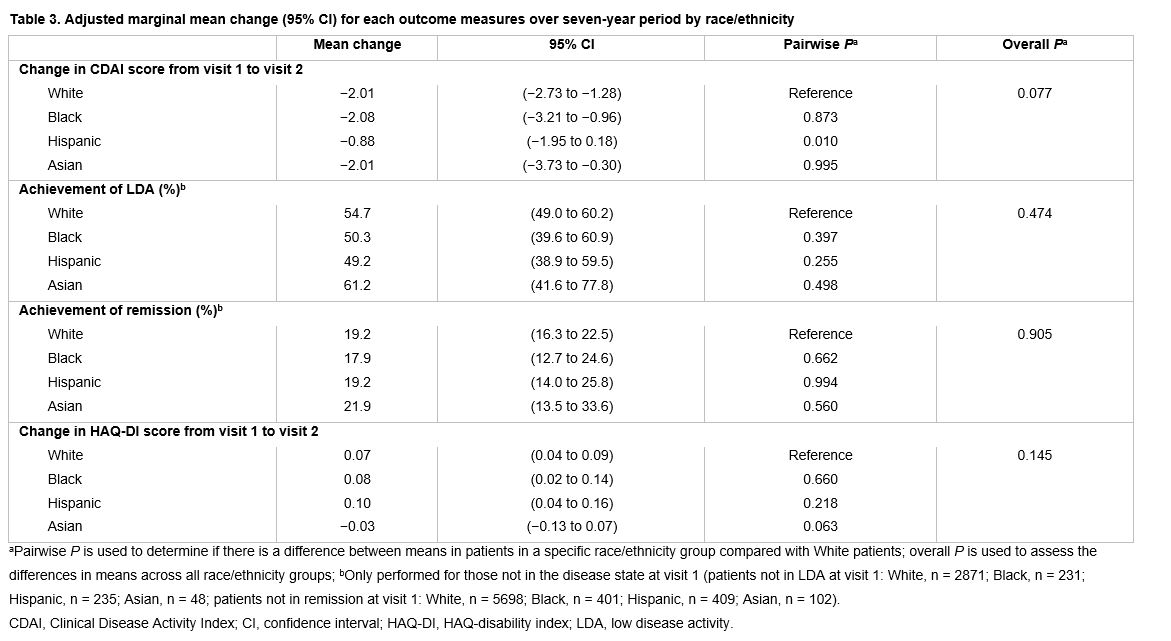
Longitudinally, CDAI scores improved for all groups from visit 1 to 2, though Hispanic patients improved significantly less than White patients (Table 3). There were no statistically significant differences in achievement of LDA or remission or change in HAQ-DI over time across groups.
Conclusion: Disease activity improved over the 7-year time period across all racial and ethnic groups. However, disparities between racial and ethnic groups in disease activity and functional status did persist over time, suggesting that further effort is needed to understand the drivers of these discrepancies and close this racial gap.
Reference:
1. Greenberg JD, et al. Am J Med 2013;126:1089–1098.
Editorial support: Michele Springer (Caudex), funded by Bristol Myers Squibb
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
O’Brien J, Park S, Blachley T, Marchese M, Middaugh N, Han X, Wittstock K, Harrold L. Disparities in Burden of Disease in Patients with RA Across Racial and Ethnic Groups [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disparities-in-burden-of-disease-in-patients-with-ra-across-racial-and-ethnic-groups/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/disparities-in-burden-of-disease-in-patients-with-ra-across-racial-and-ethnic-groups/